Differentiation Of Acceleration - Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\). 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time.
7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\).
Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\). Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time.
Derivation of Centripetal Acceleration/Radial Acceleration
Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\).
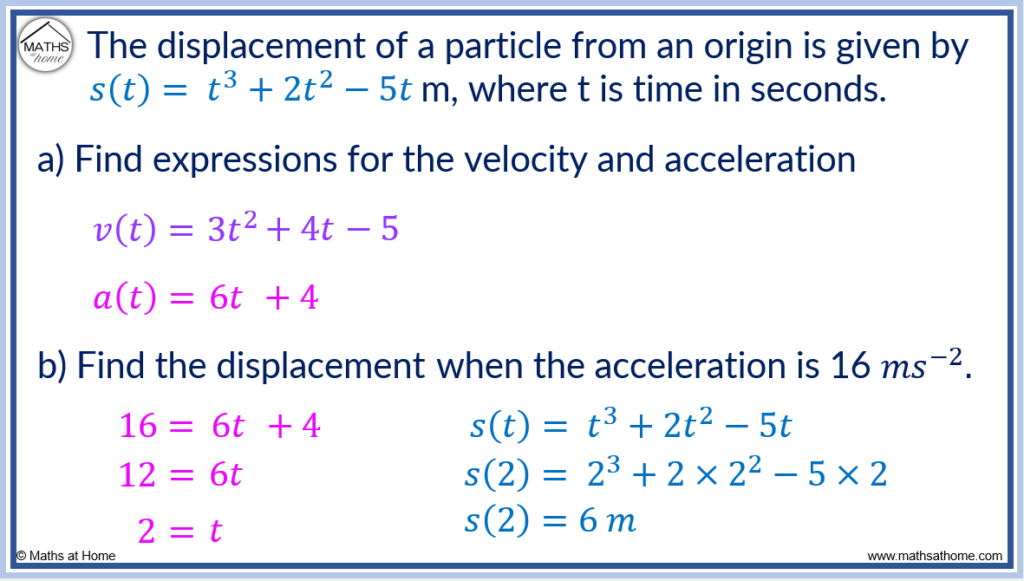
How to Find Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\).
GCSE Revision (Differentiation Displacement, Velocity and
Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\). 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time.
Find acceleration through using differentiation. Please show complete
Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\). 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it.
Texas K12 Science Curriculum Differentiation & Acceleration Summit K12
Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\). Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time.
How to Find Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\). 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it.
Acceleration Practice Problems Answer Key Studocu Worksheets Library
Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\).
Texas K12 Science Curriculum Differentiation & Acceleration Summit K12
7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\).
How to Find Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\). 7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it.
Differentiation acceleration Identifying and adapting instruction to
7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. Si units of acceleration are meters per second squared \(\left(\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)\).
Si Units Of Acceleration Are Meters Per Second Squared \(\Left(\Mathrm{M} / \Mathrm{S}^{2}\Right)\).
7 rows by definition, acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it.