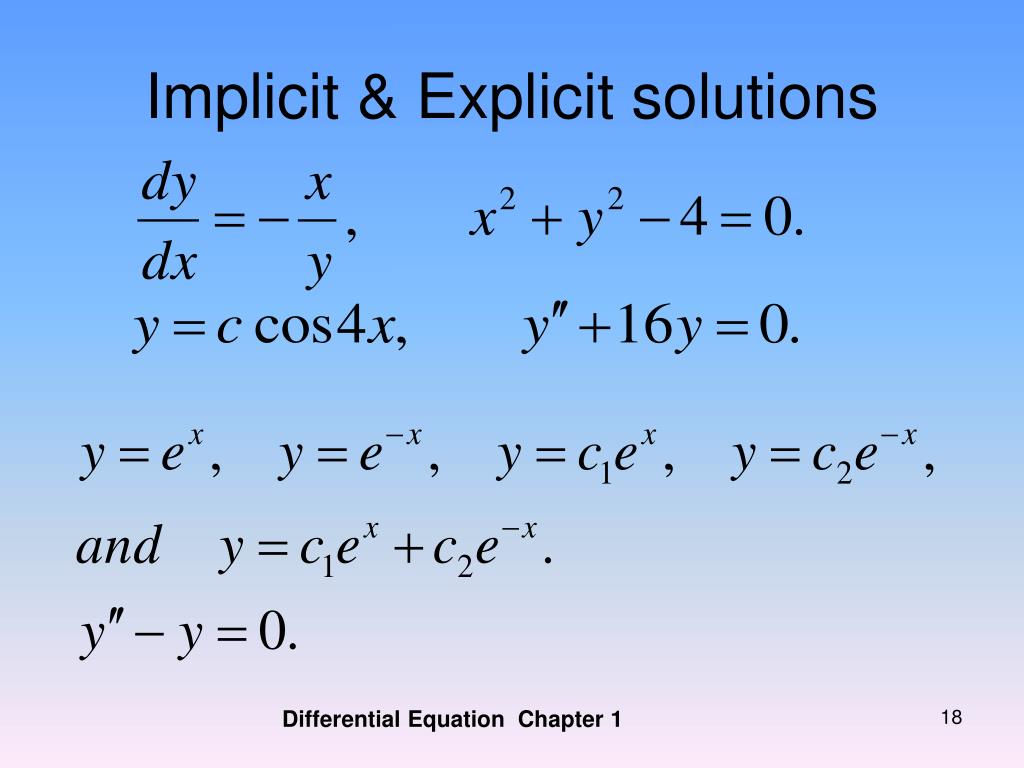
Explicit Form Differential Equations - Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. If it is of the form. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is.
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. If it is of the form. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit.
Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; If it is of the form.
Ordinary Differential Equations (A Comprehensive Resource)
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations Mr
If it is of the form. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Thus, if a differential equation.
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. If it is of the form.
Exact differential equations Yawin
Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. If it is of the form. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) =.
PPT Ordinary Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. If it is of the form. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary.
Find the explicit particular solution of the differenti... Math
Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. If it is of the form. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Thus, if a differential equation.
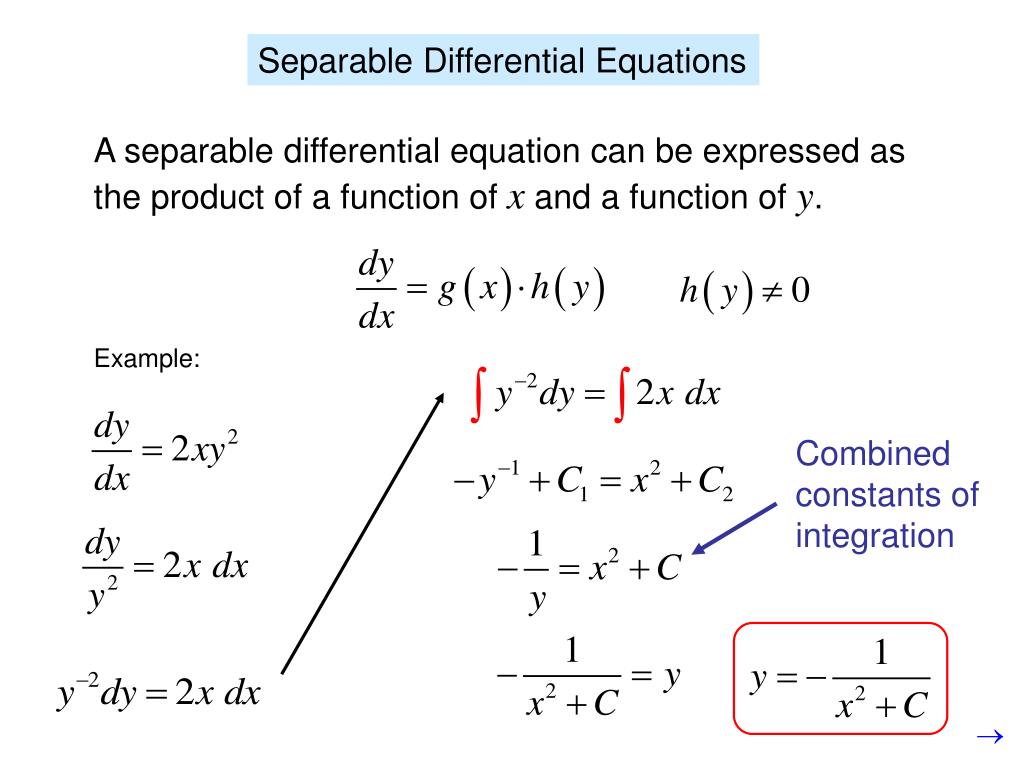
PPT Separable Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free
Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. The implicit solution of.
First Order Differential Equation Worksheet Equations Worksheets
The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is.
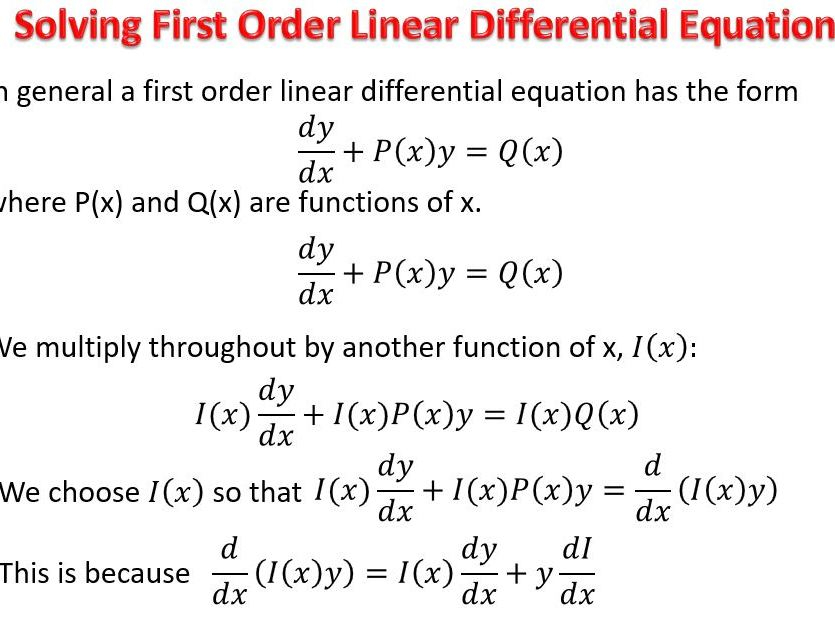
Solved A) Determine the implicit and explicit form of
Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. If it is of the form. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n).
[Solved] Find the solution of the given initial value problem in
If it is of the form. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. The implicit solution of this differential equation is.
If It Is Of The Form.
Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is.
The Implicit Solution Of This Differential Equation Is $X^2+Y(X)^2=R^2$;
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation.