Differential Equations Linear And Nonlinear - Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. An nth order differential equation. Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. Explain the law of mass. Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des. State the definition of a linear differential equation. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent.
Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the. An nth order differential equation. Explain the law of mass. Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent. Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. State the definition of a linear differential equation.
Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. An nth order differential equation. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent. Explain the law of mass. Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the.
Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems MDPI Books
A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. An.
Second Order Differential Equations
An nth order differential equation. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. Explain the law of mass. State the definition of a linear differential equation.
Differential Equations Owlcation
The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent. An nth order differential equation. Explain the law of mass. Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des.
Solved Classify each differential equations as linear or
Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the. Explain the law of mass. Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des. An nth order differential equation. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ.
[PDF] Differential Equations de A. C. King libro electrónico Perlego
Explain the law of mass. Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the. Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ..
1 ST Order Differences Between Linear Equations PDF
A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent. Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the. Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. State the definition of a linear differential.
Solved From the chapter Differential Equations
An nth order differential equation. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent. Explain the law of mass. Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\].
Linear and equations worksheet Live Worksheets
Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. State the definition of a linear differential equation. An nth order differential equation. Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des. Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the.
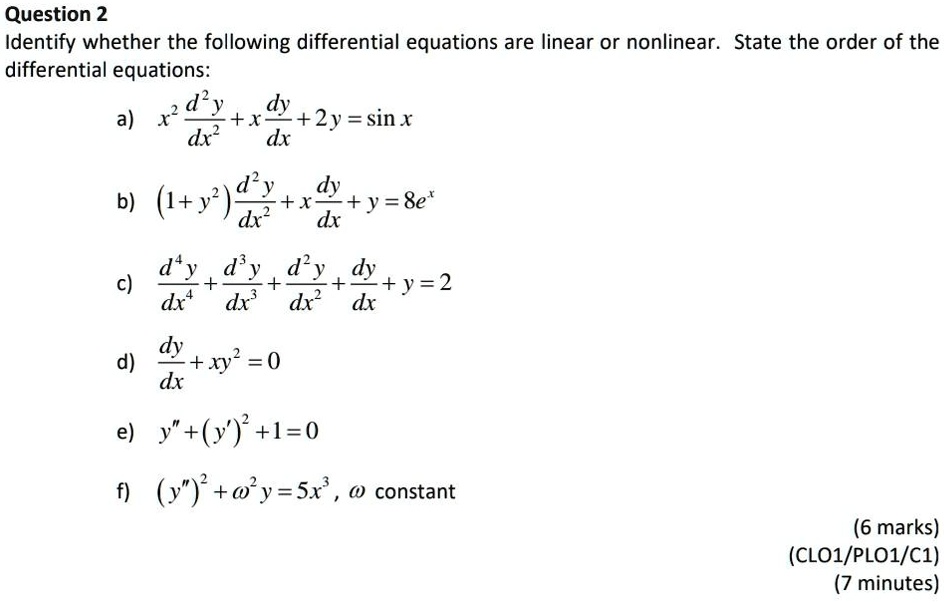
SOLVEDQuestion 2 Identify whether the following differential equations
Solve bernoulli’s equation, \[ \notag y' + p(t)y = g(t)y^n,\] when \(n \not= 0, 1\) by changing it \[. An nth order differential equation. Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Explain the law of mass.
SOLUTION linear and non linear differential equation examples
State the definition of a linear differential equation. An nth order differential equation. Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the. Explain the law of mass. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ.
State The Definition Of A Linear Differential Equation.
Differences between linear and nonlinear equations • recall that a first order ode has the. The nonlinear view of sines and cosines writes a cos(ωt)+ b sin(ωt) = a cos(ωt − φ), where a, and φ. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent. An nth order differential equation.
Solve Bernoulli’s Equation, \[ \Notag Y' + P(T)Y = G(T)Y^n,\] When \(N \Not= 0, 1\) By Changing It \[.
Differential equations are classified into linear des or nonlinear des. Explain the law of mass.



![[PDF] Differential Equations de A. C. King libro electrónico Perlego](https://www.perlego.com/_next/image?url=https:%2F%2Fwww.perlego.com%2Fbooks%2FRM_Books%2Fcup_kagcsvfg%2F9780511075209_500_750.jpg&w=768&q=50)