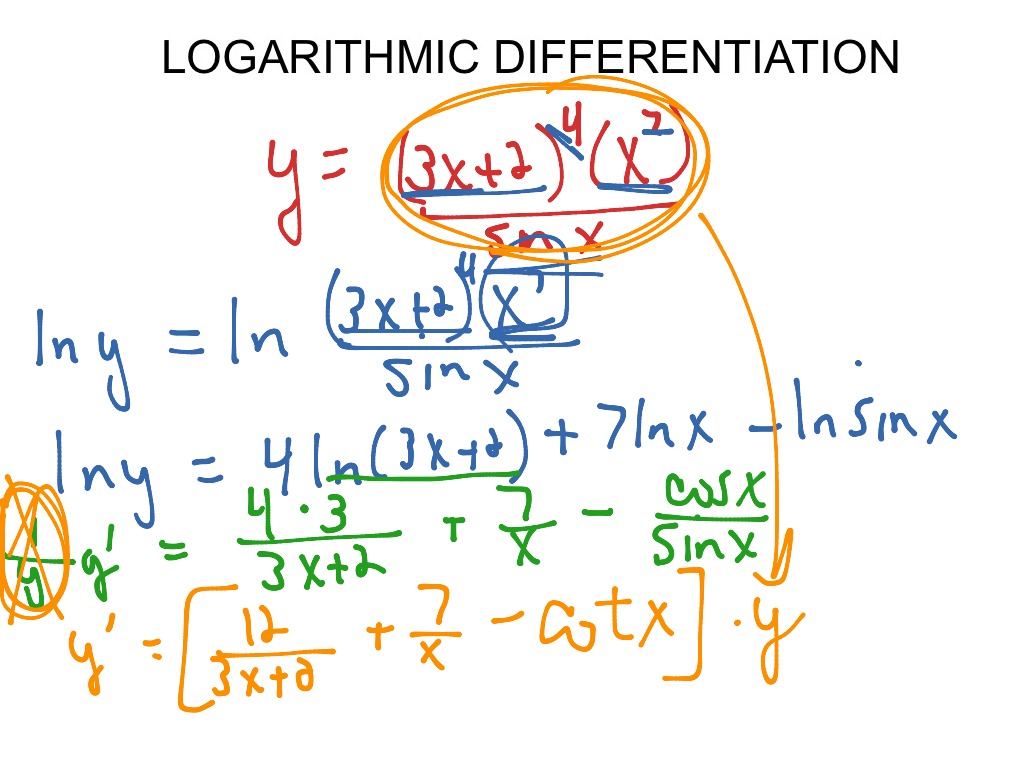
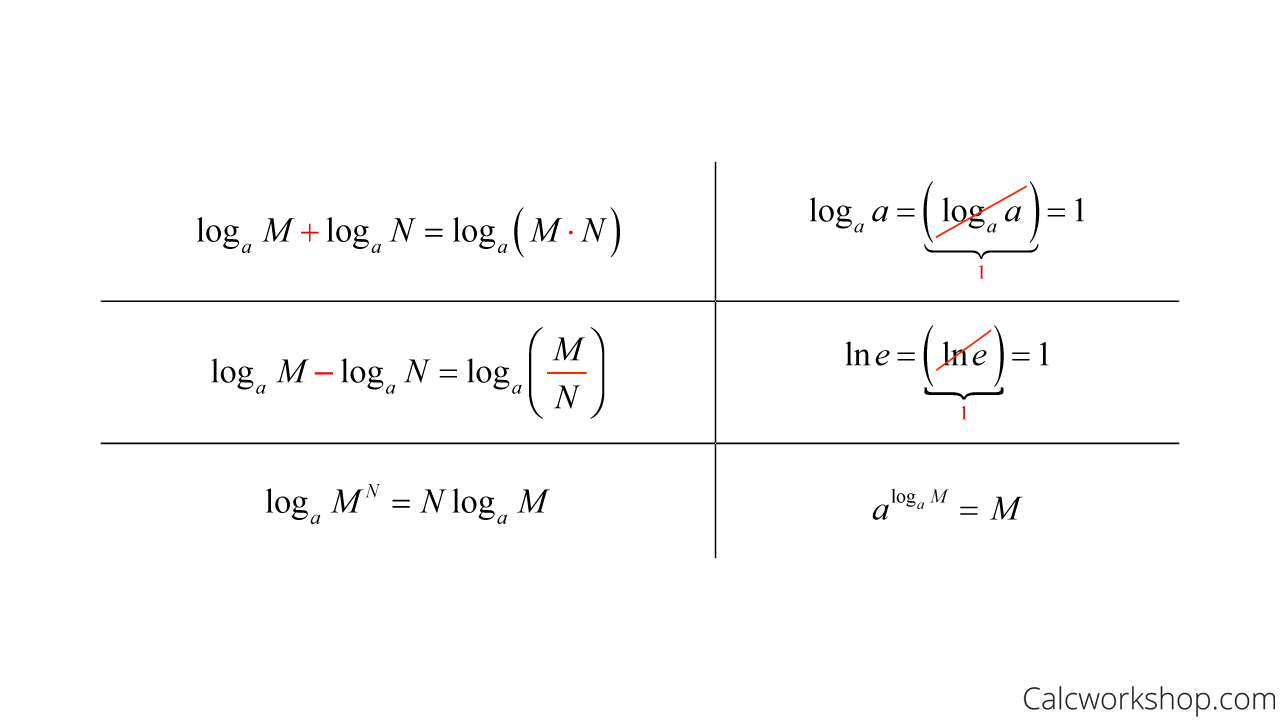
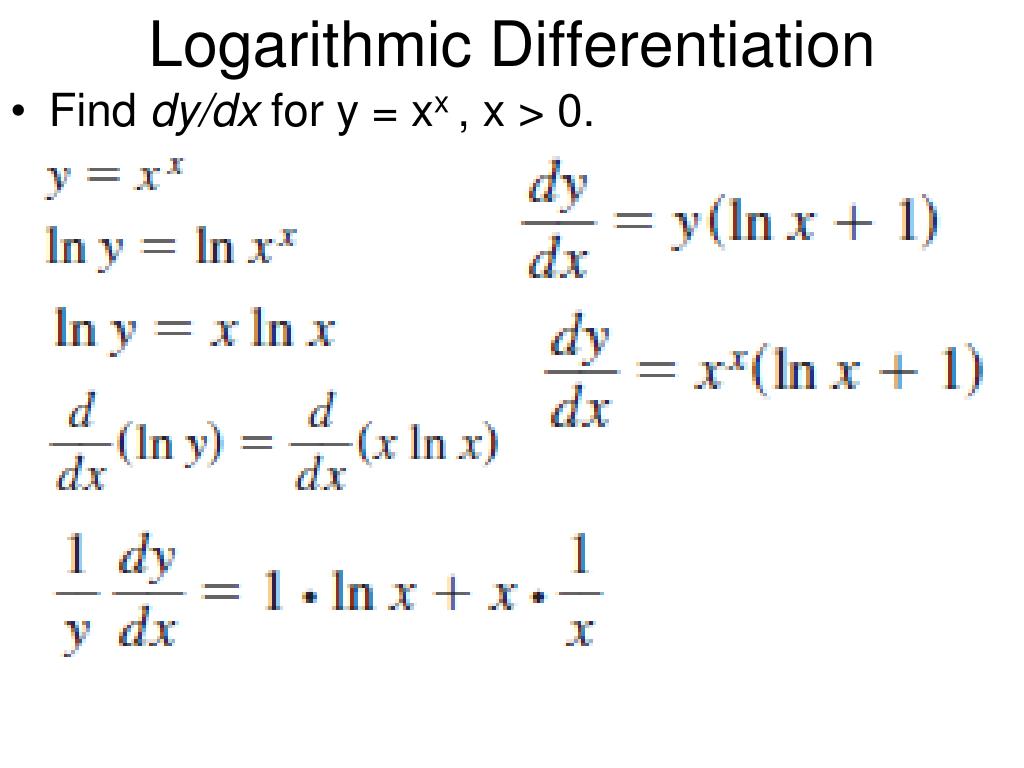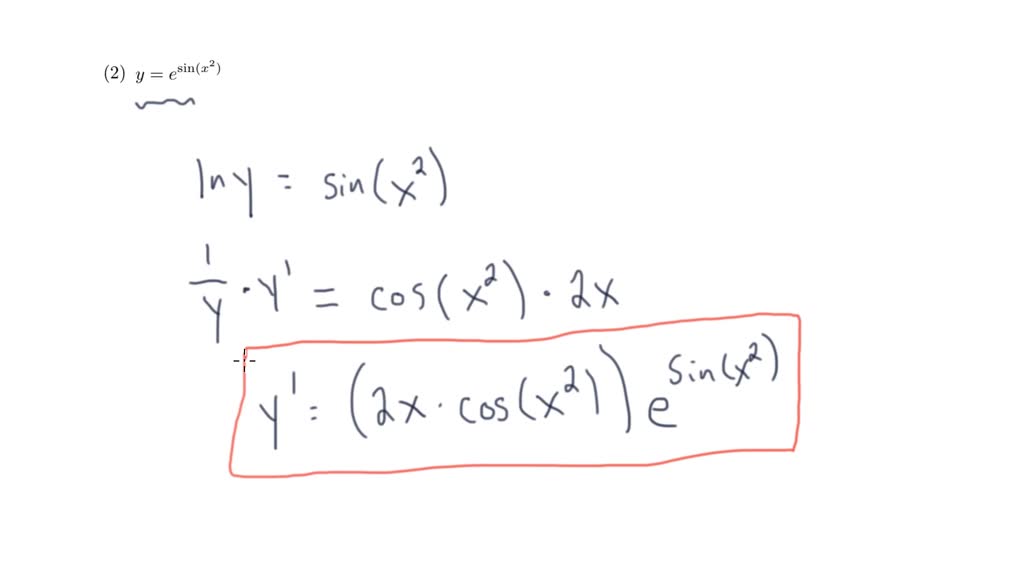Log Differentiation - Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication or division of two fucntions, a function in power of. Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of the form \(y=g(x)^{f(x)}\) or very complex functions by taking the natural logarithm of both sides and. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the derivative of ln x is 1/x. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients.
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of the form \(y=g(x)^{f(x)}\) or very complex functions by taking the natural logarithm of both sides and. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication or division of two fucntions, a function in power of. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the derivative of ln x is 1/x.
Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of the form \(y=g(x)^{f(x)}\) or very complex functions by taking the natural logarithm of both sides and. Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication or division of two fucntions, a function in power of. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the derivative of ln x is 1/x.
Differentiation Of Log X Derivatives of Logs YouTube Find if y
Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the derivative of ln x is 1/x. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural.
ShowMe logarithmic differentiation
Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the derivative of ln x is 1/x. Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as,.
Logarithmic differentiation example 1 Numerade
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication.
Question Video Logarithmic Differentiation Of Functions, 40 OFF
Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication or division of two fucntions, a function in power of. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. Logarithmic.
Differentiation Of Log X Derivatives of Logs YouTube Find if y
Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of the form \(y=g(x)^{f(x)}\) or very complex functions by taking the natural logarithm of both sides and. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base.
Logarithmic Differentiation (w/ 7 StepbyStep Examples!)
The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the derivative of ln x is 1/x. Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of the form \(y=g(x)^{f(x)}\) or very complex functions by taking.
Question Video Logarithmic Differentiation Of Functions, 40 OFF
Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such.
Log Y Differentiation at Jeremy Broady blog
Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication or division of two fucntions, a function in power of. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients. Learn more about the derivative of log x along with its proof using. Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of.
Log Y Differentiation at Jeremy Broady blog
In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients. Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of the form \(y=g(x)^{f(x)}\) or very complex functions by taking the natural logarithm of both sides and. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural.
Logarithmic Differentiation (w/ 7 StepbyStep Examples!)
Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication or division of two fucntions, a function in power of. Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. In.
Learn More About The Derivative Of Log X Along With Its Proof Using.
Logarithmic differentiation relies on the chain rule as well as properties of logarithms (in particular, the natural logarithm, or the logarithm to the base e) to transform products into sums and. Logarithmic differentiation gives an alternative method for differentiating products and quotients. Logarithmic differentiation is used when one need to find the differentiation of the complex function, such as, multiplication or division of two fucntions, a function in power of. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation.
Logarithmic Differentiation Allows Us To Differentiate Functions Of The Form \(Y=G(X)^{F(X)}\) Or Very Complex Functions By Taking The Natural Logarithm Of Both Sides And.
The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the derivative of ln x is 1/x.