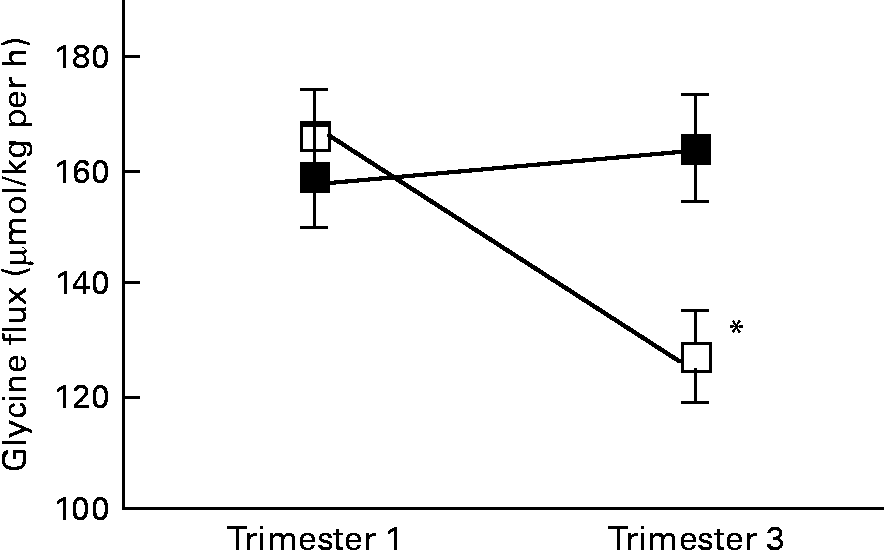
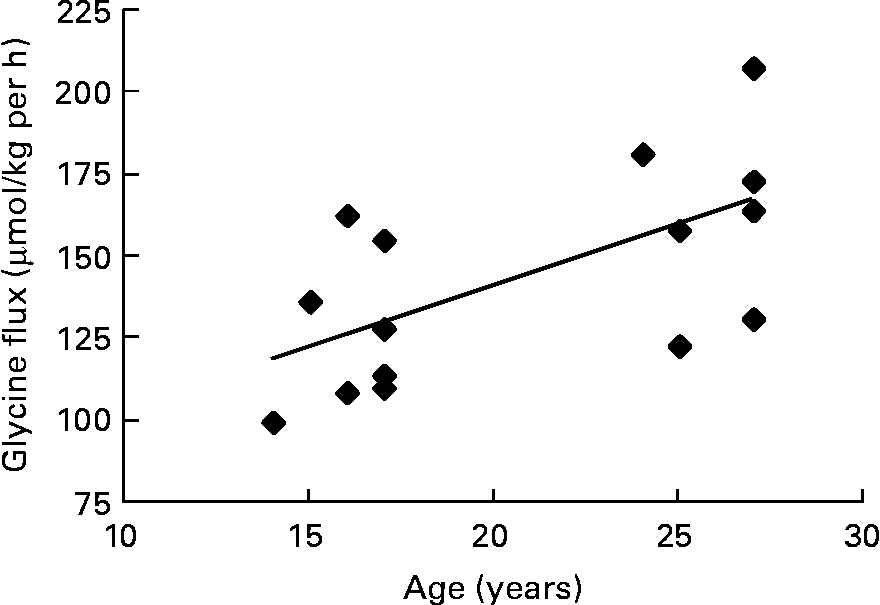Glycine During Pregnancy - Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. Glycine is transported to the. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements.
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Glycine is transported to the. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10).
Glycine is transported to the. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta.
Why Collagen is Essential During Pregnancy and Postpartum
Glycine is transported to the. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop.
Plasma concentrations of glycine (A, C) and serine (B, D) in response
Glycine is transported to the. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine.
Glycine during pregnancy can it be taken early and late, instructions
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Glycine is transported to the. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing.
(PDF) Glycine, a Dispensable Amino Acid, Is Conditionally Indispensable
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Glycine is transported to the. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing.
Glycine during pregnancy can it be taken early and late, instructions
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Glycine is transported to the. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop.
Comparing the in vivo glycine fluxes of adolescent girls and adult
Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Glycine is transported to the. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take.
Comparing the in vivo glycine fluxes of adolescent girls and adult
Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Glycine is transported to the. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing.
Glycine during pregnancy can it be taken early and late, instructions
During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Glycine is transported to the. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing.
Glycine Importance During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. Glycine is transported to the. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine.
Glycine during pregnancy can it be taken early and late, instructions
Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10). Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Glycine is transported to the. Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing.
Glycine Is Transported To The.
Subjects in this study were pregnant women who consumed isocaloric diets containing 0.88 g. During pregnancy, glycine supports the expanding uterus and skin and helps develop the placenta. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take glycine supplements. Studies have shown decreased glycine flux in pregnant adolescents, suggesting an inability to maintain endogenous glycine production (10).