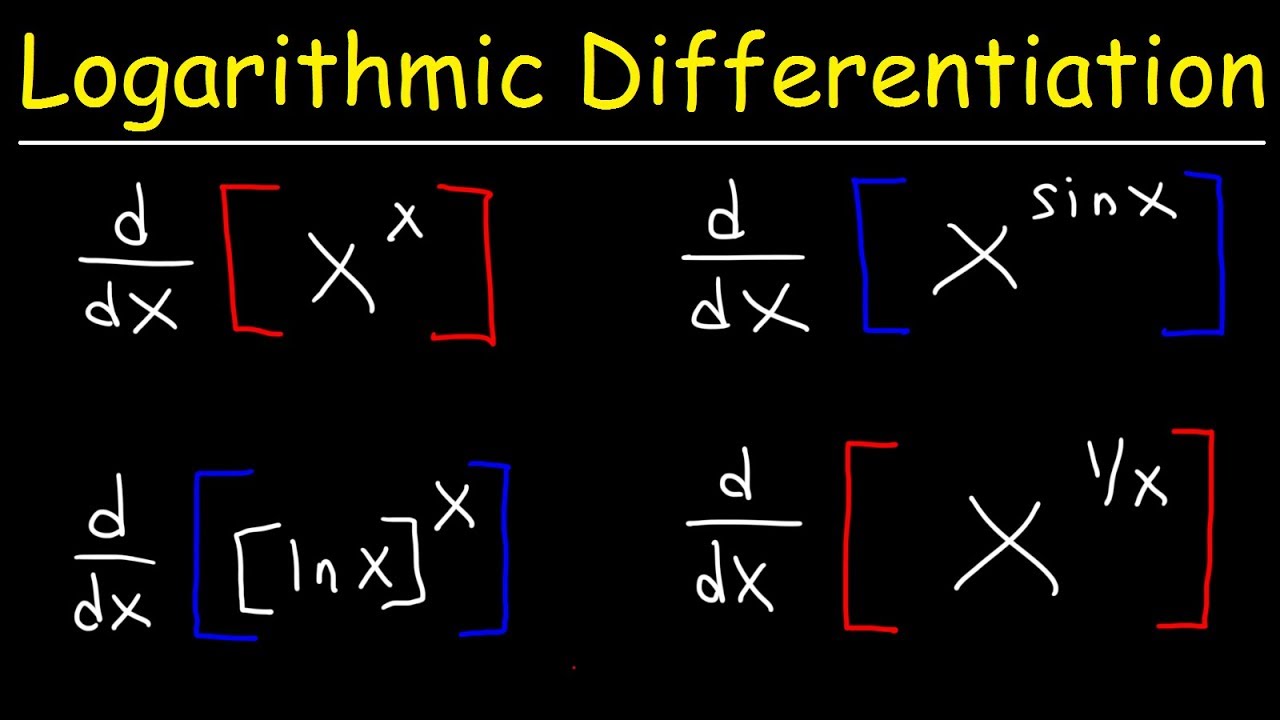
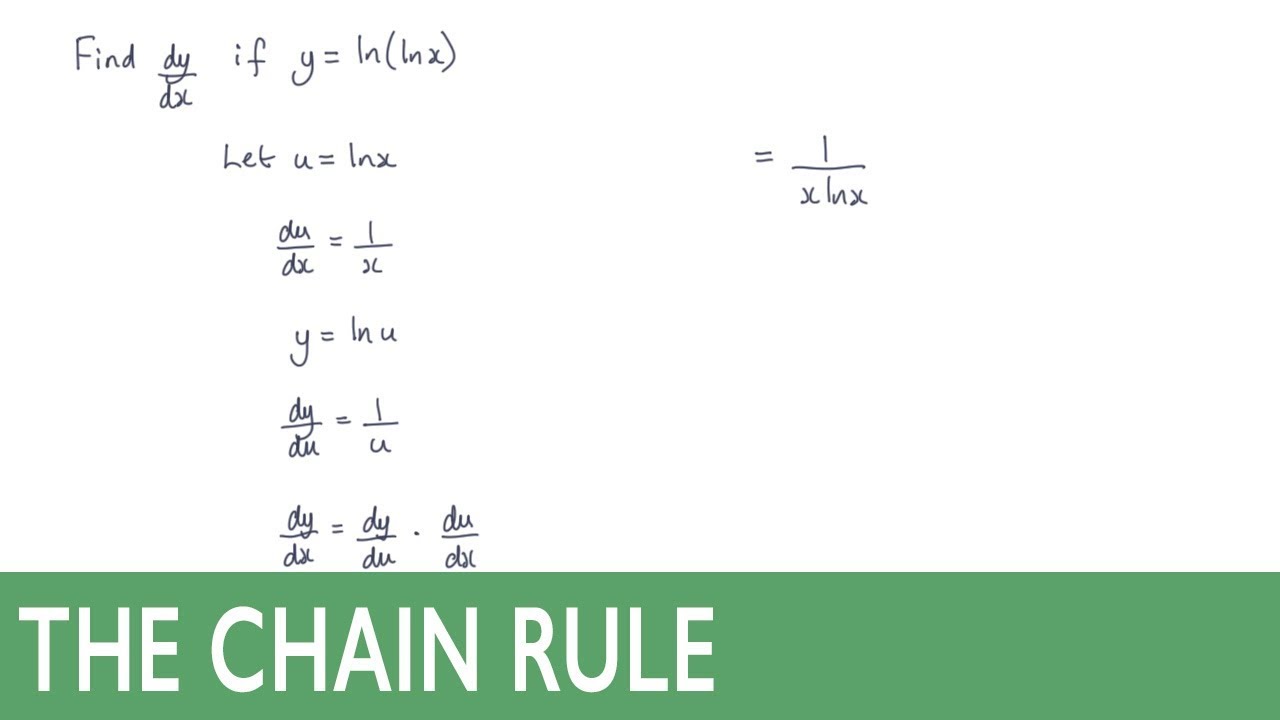
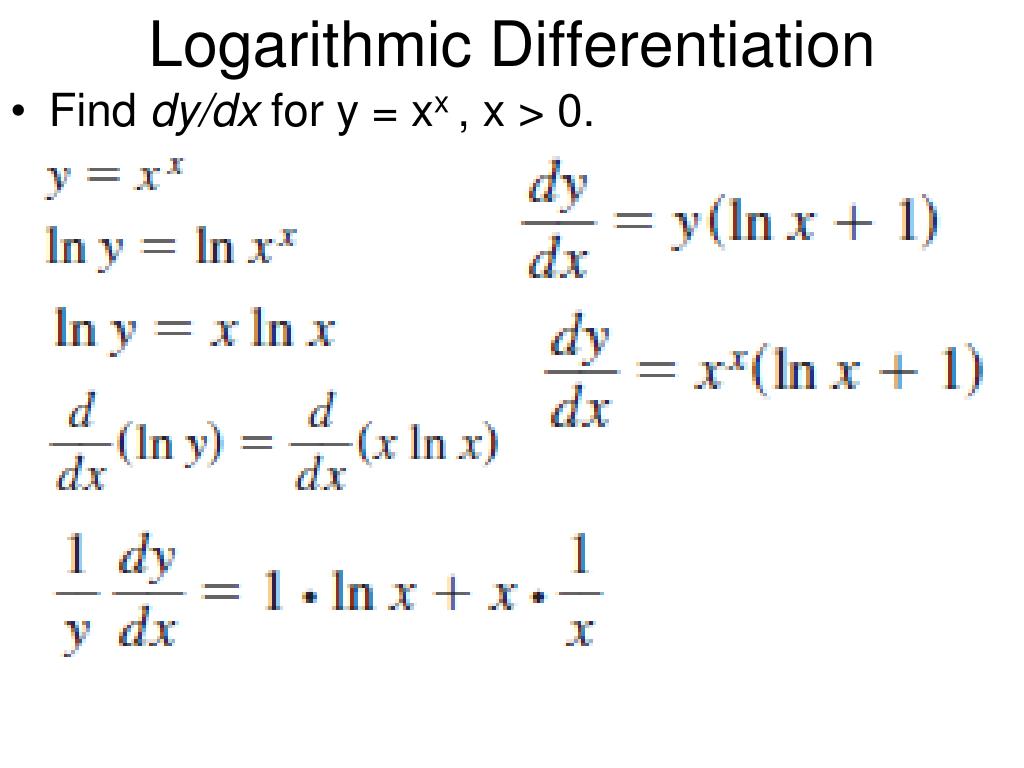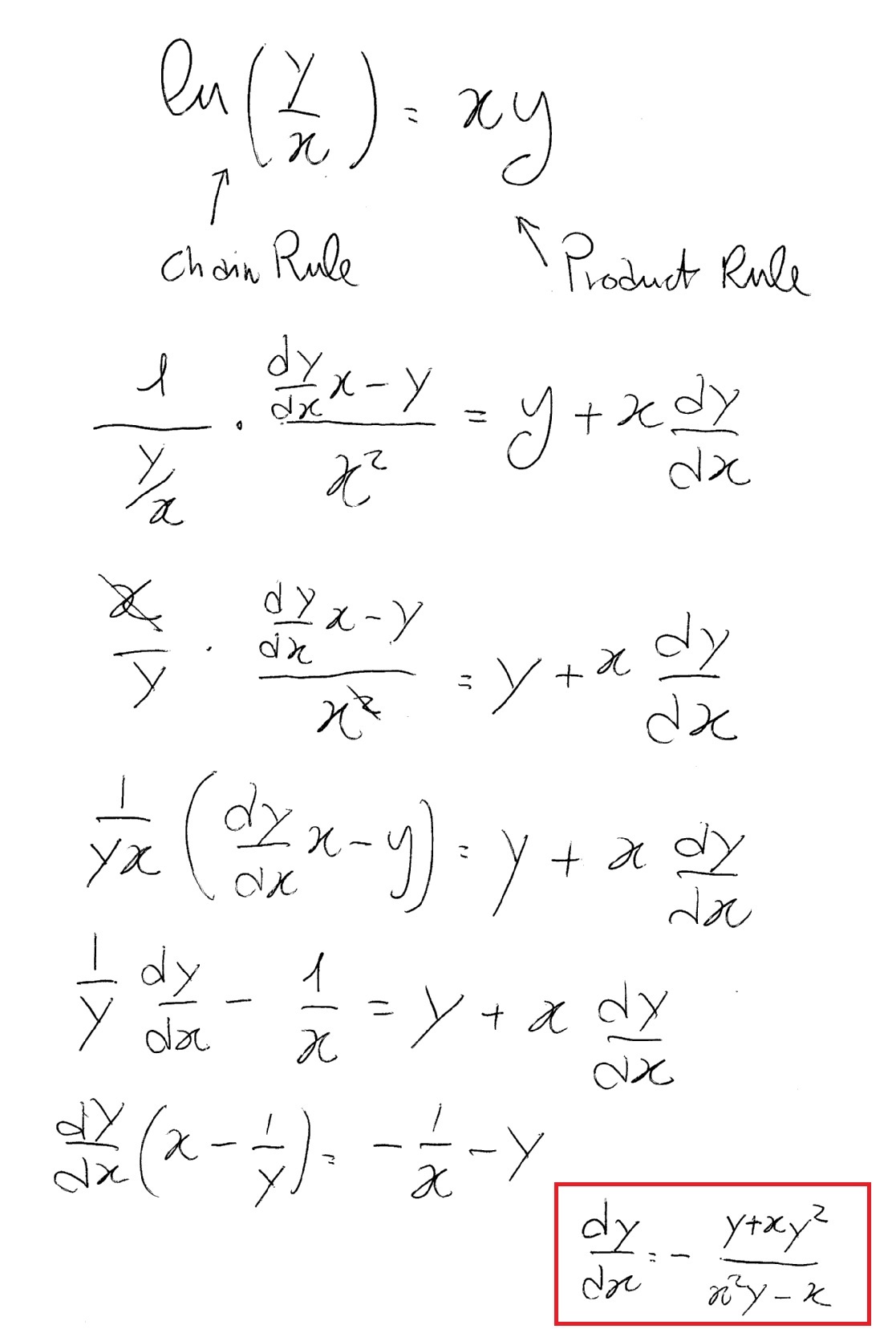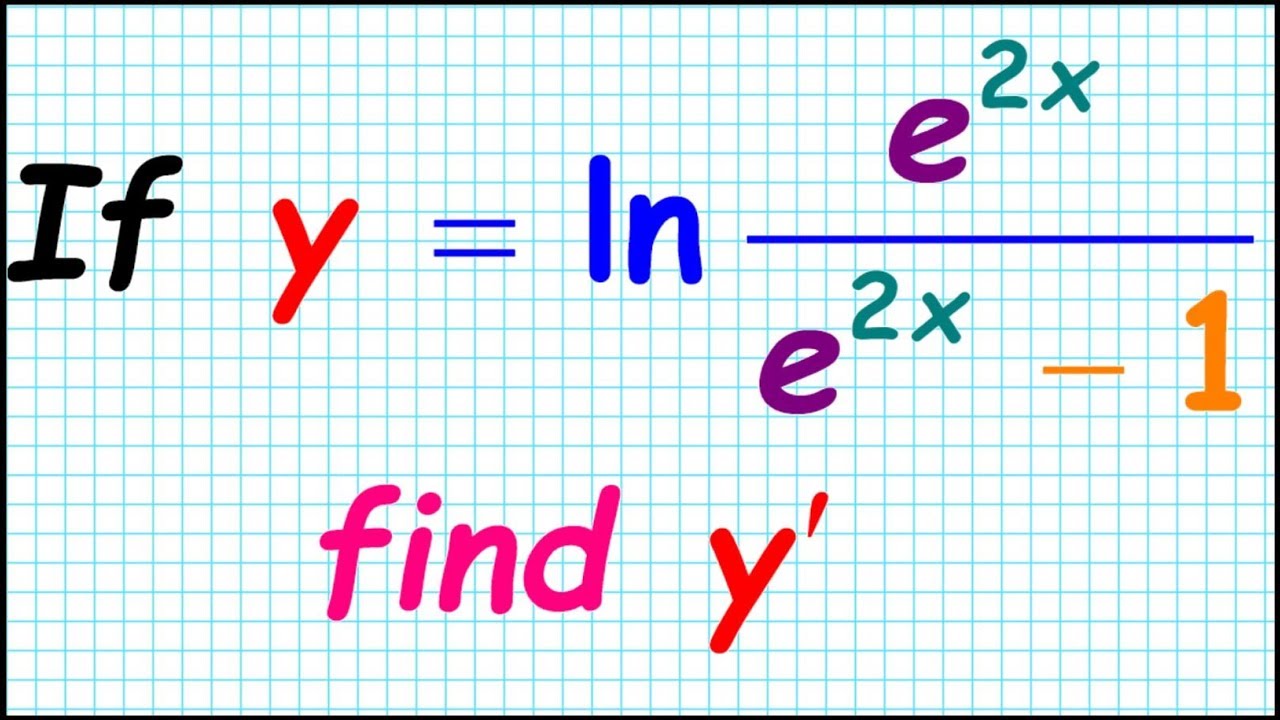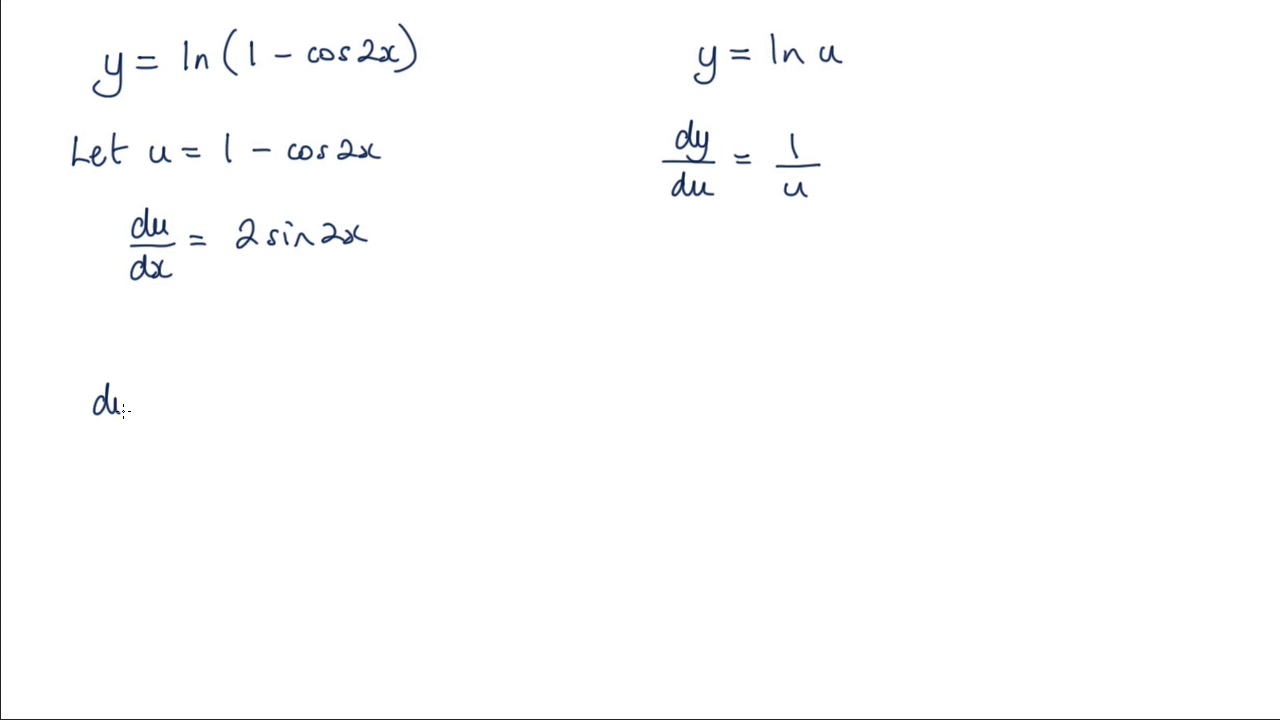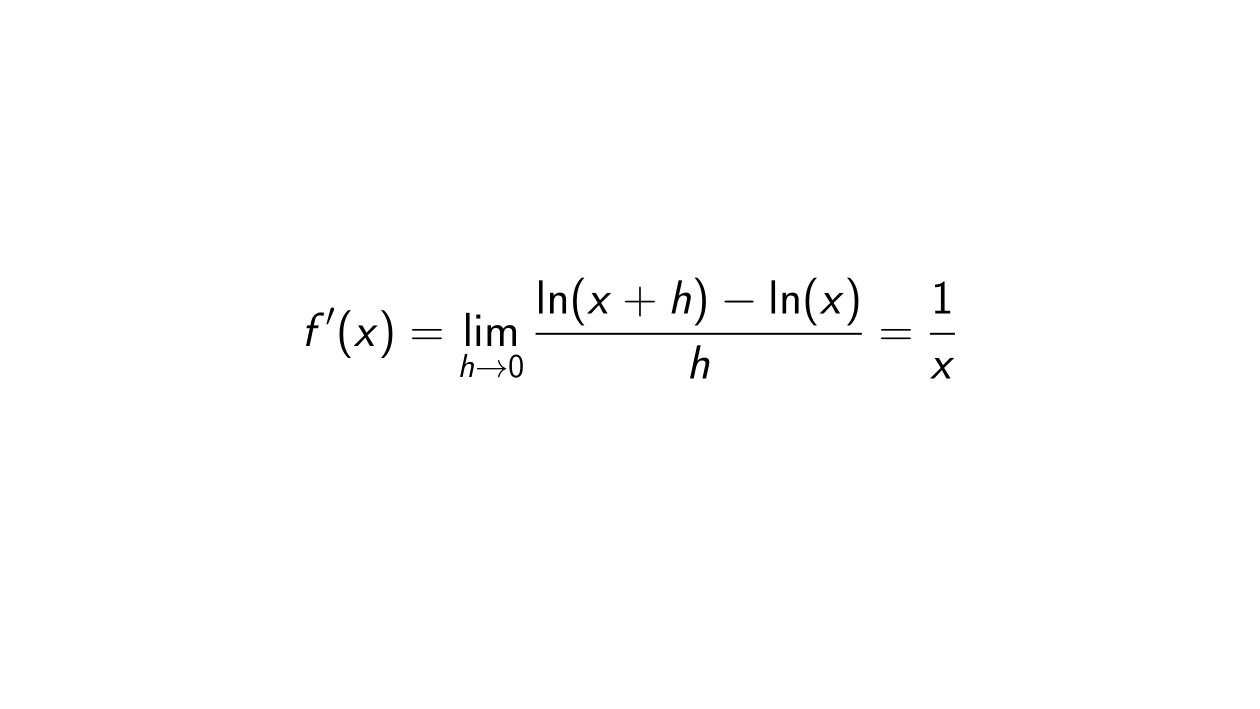Differentiate Ln 1 X - We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Y' = − 1 x. What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and. What is the derivative of y = ln(1 x)? Y = ln(1 x) this can be solved in two different ways, the simplest one is, using.
What is the derivative of y = ln(1 x)? Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. Y' = − 1 x. What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Y = ln(1 x) this can be solved in two different ways, the simplest one is, using. We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and.
We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. Y' = − 1 x. What is the derivative of y = ln(1 x)? Y = ln(1 x) this can be solved in two different ways, the simplest one is, using. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and. What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph.
Differentiate Ln X
What is the derivative of y = ln(1 x)? Y = ln(1 x) this can be solved in two different ways, the simplest one is, using. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. What is the derivative of ln(1.
Differentiate Ln X
We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? What is the derivative of y =.
Differentiate Ln X
What is the derivative of y = ln(1 x)? We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g.
Differentiate Ln X
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and. What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow.
Differentiate Ln X
What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students.
Differentiate Ln X
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and. Y' = − 1 x. Y = ln(1 x) this can be solved in two different ways, the simplest one is,.
Differentiate Ln X
What is the derivative of y = ln(1 x)? We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x).
Differentiate Ln X
Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d.
Differentiate Ln X
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and. Y' = − 1 x. We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to.
Differentiate Ln X
Y' = − 1 x. What is the derivative of ln(1 x)? Y = ln(1 x) this can be solved in two different ways, the simplest one is, using. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us.
What Is The Derivative Of Ln(1 X)?
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = ln(x) f (x) = ln (x) and. We could use the chain rule right away, but the properties of logarithms allow us to avoid that. Y' = − 1 x. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
Type In Any Function Derivative To Get The Solution, Steps And Graph.
Y = ln(1 x) this can be solved in two different ways, the simplest one is, using. What is the derivative of y = ln(1 x)?