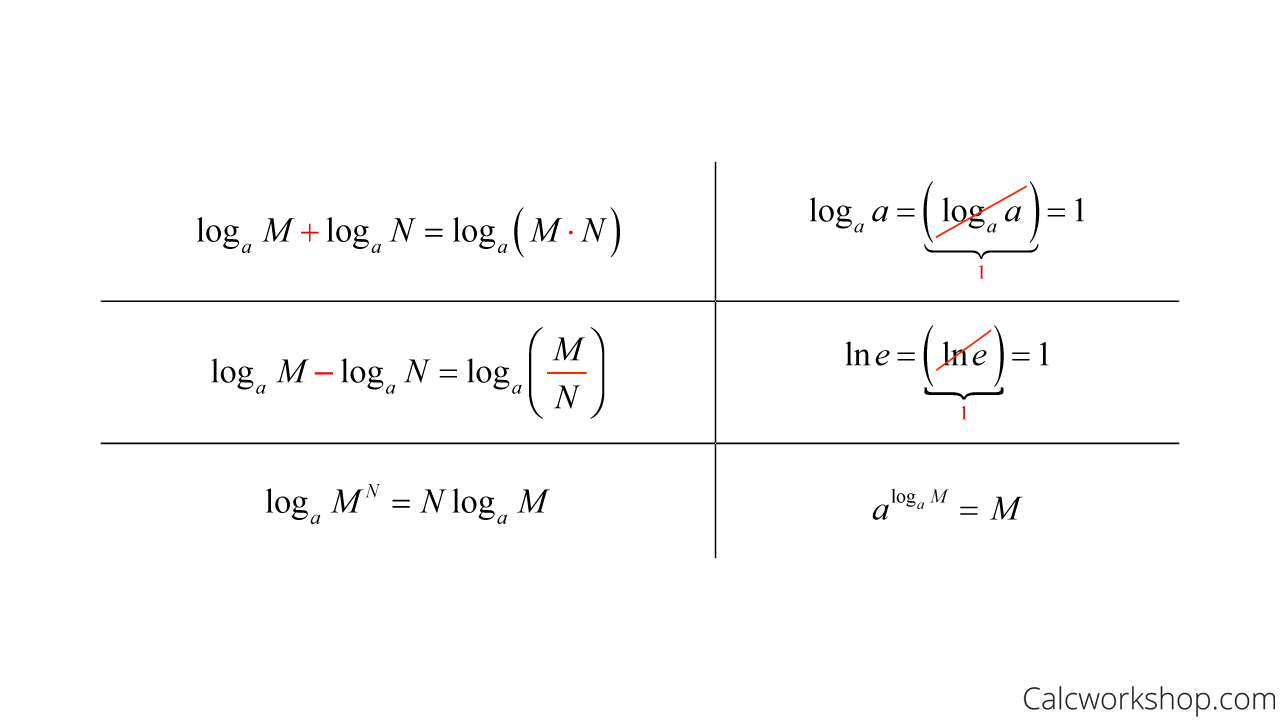
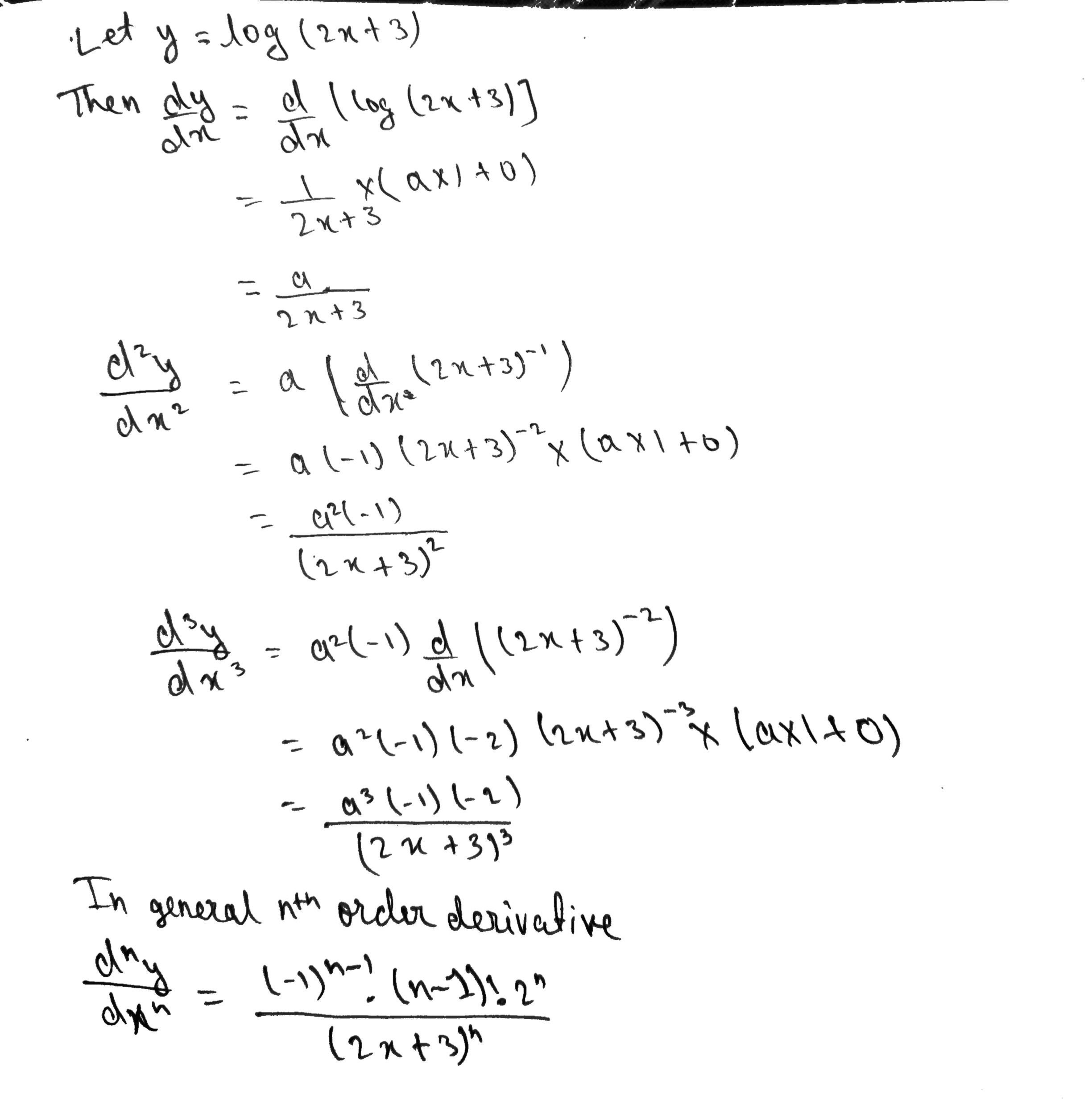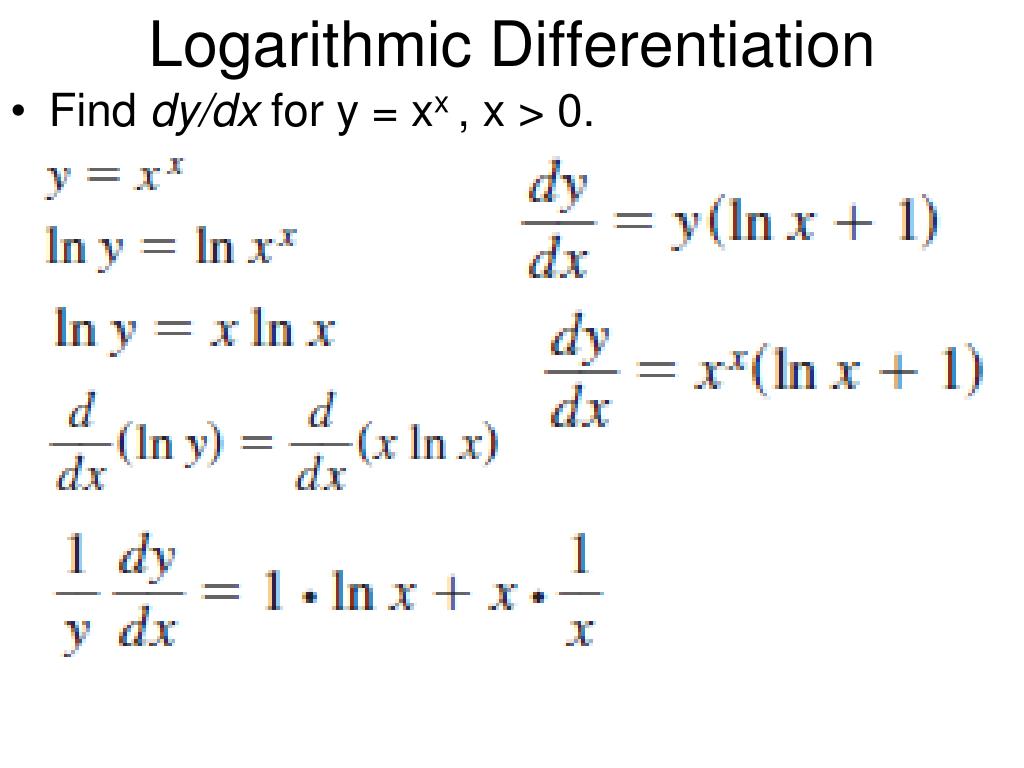Differentiation Of Log 1 X - In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with.
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation.
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with.
Derivative of log 2x iapsawe
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of the natural logarithm function,.
Differentiation Of Log X Derivatives of Logs YouTube Find if y
In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g.
Logarithmic Differentiation (w/ 7 StepbyStep Examples!)
The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). Logarithmic differentiation gives.
Log Y Differentiation at Jeremy Broady blog
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of the natural logarithm function,.
√1000以上 log((1 x)/(1x)) expansion 199008Log((1+x)/(1x)) expansion
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the.
Solved Question 9 Calculate the derivative by logarithmic
In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g.
Differentiation of Logarithmic Functions AlvinexReed
The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). In this section.
Differentiation Of Log X Derivatives of Logs YouTube Find if y
In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). The derivative of the natural logarithm function,.
Logarithmic Differentiation (w/ 7 StepbyStep Examples!)
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives.
Log(1+X) lacemyaf
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives.
Logarithmic Differentiation Gives An Alternative Method For.
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = log(x) f (x) = log (x). In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of the natural logarithm function, ln(x), is 1/x, which differs from the derivatives of logarithmic functions with.