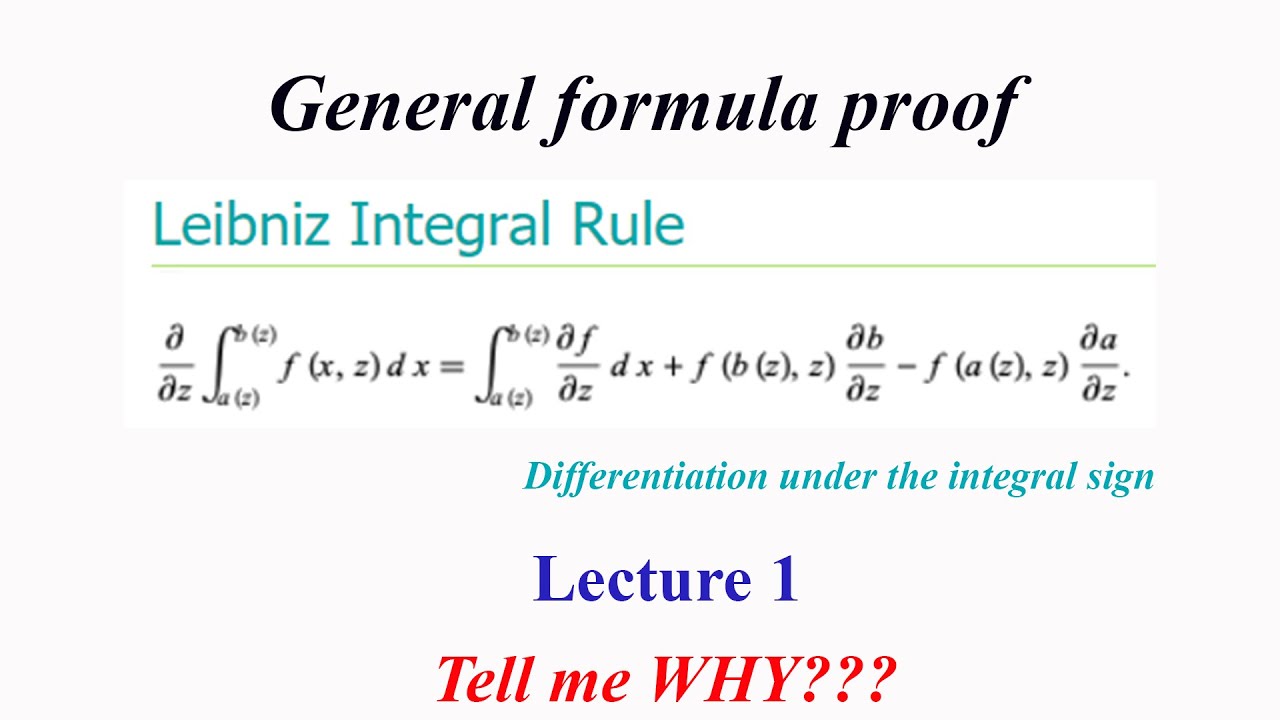
Differentiating Under The Integral - Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x. If you have chosen the generalization right, the resulting integral will be easier to solve, so. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Kc border differentiating an integral: Differentiate under the integral sign. Under fairly loose conditions on the. Find the solution of the following integral equation:
Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Φ(x) + |x − s|φ(s)ds = x, −1 ≤ x ≤ 1. Under fairly loose conditions on the. Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Find the solution of the following integral equation: Eventually xn belongs to ux,. If you have chosen the generalization right, the resulting integral will be easier to solve, so. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x.
Kc border differentiating an integral: Φ(x) + |x − s|φ(s)ds = x, −1 ≤ x ≤ 1. Eventually xn belongs to ux,. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. If you have chosen the generalization right, the resulting integral will be easier to solve, so. Find the solution of the following integral equation: Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x. Differentiate under the integral sign.
[Solved] Please help me solve this differentiating under the integral
Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Eventually xn belongs to ux,. Differentiate under the integral sign. Find the solution of the following integral equation: Kc border differentiating an integral:
SOLUTION Notes on differential under integral sign Studypool
Eventually xn belongs to ux,. If you have chosen the generalization right, the resulting integral will be easier to solve, so. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Find the solution of the following integral equation: Differentiate under the integral sign.
Integral Sign
Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Eventually xn belongs to ux,. If you have chosen the generalization right, the resulting integral will be easier to solve, so. Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals.
Differentiation Under The Integral Sign Problems Risala Blog
Differentiate under the integral sign. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Find the solution of the following integral equation:
SOLUTION The method of differentiating under the integral sign
Kc border differentiating an integral: Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x. Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Under fairly loose conditions on the. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals.
Differentiating Under The Integral Sign PDF Integral Function
Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x. Eventually xn belongs to ux,. Kc border differentiating an integral: Differentiate under the integral sign. Φ(x) + |x − s|φ(s)ds = x, −1 ≤ x ≤ 1.
[Solved] Please help me solve this differentiating under the integral
Under fairly loose conditions on the. If you have chosen the generalization right, the resulting integral will be easier to solve, so. Eventually xn belongs to ux,. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =.
Differentiating Under The Integral Sign PDF Integral Derivative
Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Eventually xn belongs to ux,. Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x. Differentiate under the integral sign. Kc border differentiating an integral:
integration Gaussian Integral Problem Confusion Mathematics Stack
Find the solution of the following integral equation: Φ(x) + |x − s|φ(s)ds = x, −1 ≤ x ≤ 1. Differentiate under the integral sign. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that.
Integral Sign
Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x. Differentiate under the integral sign. Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Kc border differentiating an integral:
If You Have Chosen The Generalization Right, The Resulting Integral Will Be Easier To Solve, So.
Differentiate under the integral sign. Leibniz’ rule 3 xn → x. Where in the first integral x ≥ s and |x−s| =. Eventually xn belongs to ux,.
Differentiation Under The Integral Sign Is An Operation In Calculus Used To Evaluate Certain Integrals.
Find the solution of the following integral equation: Kc border differentiating an integral: Since f is continuous in x, f(xn,ω) → f(x,ω) for each ω. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that.
Under Fairly Loose Conditions On The.
Φ(x) + |x − s|φ(s)ds = x, −1 ≤ x ≤ 1.