Kocuria Rosea Differential And Selective Plating - Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism.
Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria.
Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that.
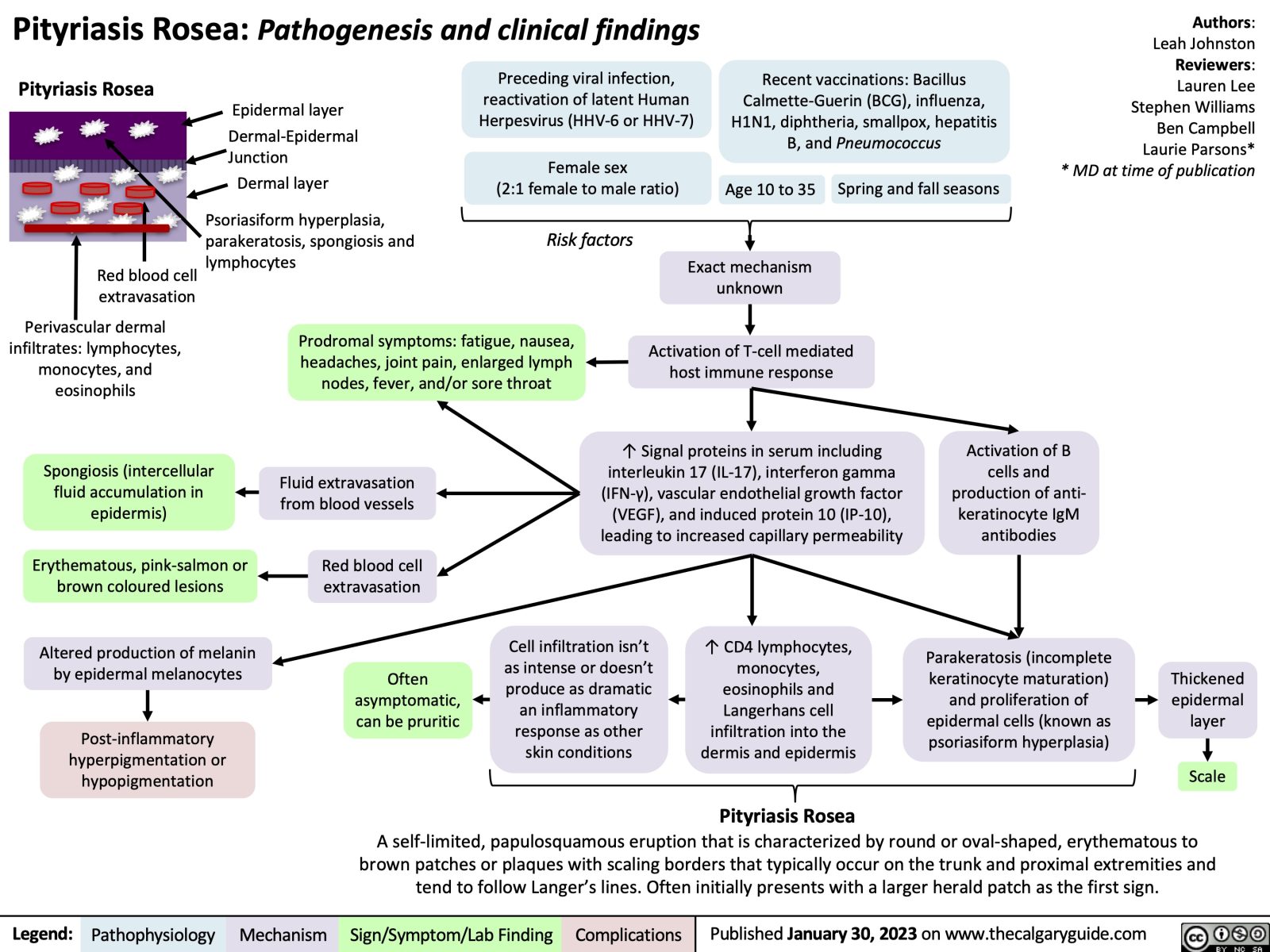
Pityriasis Rosea Calgary Guide
Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that.
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Kocuria rosea, Gram
Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k.
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Kocuria rosea, Gram
Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that.
Kocuria rosea Live Biology Supplies Darwin Biological
Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are.
PPT Selective and Differential Media PowerPoint Presentation, free
Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism.
Kocuria rosea Live Biology Supplies Darwin Biological
Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k.
Kocuria rosea, coccoid prokaryote, SEM Stock Image C032/2201
Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are.
Selective Plating 1 Side Selective Plating Malaysia, Johor, Ulu Tiram
Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are.
Kocuria rosea, coccoid prokaryote, SEM Stock Image C032/2198
Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism.
(PDF) Keratinolytic activity of Kocuria rosea
Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Sepsis and peritonitis caused by k. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria. Phylococcal pathologies might have been caused by kocuria species, although it is plausible that.
Sepsis And Peritonitis Caused By K.
Here, we describe the genome sequences of five strains of k. Kocuria species, which were uncommon in causing human infections, are. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using 16s rdna sequence indicated that the organism. Rosea in our case yielded two identical kocuria.