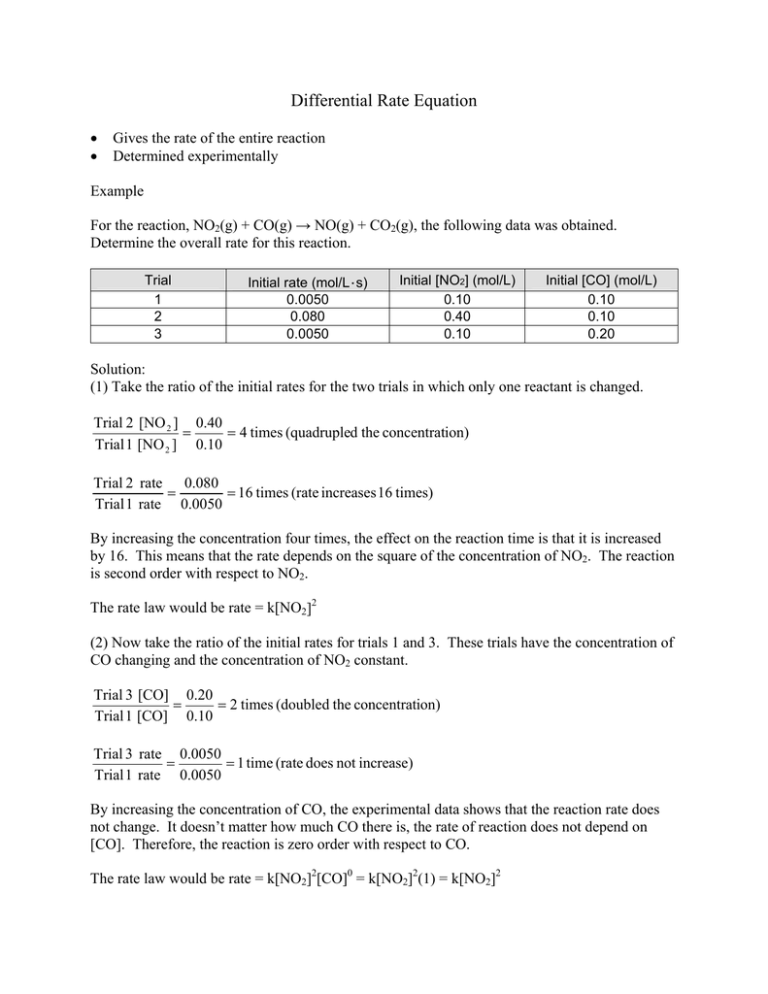
Differential Rate - Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: The differential rate law and the. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration. Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions.
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration. The differential rate law and the. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit.
There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration. The differential rate law and the. Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or.
Differential Rate Law Equation Method… Chemistry in Hindi
There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted.
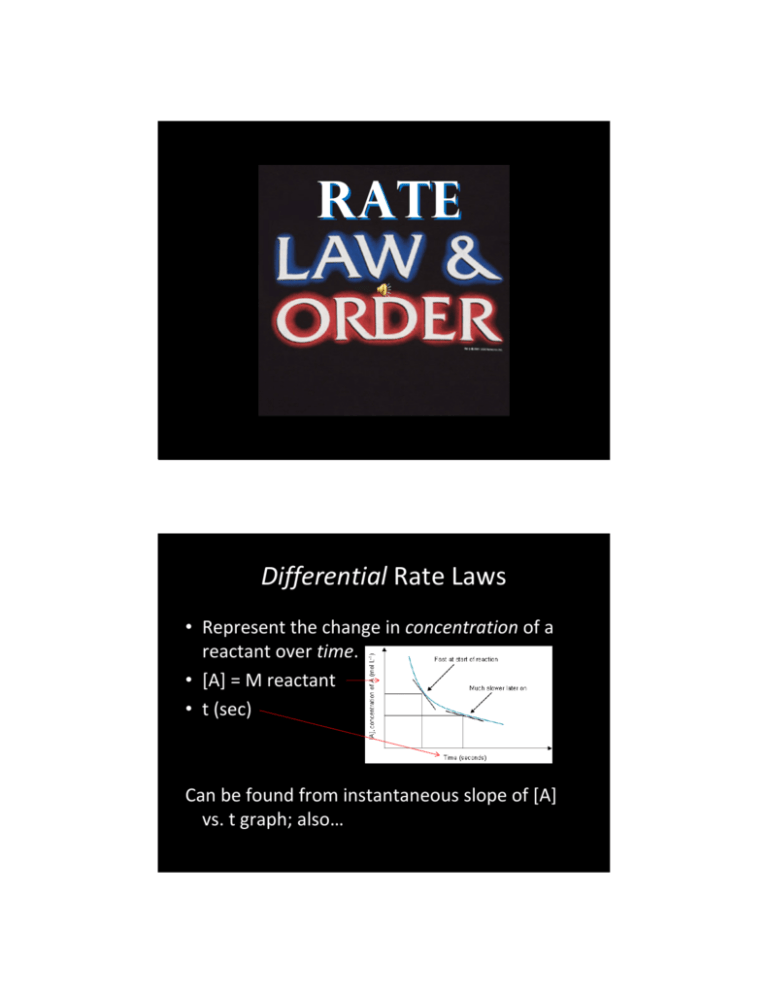
The upper and lower curves show the differential rate and the
Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in.
Differential Rate Equation
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. The differential rate law and the. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. Differential.
Differential Rate Laws
Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. The differential rate law and the. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. Differential.
How to Set the Night Differential Rate? PayrollHero Support
Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration. A differential rate law expresses the.
How to Set the Night Differential Rate? PayrollHero Support
Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration. The differential rate law and the. There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. Rate laws (sometimes called differential.
Differential Equations (Definition, Types, Order, Degree, Examples)
The differential rate law and the. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate.
Trade Interest Rate Differentials
Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. The differential rate law and the. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. Differential rate laws express the rate of.
Interest Rate Differential (IRD) Meaning, Formula, Calculations
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of substance reacted or produced per unit. Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws).
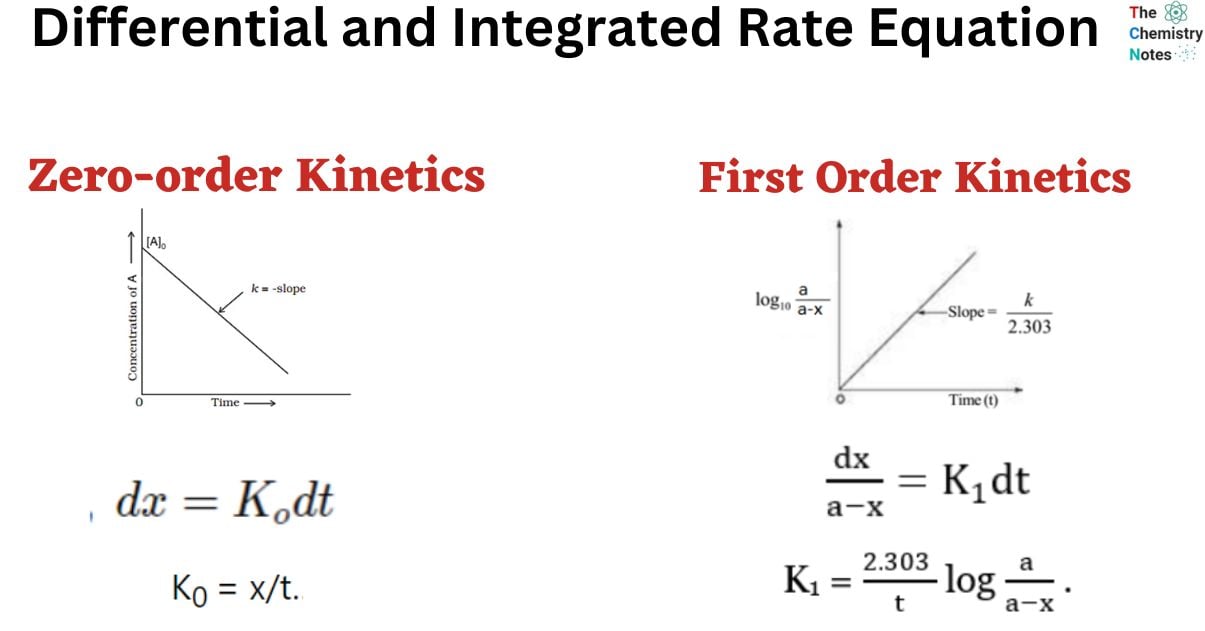
Differential and Integrated Rate Equation
There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction.
Differential Rate Laws Are Used To Express The Rate Of A Reaction In Terms Of Change In The Concentration.
Rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions. There are two forms of a rate law for chemical kinetics: The differential rate law and the. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one.
The Rate Of A Chemical Reaction Is The Amount Of Substance Reacted Or Produced Per Unit.
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or.