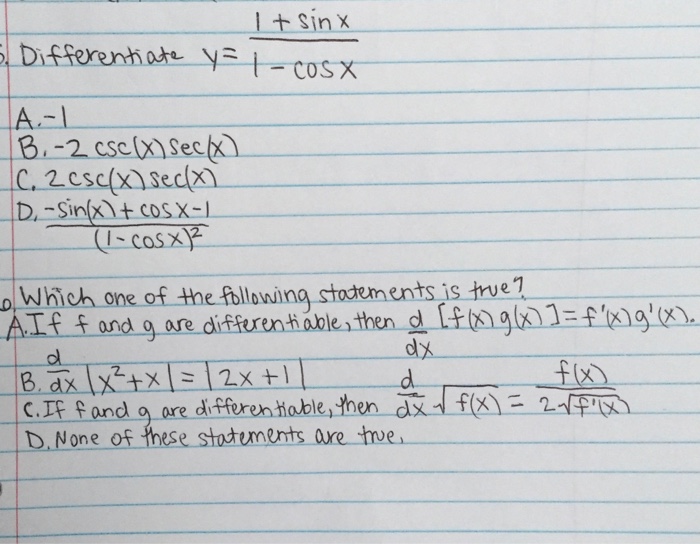Differentiate 1 1 Cosx - Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Type in any function derivative. Differentiate both sides of the equation. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient.
Differentiate both sides of the equation. Type in any function derivative. Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions.
Type in any function derivative. Differentiate both sides of the equation. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)).
The 1 cosx Formula Understanding Trigonometric Identities
Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Differentiate both sides of the equation. Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. Type in any function derivative. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)).
y = cot^1(cosxsinx/cosx+sinx) Find the derivative Maths Inverse
Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. Differentiate both sides of the equation. Type in any function derivative. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient.
Dy/dx + y = 1+sinx/1+cosx Maths Linear Equations in Two Variables
You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Type in any function derivative. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions.
Ex 5.5, 10 Differentiate x^(x cos x) + (x^2 + 1)/(x^2 1)
You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Differentiate both sides of the equation. Type in any function derivative. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2.
What Is 1 Cosx
Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Differentiate both sides of the equation. Type in any function derivative. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2.
Ex 9.3, 1 Find general solution dy/dx = 1 cos x/1+cosx
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Differentiate both sides of the equation. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Type in any function derivative.
Dy/dx + y = 1+sinx/1+cosx Maths Linear Equations in Two Variables
Type in any function derivative. Differentiate both sides of the equation. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions.
1cosx Identity, Proof 1cosx Formula [in terms of sin] iMath
Type in any function derivative. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2.
[Solved] Differentiate. cos(x Differentiate y = 1 + sin(ac) Course Hero
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions. Type in any function derivative. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient.
Solved a. Differentiate y=1+sinx / 1cosx&b. Which of the
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. Type in any function derivative. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions.
Compute Answers Using Wolfram's Breakthrough Technology & Knowledgebase, Relied On By Millions.
Differentiate both sides of the equation. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)). Y′ = −2sinx (1 −cosx)2. You can differentiate this function by using the quotient.




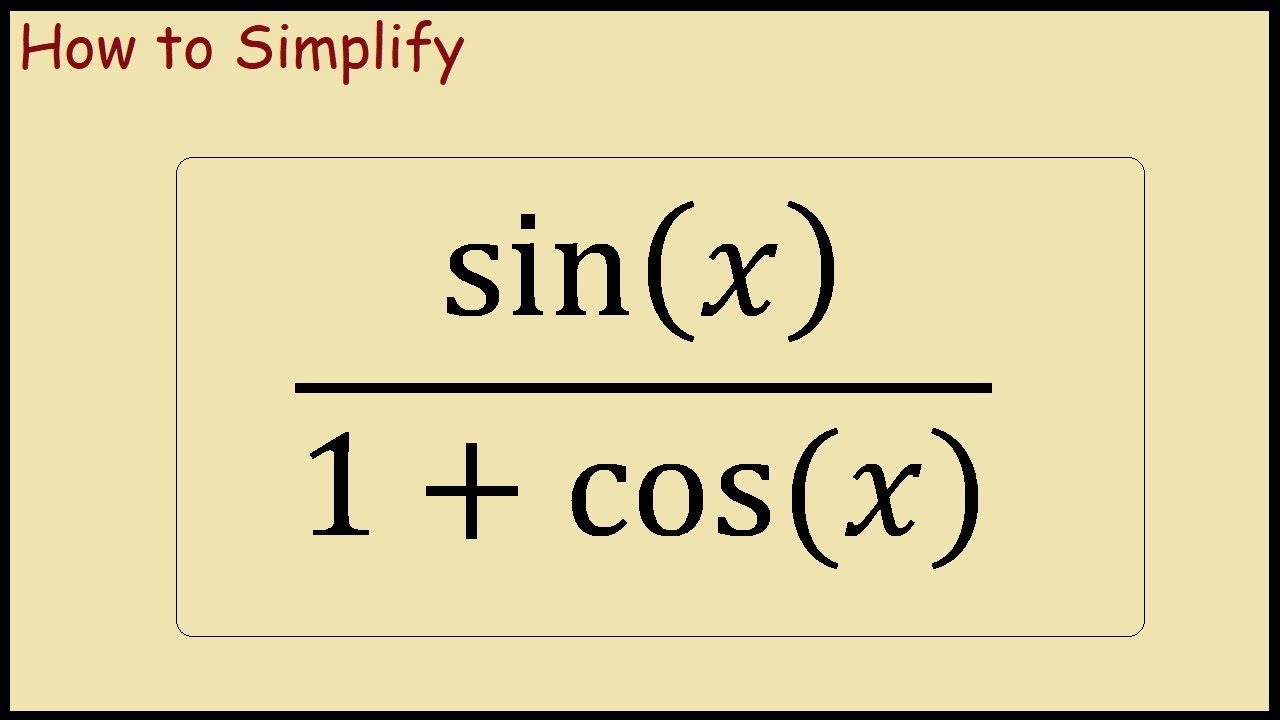


![1cosx Identity, Proof 1cosx Formula [in terms of sin] iMath](https://www.imathist.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/1-cosx-Formula.webp)