Differential Diagnosis Of Bradycardia - Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management of bradycardia. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular failure from massive pe. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where. This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia.
Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management of bradycardia. Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia. This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular failure from massive pe. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where.
Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management of bradycardia. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular failure from massive pe. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where. Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia.
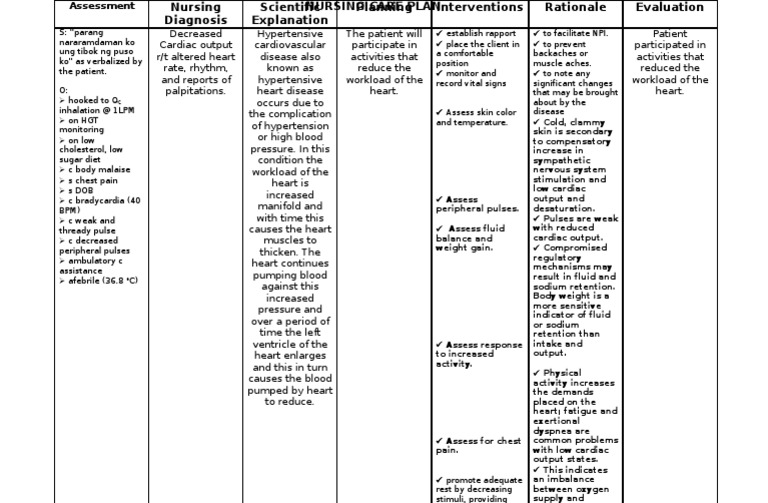
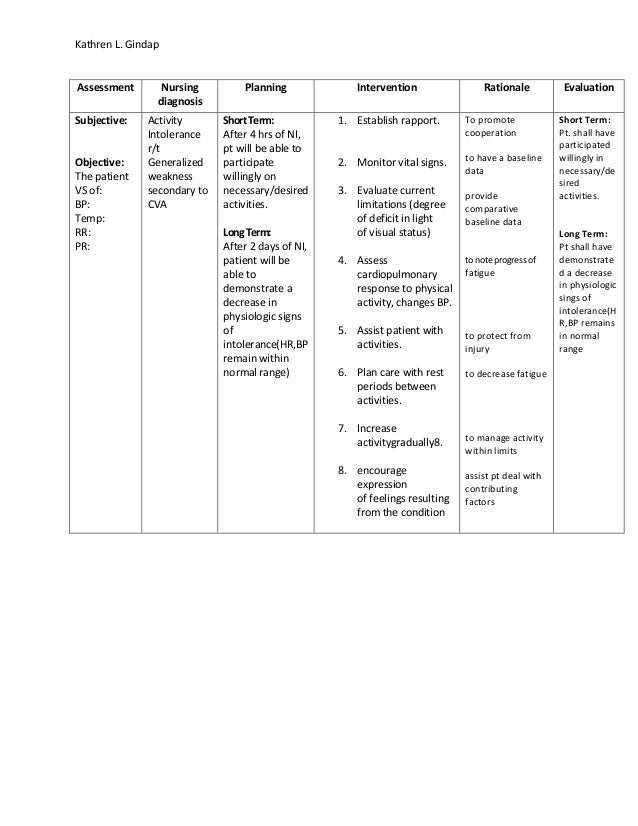
77 2 NURSING DIAGNOSIS FOR BRADYCARDIA
Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular failure from massive pe. This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia.
77 2 NURSING DIAGNOSIS FOR BRADYCARDIA
Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia. Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular failure from massive pe. Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where. Cardiac.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management of bradycardia. Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of.
Pin on Paramedic
Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular failure from massive pe. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction;
The Differential Diagnosis of the Breathless Patient DocsLib
This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management of bradycardia.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management of bradycardia. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
Cardiac disease myocardial ischaemia / infarction; Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where. Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. This blog is written and.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where. This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. Includes an algorithm for the evaluation of bradycardia. Cardiac.
Includes An Algorithm For The Evaluation Of Bradycardia.
Differential diagnosis of the underlying causes of bradycardia. Quick review of the differential diagnosis for symptomatic bradycardia. This blog is written and reviewed by emergency physicians. The differential diagnosis of bradycardia here is broader than usual and may include such entities as severe hypoxemia and right ventricular failure from massive pe.
Cardiac Disease Myocardial Ischaemia / Infarction;
Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management of bradycardia. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm with evidence of low perfusion considered a reflection of a life threatening situation where.