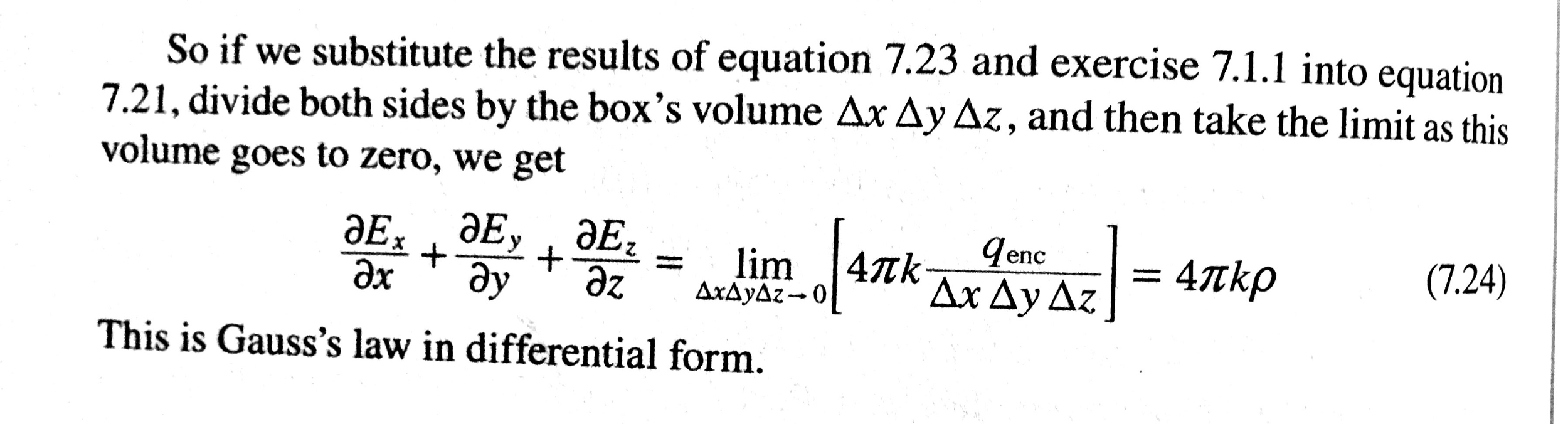Gauss Law Differential Form - The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field.
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space.
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any.
electrostatics Problem in understanding Differential form of Gauss's
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and.
Solved Gauss's law in differential form relates the electric
(1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. It.
Solved Using the differential form of Gauss's law, determine
It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field.
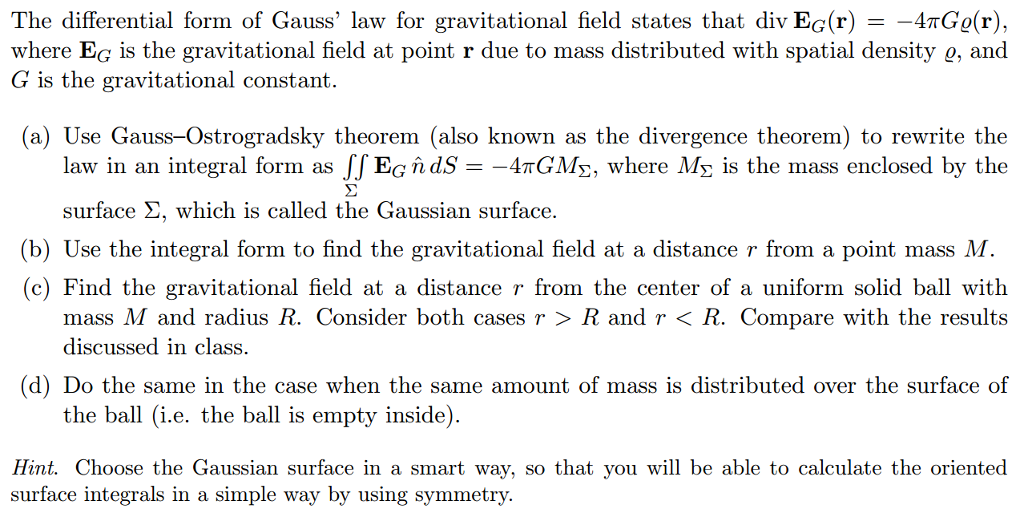
Solved The differential form of Gauss' law for gravitational
It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and.
Differential Integral Form Gauss Law Stock Vector (Royalty
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. (1) in the following part,.
Solved 1. Gauss' law in differential form involves the
It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution.
Solved BOX 7.1 Gauss's Law in Integral and Differential Form
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. (1) in the following part,.
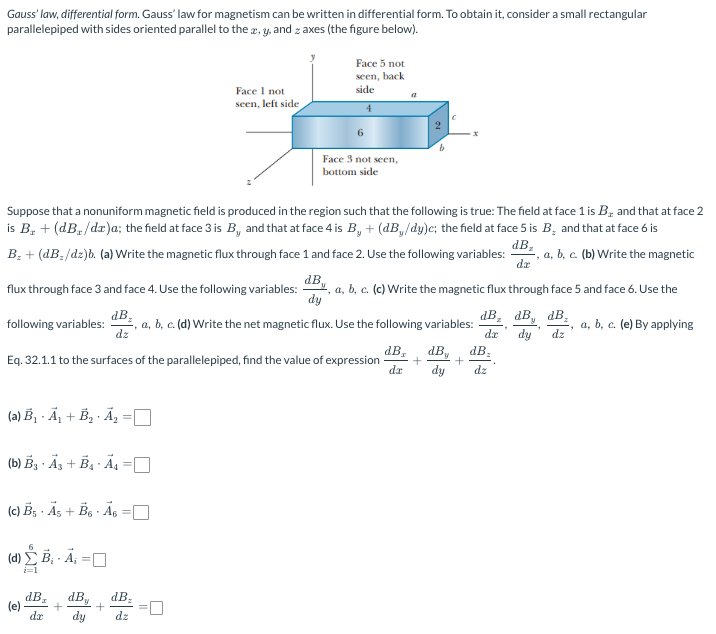
Solved Gauss' law, differential form. Gauss' law for
Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. (1) in the following part,.
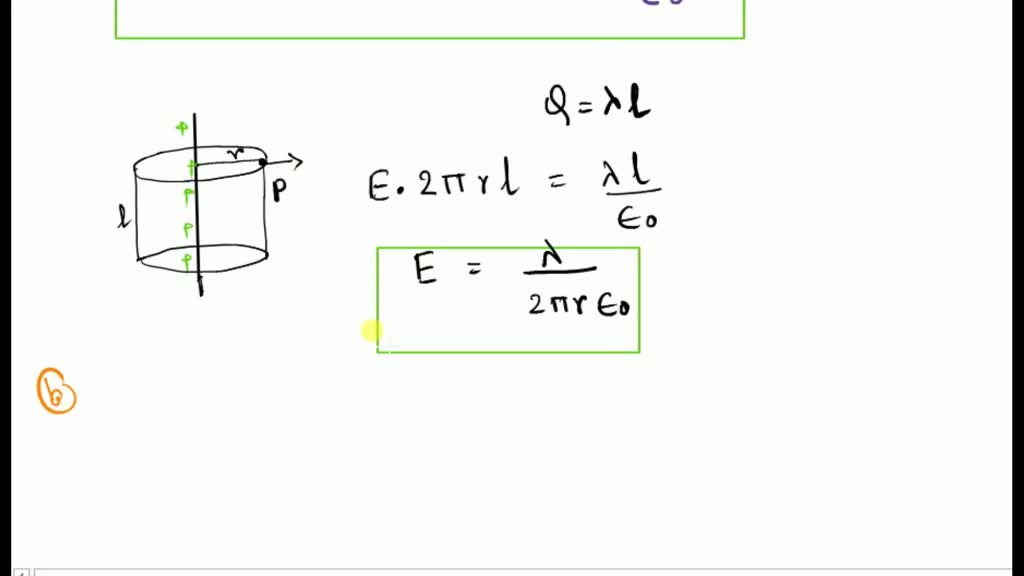
SOLUTION Integral and differential form of gauss s law Studypool
(1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. It states that the divergence of.
SOLVED (a) Define Gauss Law of Electrostatics in Differential form. (b
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. It states that the divergence.
It States That The Divergence Of The Electric Field At Any.
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. The differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. Gauss' law in differential form lends itself most easily to finding the charge density when we are give the field.