Fever Differential Diagnosis - Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f).
Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo).
Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis for Unexplained Fever in Immunosuppressed
Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Peripheral temperature.
Types of Fever Differential Diagnosis Isabel Healthcare
Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Peripheral temperature.
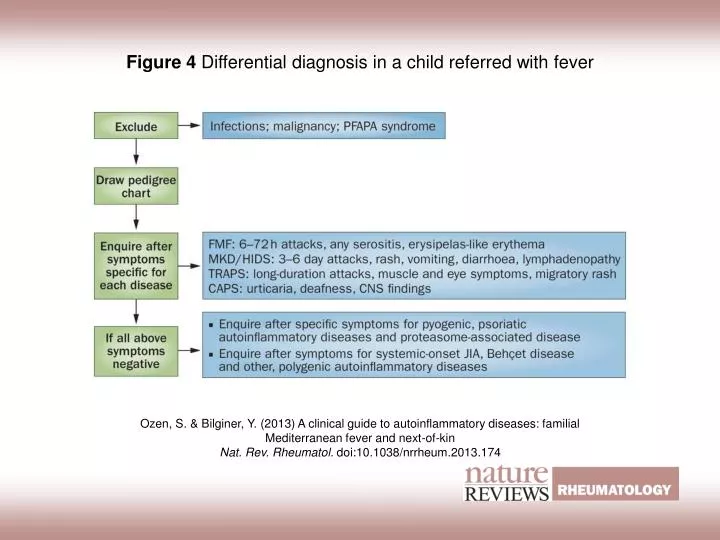
PPT Figure 4 Differential diagnosis in a child referred with fever
Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Peripheral temperature.
Typhoid Fever Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care Plan
Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as.
Relapsing fever differential diagnosis wikidoc
Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Peripheral temperature.
Fever and Rash Differential Diagnosis PDF
Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused.
Fever Differential Diagnosis FEVER DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS (IM
Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused.
1 Minute Read Types of Fever Differential Diagnosis
Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo). Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Peripheral temperature.
Fever Differential Diagnosis
Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without.
Types of Fever Differential Diagnosis Isabel Healthcare
Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Learn about fever, a nonspecific symptom that may be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions. Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without.
Learn About Fever, A Nonspecific Symptom That May Be Caused By Infectious And Noninfectious Conditions.
Peripheral temperature is not clinically accurate and central measurements are the preferred. Most febrile illnesses either resolve before a diagnosis can be made or develop distinguishing characteristics that lead to a diagnosis. Defined as temperature ≥38°c (100.4°f). Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown origin (fuo).