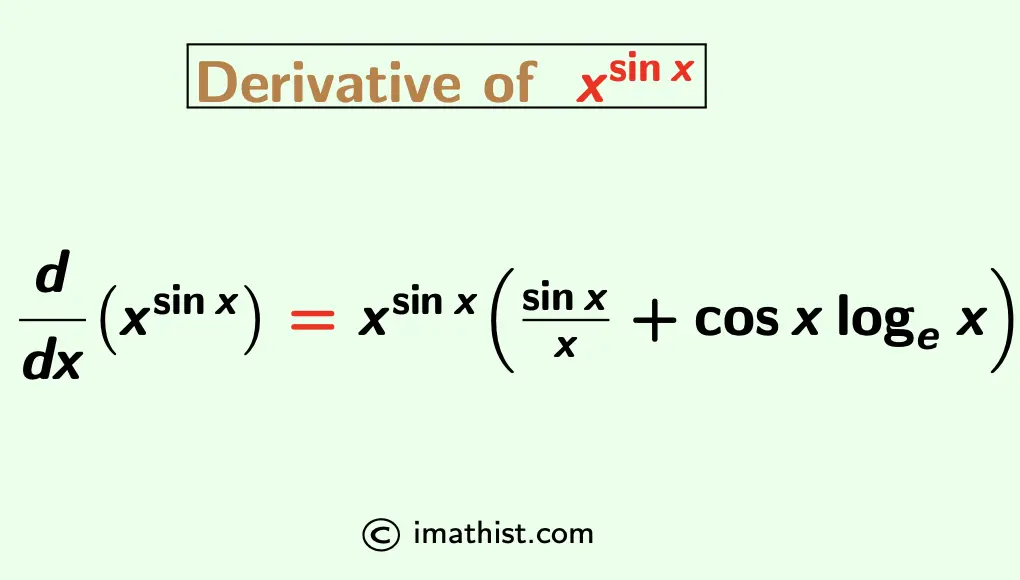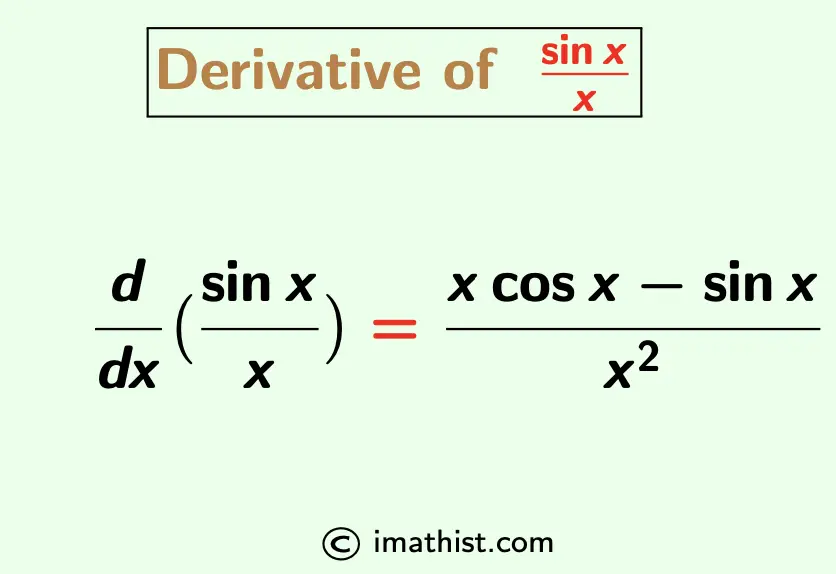Differentiate X Sinx - How do you differentiate xsin(x)? When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify. (x s i n x + c o s x) (e x + x 2 l o g x) The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles.
When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: (x s i n x + c o s x) (e x + x 2 l o g x) Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify. The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. How do you differentiate xsin(x)? Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits.
Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify. (x s i n x + c o s x) (e x + x 2 l o g x) When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. How do you differentiate xsin(x)? The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles.
Differentiate sinx/x from the first principle Math Limits and
How do you differentiate xsin(x)? Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify. The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. Doing this requires using the.
Derivative of x^sinx Formula, Proof x^sinx Derivative iMath
Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: (x s i n x + c o s x) (e x + x 2 l o g x) The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. How do you differentiate xsin(x)?
Differentiate e^sinx with respect to cos x
(x s i n x + c o s x) (e x + x 2 l o g x) When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. How.
differentiate cosx^sinx w.r.t x
Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify. How do you differentiate xsin(x)? Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. (x s i n x + c o s x) (e x + x 2 l o g x) When we have a function of.
Derivative of trigonometric function sinx and Class Eleven Maths
Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify. The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. (x s i n x + c o s x) (e x + x 2 l o g x) How.
Ex 5.4, 1 Differentiate ex / sinx Chapter 5 NCERT Ex 5.4
How do you differentiate xsin(x)? Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx +.
Derivative of sinx/x sinx/x Derivative iMath
The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. How do you differentiate xsin(x)? Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify.
What Is The Derivative Of Sinx Cosx at James Arlene blog
The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. How do.
Ex 5.5, 9 Differentiate x^sin x + (sin x)^cos x Chapter 5 Class 12
Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its power, perhaps the. The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms.
Misc 4 Differentiate sin1 (x root x) Chapter 5 NCERT
Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: How do you differentiate xsin(x)? The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles. Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify. When we have a function of #x# like #y=x^sin x#, where a single term contains #x# in both its base and its.
When We Have A Function Of #X# Like #Y=X^sin X#, Where A Single Term Contains #X# In Both Its Base And Its Power, Perhaps The.
Doing this requires using the angle sum formula for sin, as well as trigonometric limits. How do you differentiate xsin(x)? Differentiate the following functions with respect to x: Dy dx = (xsinx)(cosxlnx + sinx x) take natural logarithms to both sides and simplify.
(X S I N X + C O S X) (E X + X 2 L O G X)
The derivative of \sin(x) can be found from first principles.