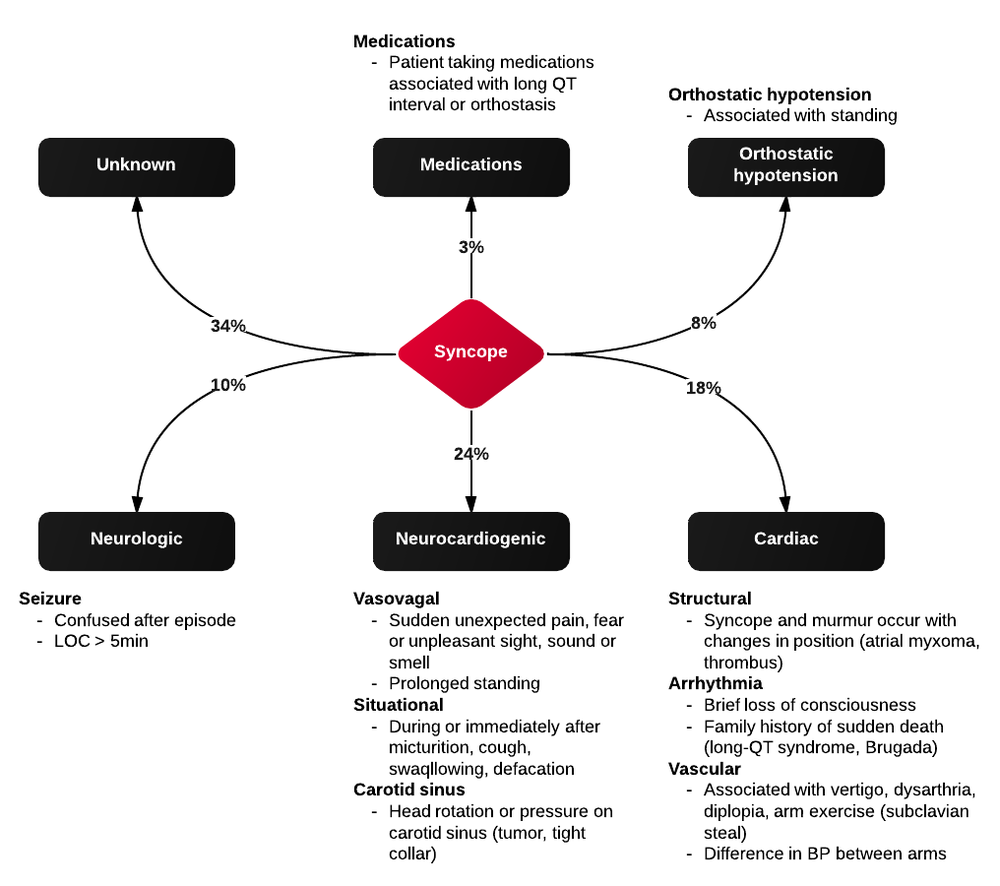
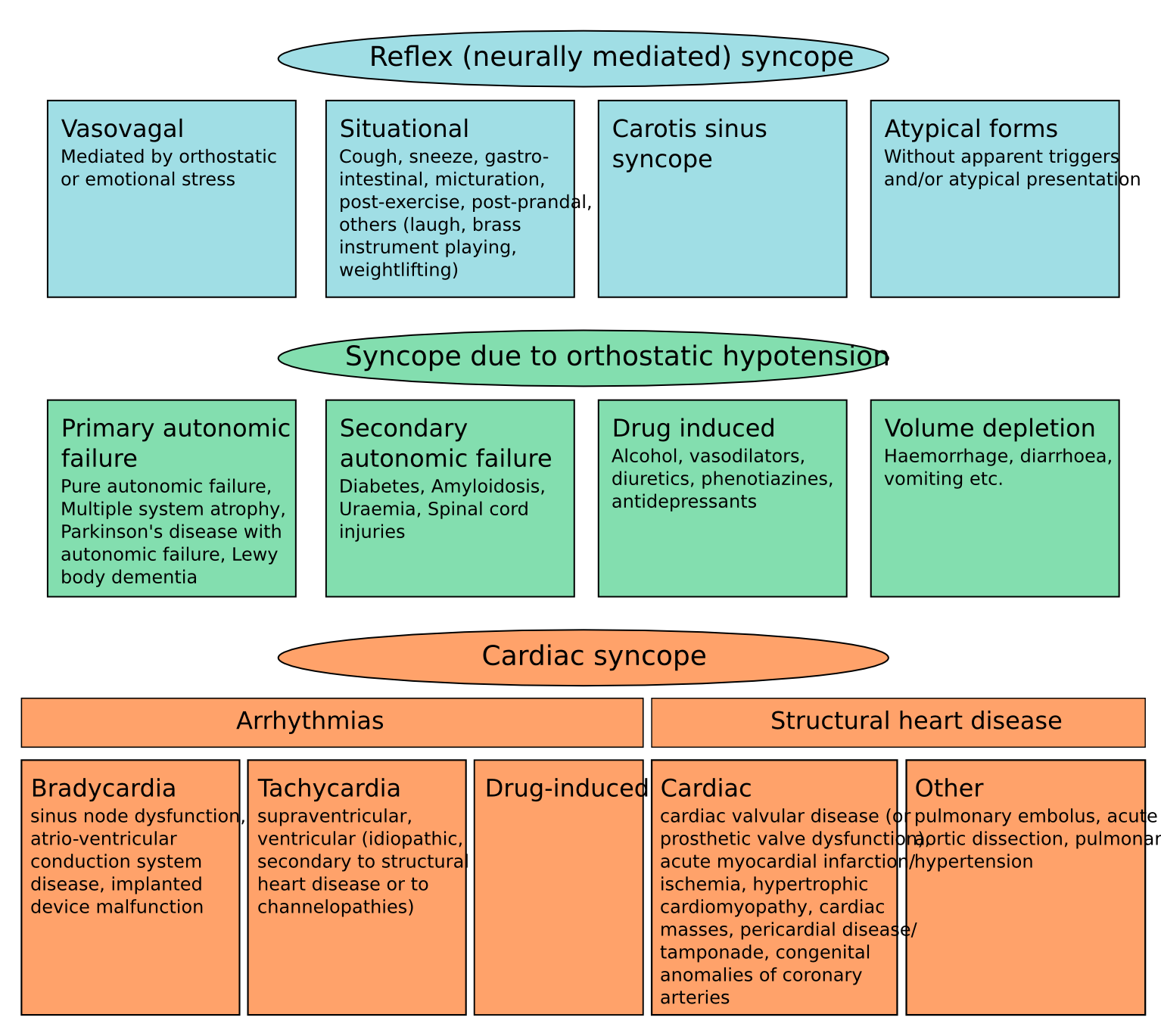
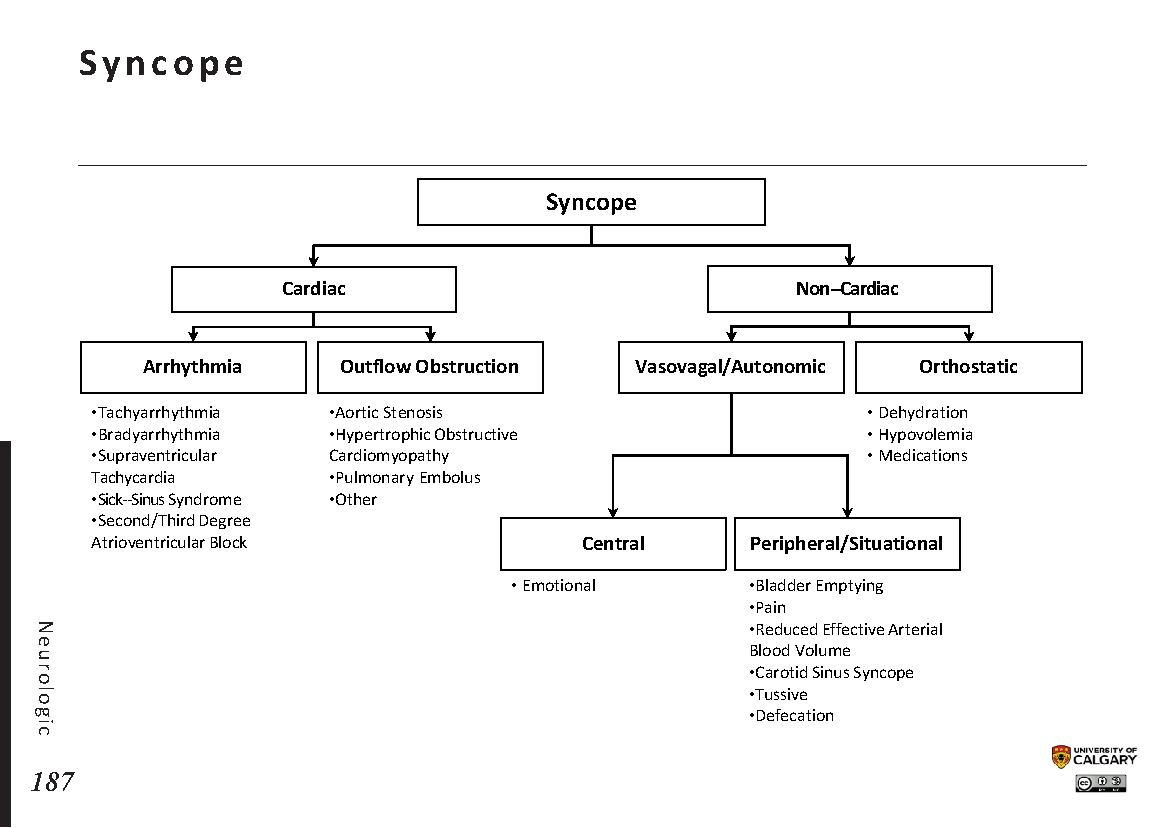
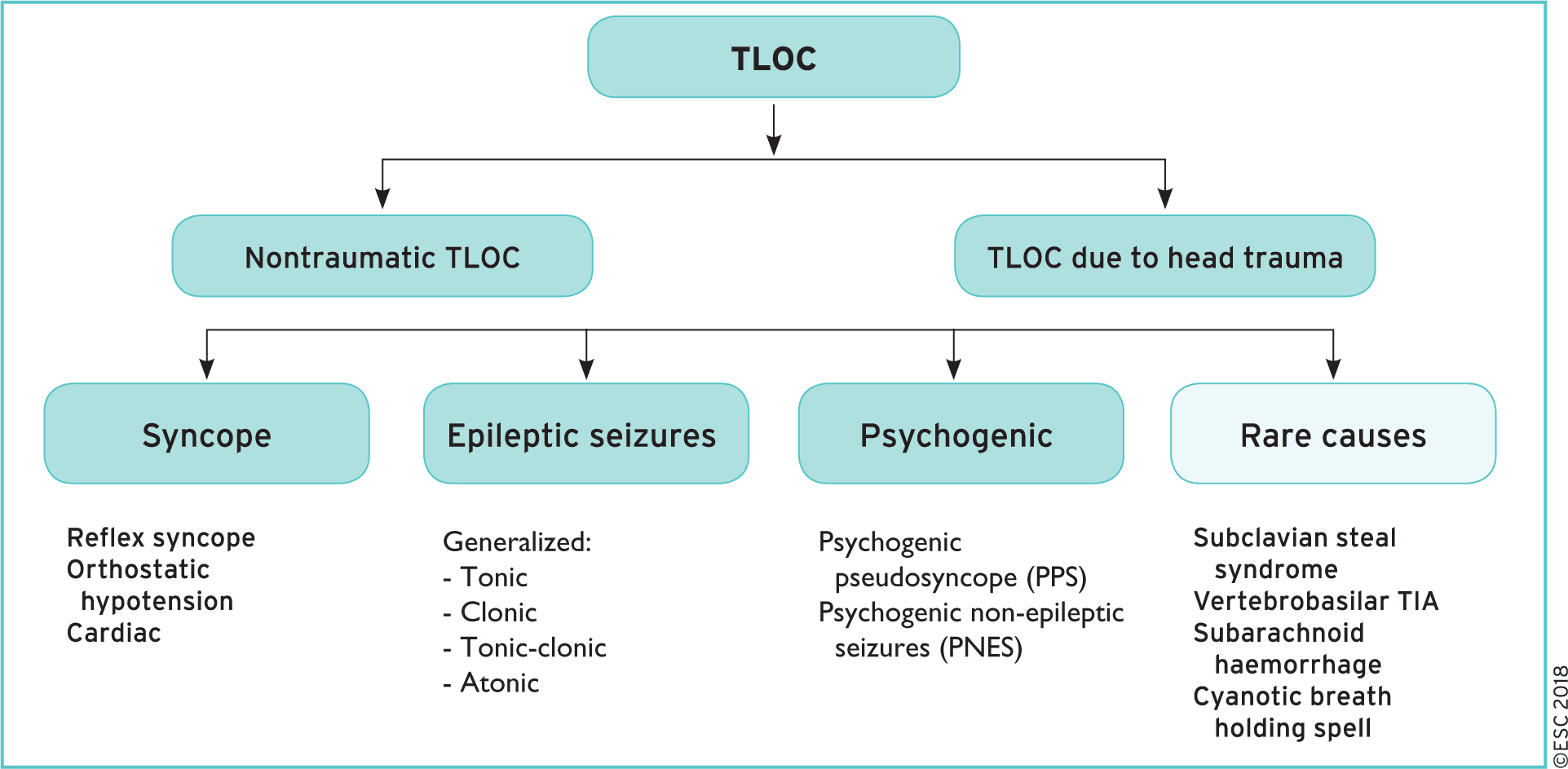
Differentials Of Syncope - Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a.
Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension.
Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of.
syncope Dentowesome
Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a.
Differential Diagnosis of Syncope
Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension.
Syncope Textbook of Cardiology
Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of.
SYNCOPE Blackbook Blackbook
Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a.
Treatment of Reflex Syncope
Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1.
Treatment of Reflex Syncope
Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1.
Syncope vs NearSyncope REBEL EM Emergency Medicine Blog
Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1.
Syncope Cardio Guide
Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension.
Syncope REBEL EM Emergency Medicine Blog
Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a.
Syncope Obgyn Key
Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a.
Syncope Is Classified As Neurally Mediated, Cardiac, And Orthostatic Hypotension.
Syncope is classified as neurally mediated, cardiac, and orthostatic hypotension. Important differential diagnosis for syncope include 1. Syncope is a sudden and transient loss of consciousness that is associated with a loss of. Syncope is a clinical syndrome in which transient loss of consciousness (tloc) is caused by a.