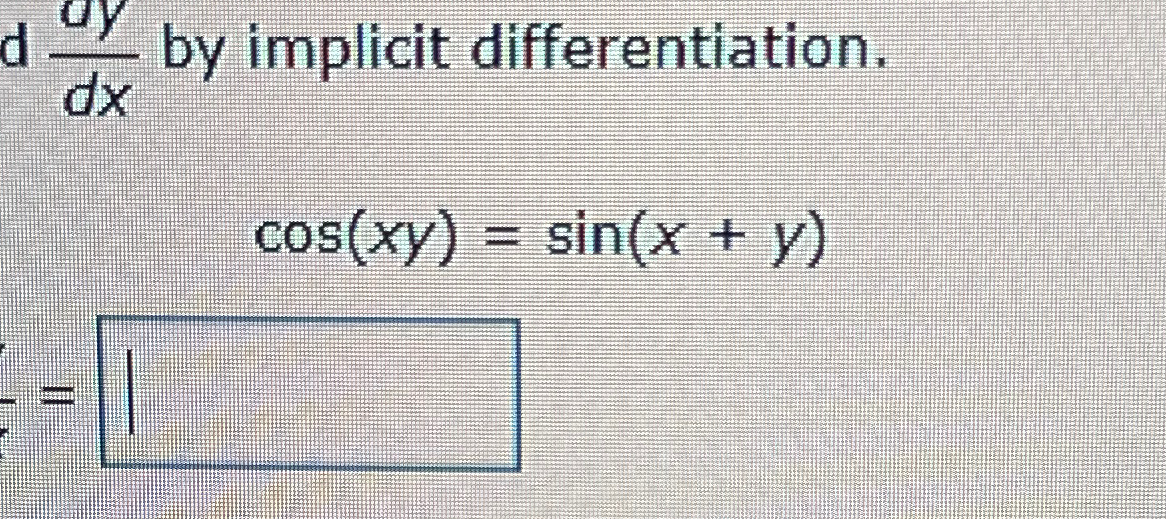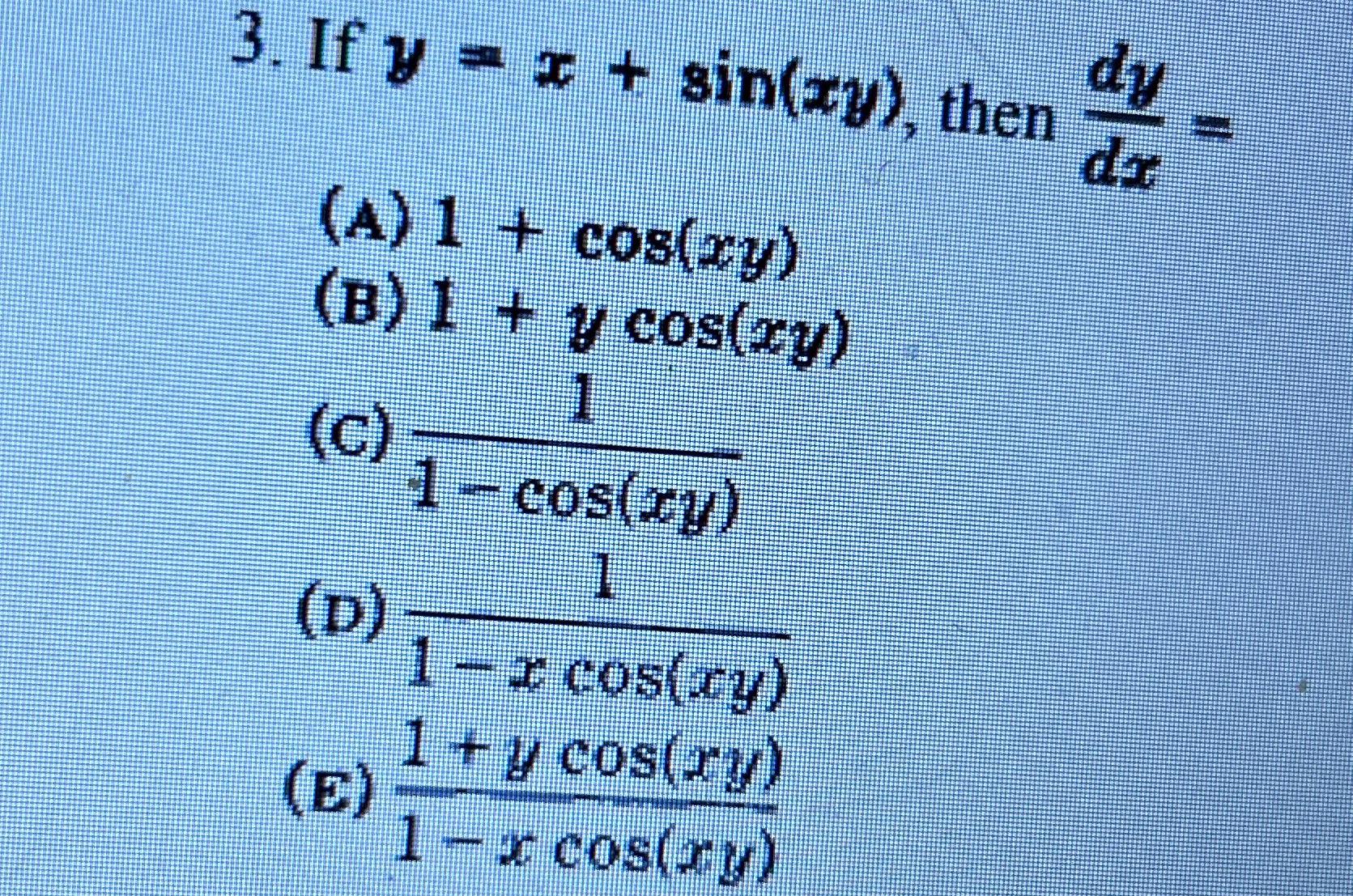Differentiation Of Cos Xy - Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = cos(x) f (x) = cos (x). The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change. D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule: Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d x. What is the derivative of cos(xy)?
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = cos(x) f (x) = cos (x). D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d x. What is the derivative of cos(xy)? Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule:
Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d x. D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = cos(x) f (x) = cos (x). The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more What is the derivative of cos(xy)? D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule:
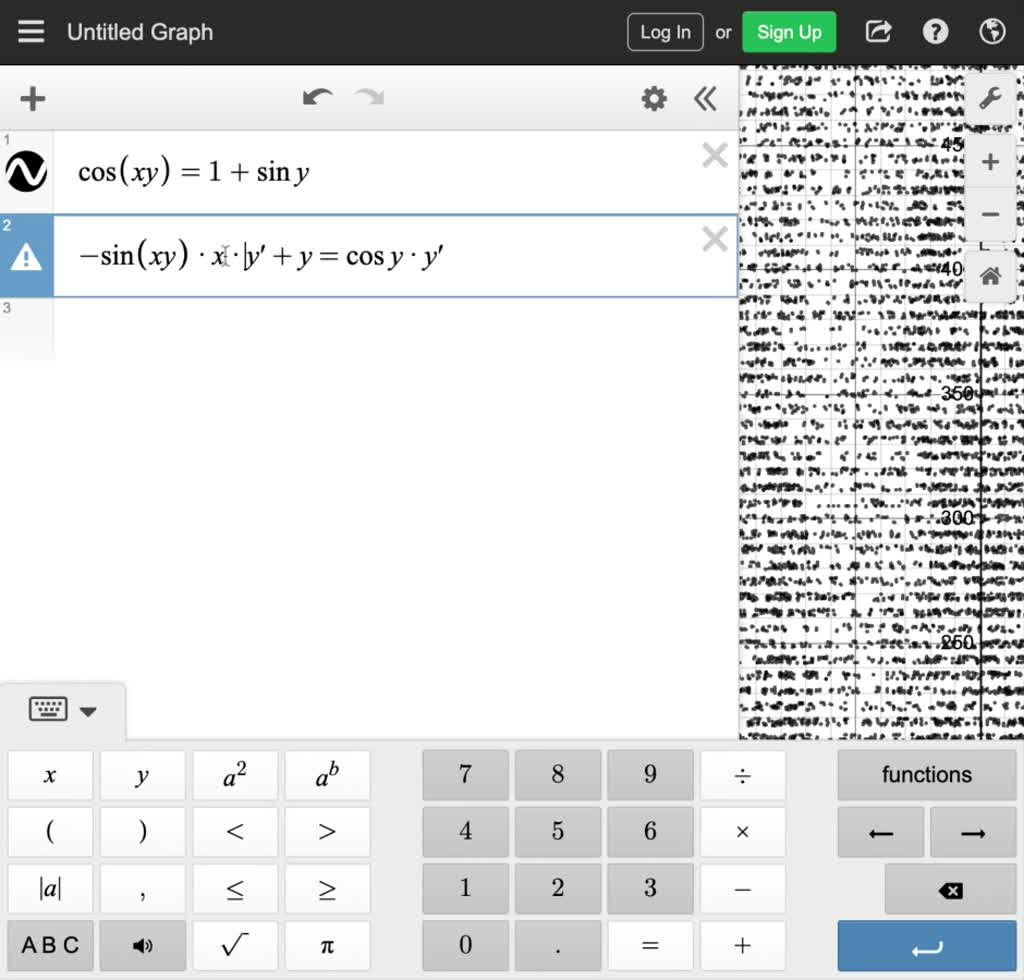
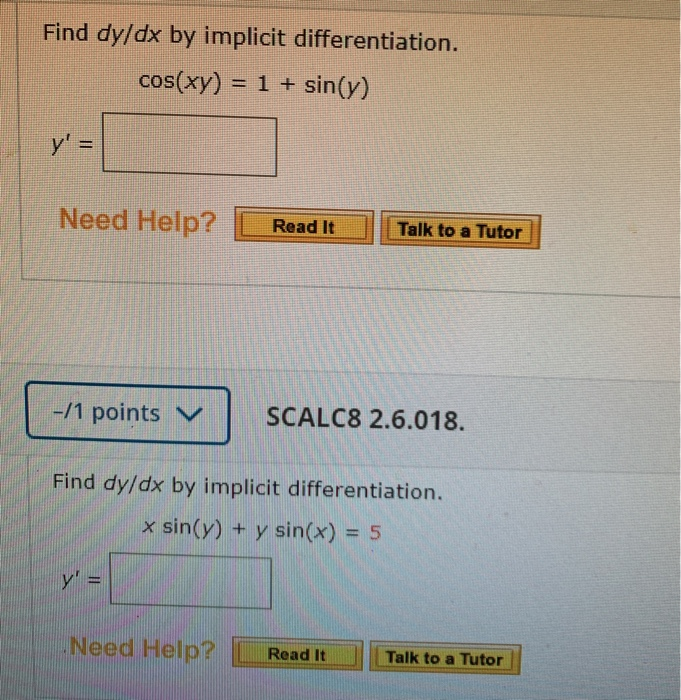
SOLVED Find dy/dx by implicit differentiation. cos(xy) = 1 + siny
D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule: Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d x. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more What is the derivative of cos(xy)?
Solved ddydx by implicit differentiation.cos(xy)=sin(x+y)
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule: \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x).
Solved Find dy/dx by implicit differentiation. cos(xy) = 1 +
What is the derivative of cos(xy)? Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d x. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d.
Solved If y=x+sin(xy), then
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = cos(x) f (x) = cos (x). Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then.
Solved Given the following differential equation ( cos(xy?)
What is the derivative of cos(xy)? D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule: \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′.
Solved Find dy/dx by implicit differentiation. cos (xy)=sin (x+y) dy
D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = cos(x) f (x) = cos (x). Replace y' y ′.
[Solved] Find dy / dx by implicit differentiation. cos( xy ) = 1 + sin
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that.
Solved Given the following differential equation (cos(xy) +
\int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change. What is the derivative of cos(xy)? D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule: Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))].
[Solved] Find dy / dx by implicit differentiation. cos( xy ) = 1 + sin
What is the derivative of cos(xy)? D dx cos(xy) = −sin(xy) ⋅ d dx (xy) then the. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change.
Solved Use implicit differentiation to find dy/dx. Cos xy +
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = cos(x) f (x) = cos (x). Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics. D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use.
Free Math Problem Solver Answers Your Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Calculus, And Statistics.
What is the derivative of cos(xy)? \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = cos(x) f (x) = cos (x). D dx cos(xy) = −(y + x dy dx)sin(xy) use the chain rule:
D Dx Cos(Xy) = −Sin(Xy) ⋅ D Dx (Xy) Then The.
The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change. Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d x.