Hip Joint Pain Differential Diagnosis - Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4). Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly. Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. A focused history and physical examination can. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. A focused history and physical. The differential diagnosis of hip pain is broad, presenting a. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 14).
A focused history and physical examination can. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 14). Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. A focused history and physical. The differential diagnosis of hip pain is broad, presenting a. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4). Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly.
A focused history and physical examination can. The differential diagnosis of hip pain is broad, presenting a. Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly. A focused history and physical. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 14). Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4).
Joint Pain Differential Diagnosis DDx for Doctors
Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly. A focused history and physical examination can. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: A focused history and physical. Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages.
Hip Differential Diagnosis Handbook Clinical Physio
A focused history and physical examination can. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 14). A focused history and physical. Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations:
Differential Diagnosis of Hip Pain Learn More
Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4). A focused history and physical. Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. A focused history and physical examination can.
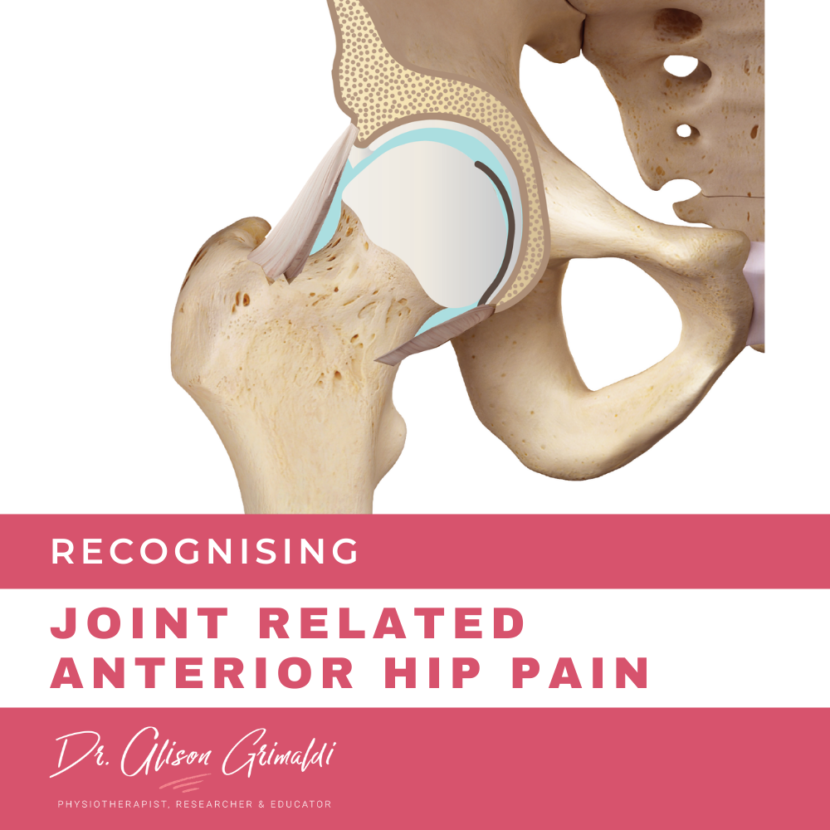
Anterior Hip Pain Differential Diagnosis
Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4). A focused history and physical examination can. Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly. Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories.
SOLUTION Orthopaedics differential diagnosis of joint pain Studypool
Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. A focused history and physical examination can. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4).
Differential Diagnosis of Anterior Hip Pain Joint Dr Alison Grimaldi
Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly. Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4). A focused history and physical. The differential diagnosis of hip pain is broad, presenting a.
Differential Diagnosis Hip Pain PDF Knee Osteoarthritis
A focused history and physical. Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 14). Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages.
(PDF) Differential Diagnosis of Pain Around the Hip Joint Lisa Tibor
Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 14). Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: A focused history and physical. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4). Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories.
1. Differential diagnosis of pelvic and hip pain Download Table
Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 1 4). Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly. Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. A focused history and physical examination can.
SOLUTION Orthopaedics differential diagnosis of joint pain Studypool
Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. A focused history and physical. A focused history and physical examination can. The differential diagnosis of hip pain is broad, presenting a.
Anterior, Lateral, Or Posterior (Figure 1 4).
Musculoskeletal sources of adult hip pain can be divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior categories. Anterior, lateral, or posterior (figure 14). Hip pain is a common and disabling condition that affects patients of all ages. The differential diagnosis of hip pain is broad, presenting a.
A Focused History And Physical Examination Can.
A focused history and physical. Hip pain is often localized to one of three locations: Hip pain is usually located anteriorly, laterally, or posteriorly.