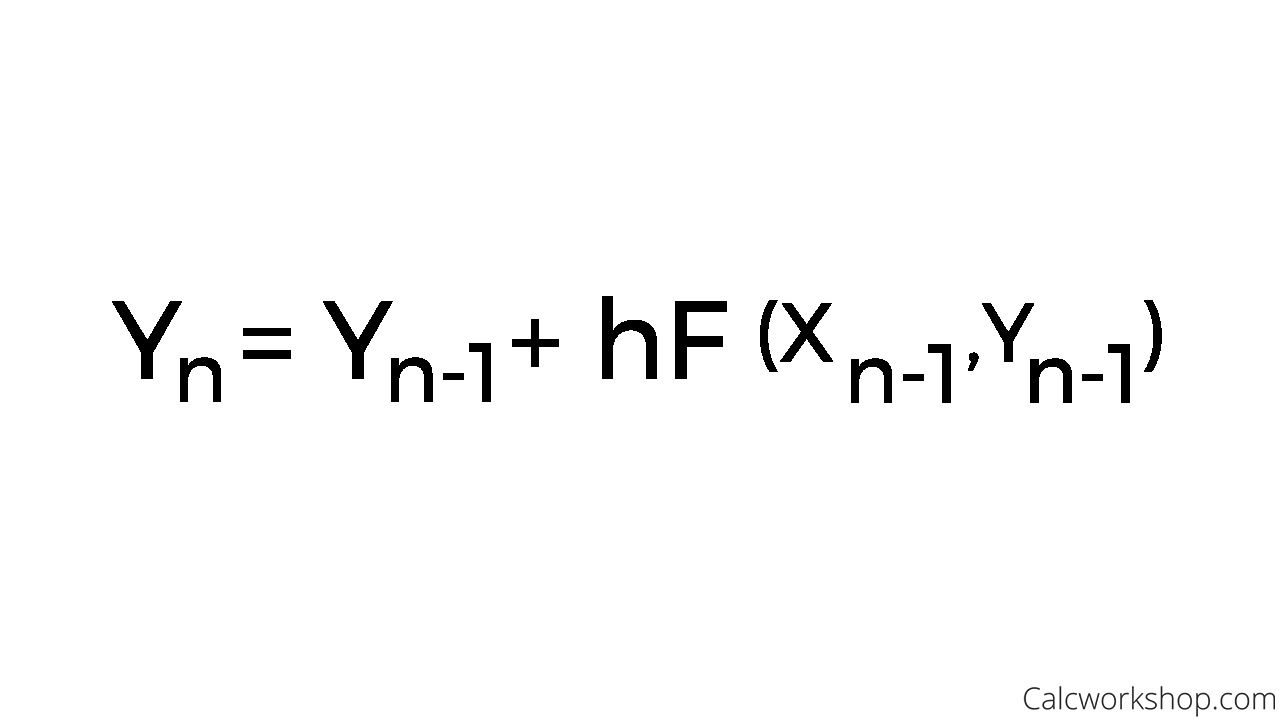Euler's Method Differential Equations - Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
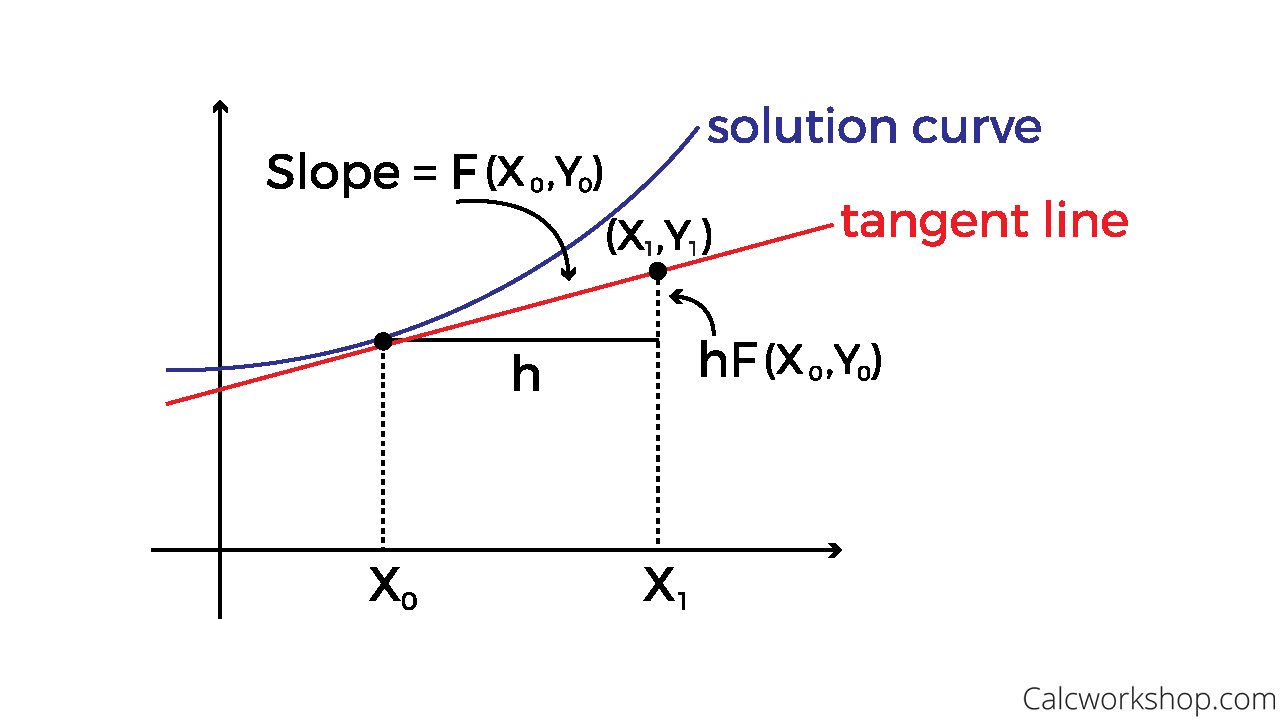
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
Euler`s Method for Ordinary Differential Equations
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
Answered Use Euler's method to solve the… bartleby
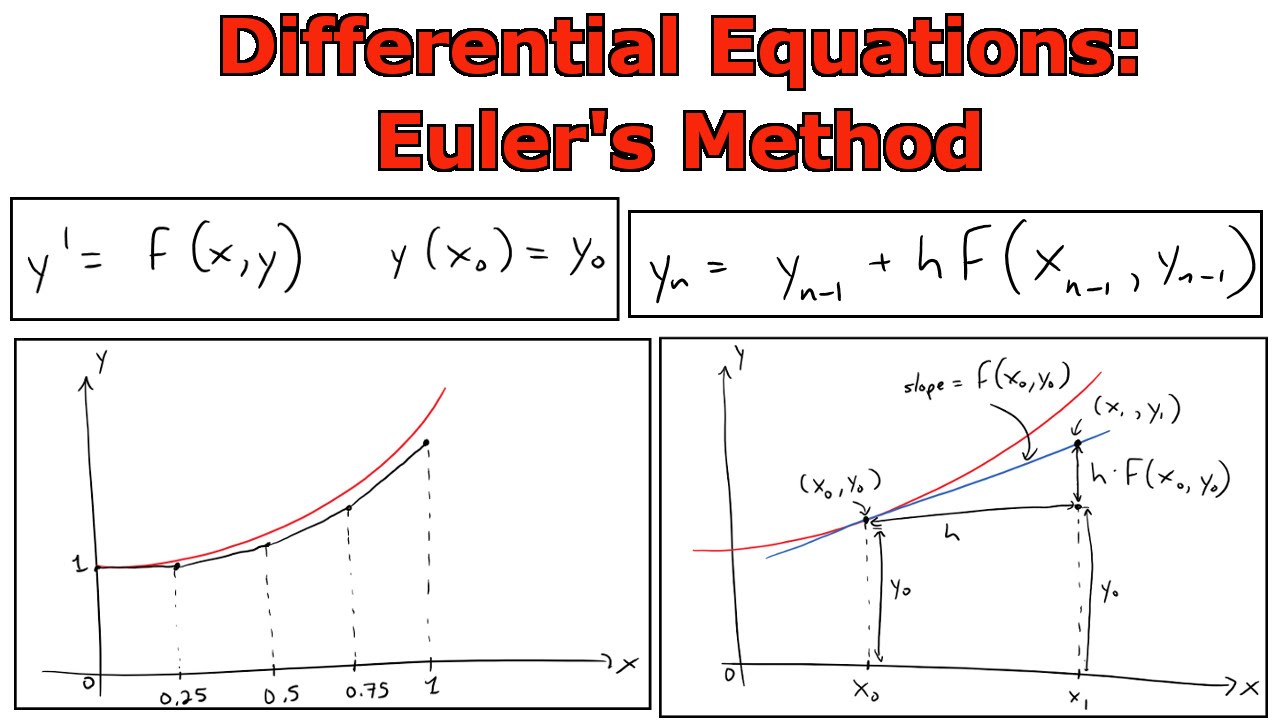
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
8.02 Euler’s Method for Solving Ordinary Differential Equations
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
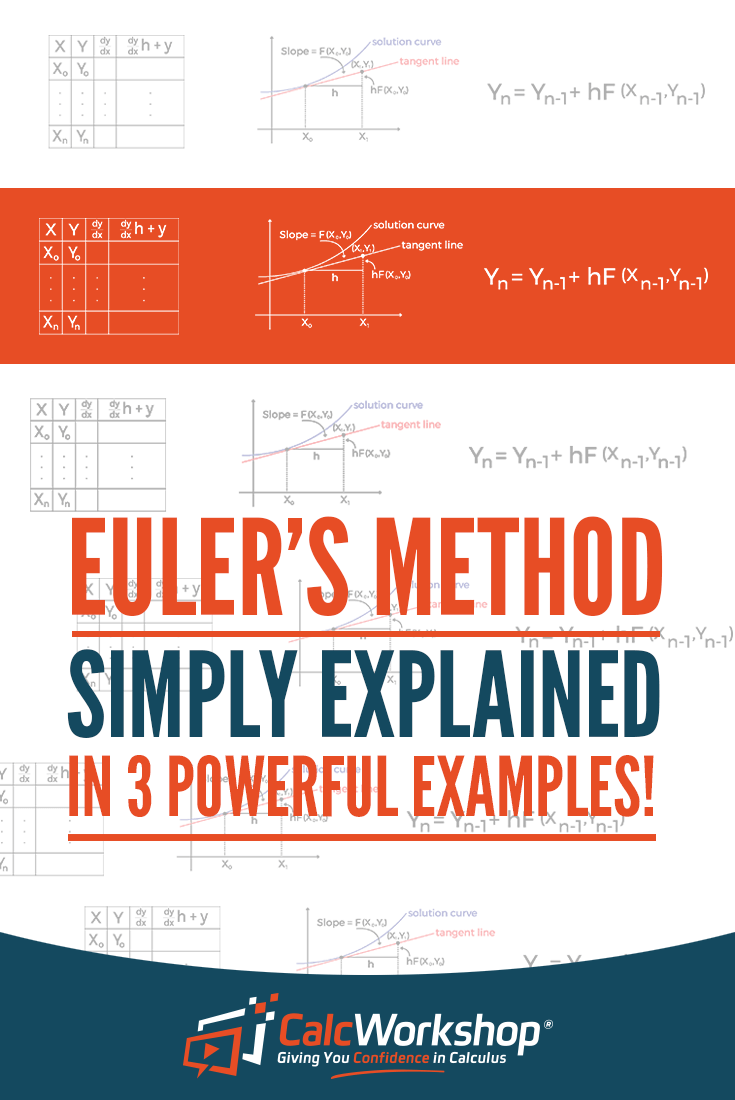
How to do Euler's Method? (Simply Explained in 4 Powerful Examples)
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
How to do Euler's Method? (Simply Explained in 4 Powerful Examples)
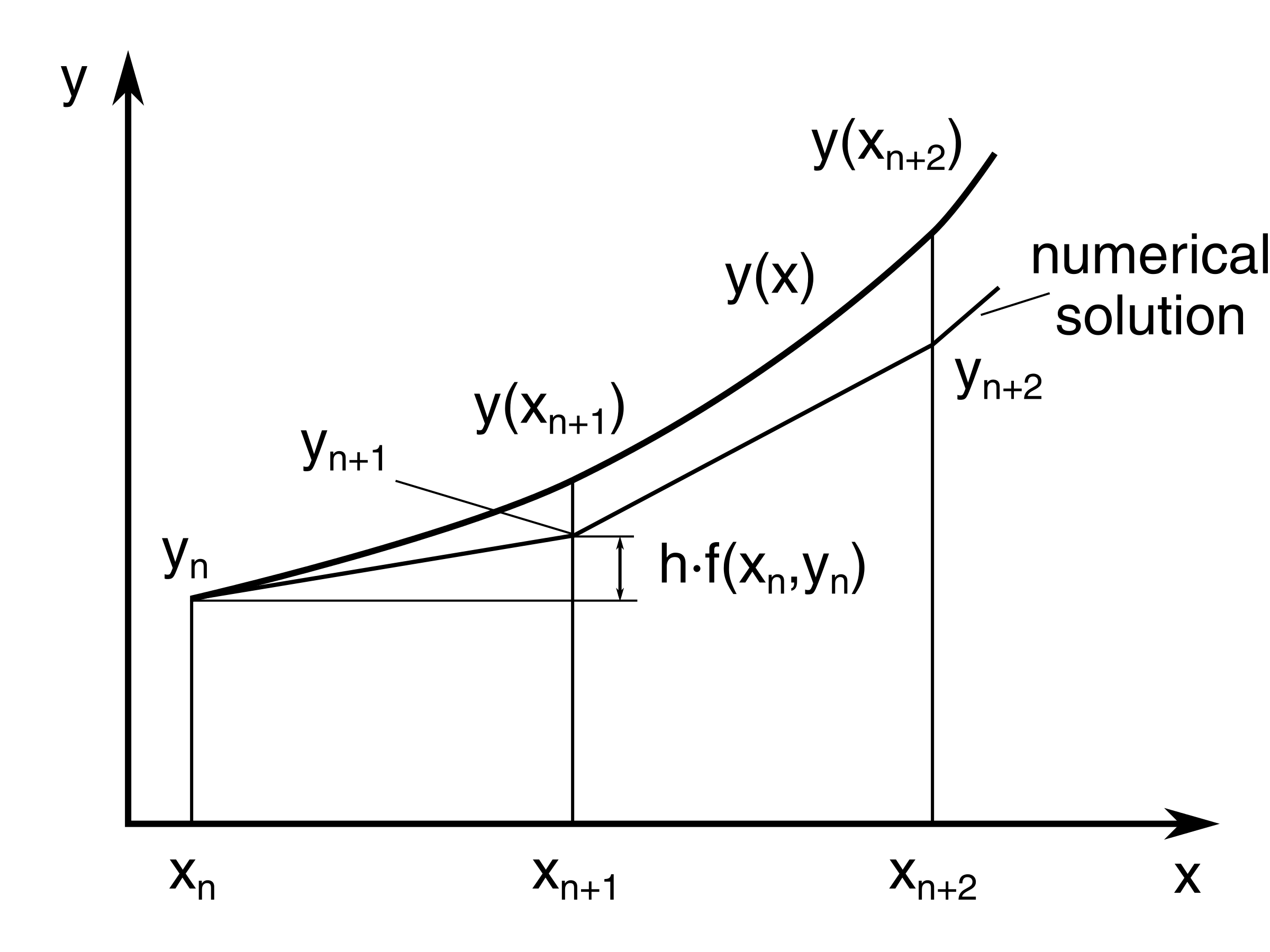
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
Euler's Method on differential equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
Euler's Method Explained With Examples, 40 OFF
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
SOLUTION Cauchy euler s differential equations Studypool
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).
Euler's Method Explained with Examples
Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)).