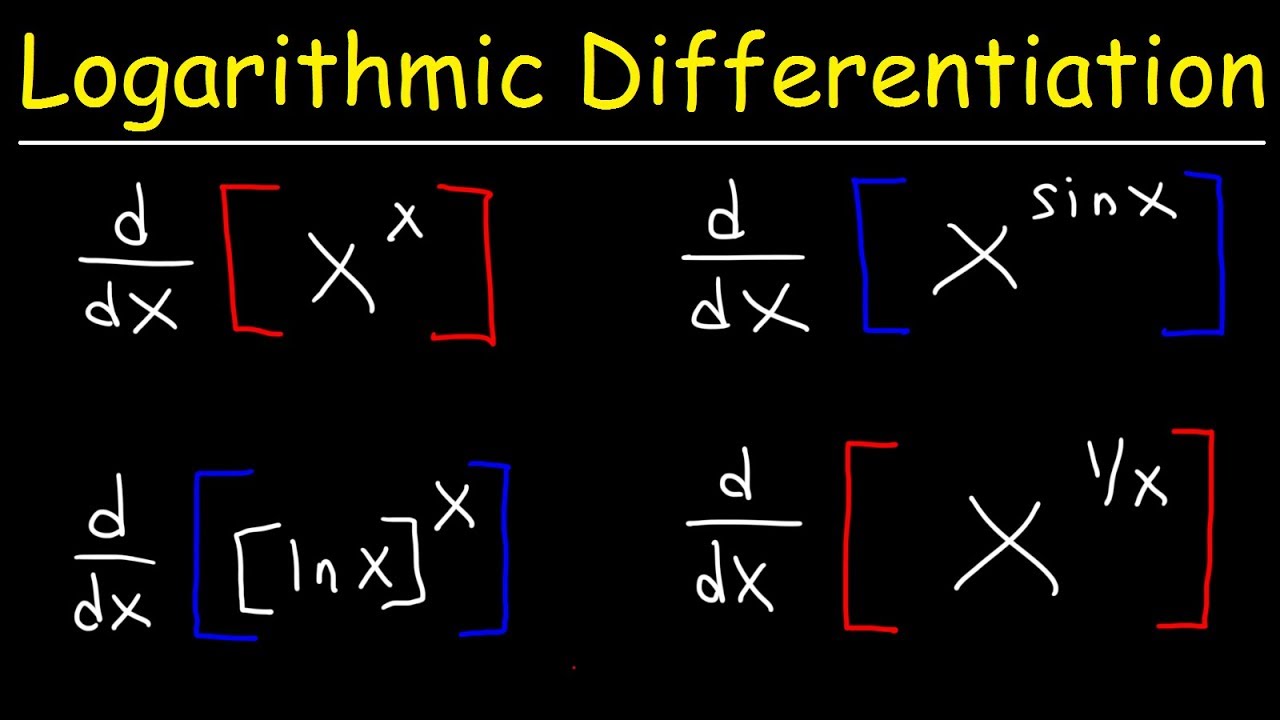
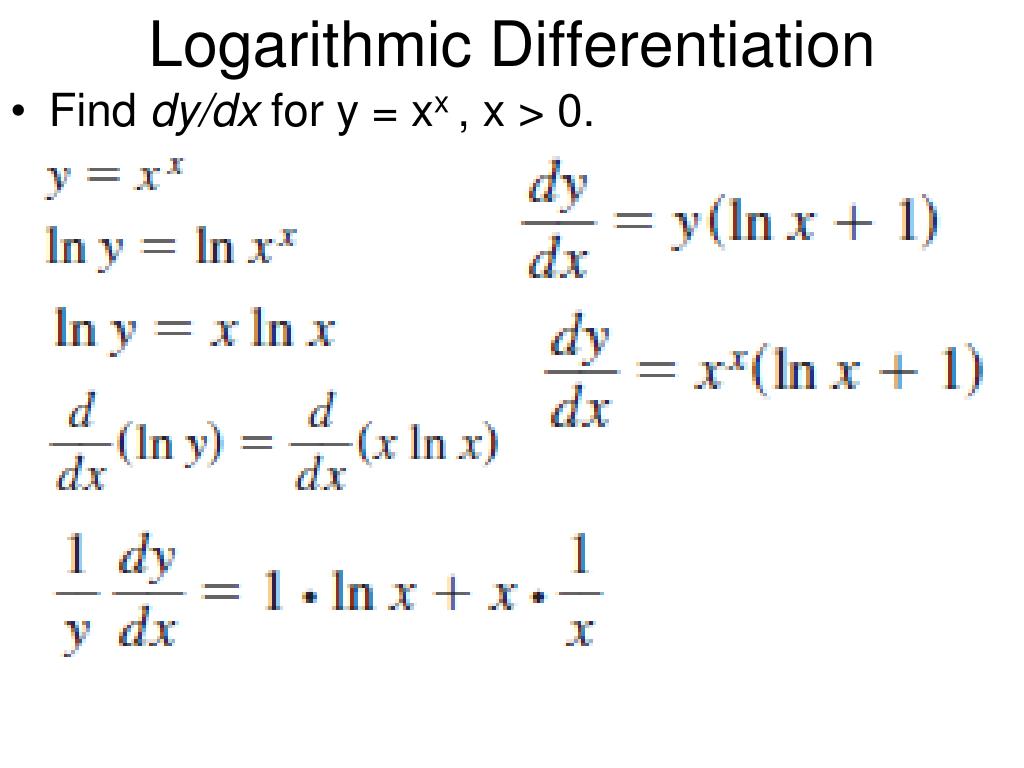How To Differentiate A Log Function - \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.
We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.
However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both.
Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x
We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both.
calculus Differentiate the Function y=\log_2(e^{x} \cos(\pi x
Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with.
Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x
\[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.
Ex 5.4, 8 Differentiate log (log x) Chapter 5 Class 12
Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(.
Differentiate Ln X
However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.
Differentiate Ln X
\[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with.
Understanding the Properties of Log Functions
Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with.
Differentiate Ln X
We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(.
Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x
Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form.
HOW TO DIFFERENTIATE USING LOG
\[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. Logarithmic differentiation is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with. We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form.
Logarithmic Differentiation Is A Technique That Allows Us To Differentiate A Function By First Taking The Natural Logarithm Of Both.
We can also use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate functions in the form. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. \[y = {\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^{g\left(. However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with.