Poorly Differentiated Malignant Tumor - Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and.
Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and.
It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage.
Characteristics of patients included in nonmalignant tumor patients
The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body.
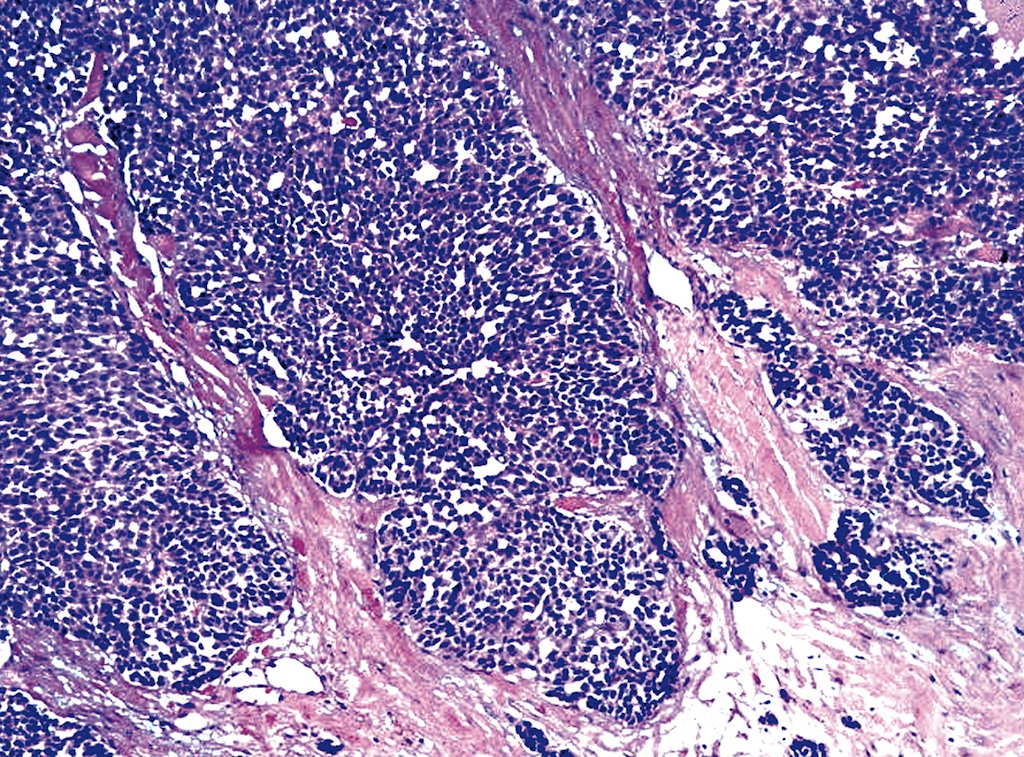
Poorly differentiated carcinoma metastatic to cecum showing sheets of
Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Carcinoma.
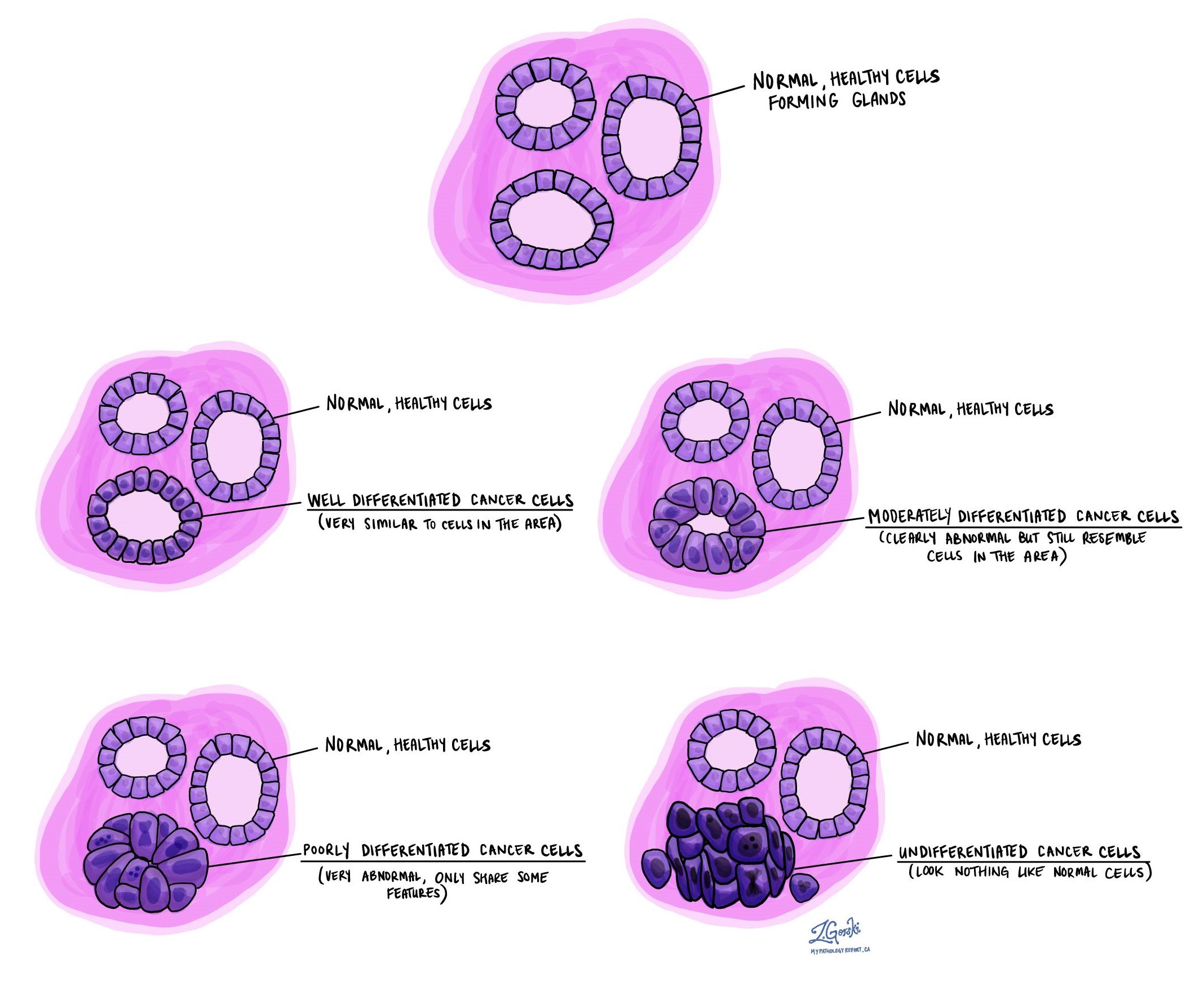
6 Examples of normal, poorly,moderately, and welldifferentiated
Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive.
Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Smear shows cohesive
Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. It is now clear that some patients with poorly.
A poorlydifferentiated malignant mesothelioma consisting of
Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and..
poorly differentiated carcinoma pathology
The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups.
Photographs showing a cellular poorly differentiated tumor composed of
Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer).
Microscopy image of a poorlydifferentiated, highgrade malignant tumor
Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Carcinoma.
Cellular highgrade malignant tumor composed of small monomorphic
However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and..
Differentiated MyPathologyReport.ca
However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the. The.
Poorly Differentiated Carcinoma Is A Diagnosis, Not A Stage.
It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. However, 20 to 25 percent of cups are poorly differentiated and cannot be precisely characterized by histologic examination. Carcinoma of unknown primary (cup) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the body but the.