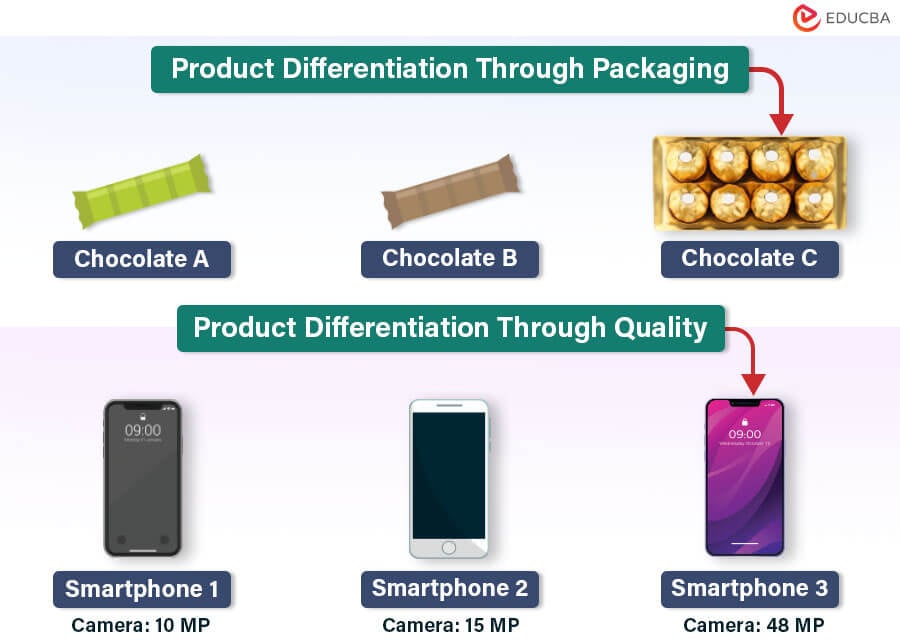
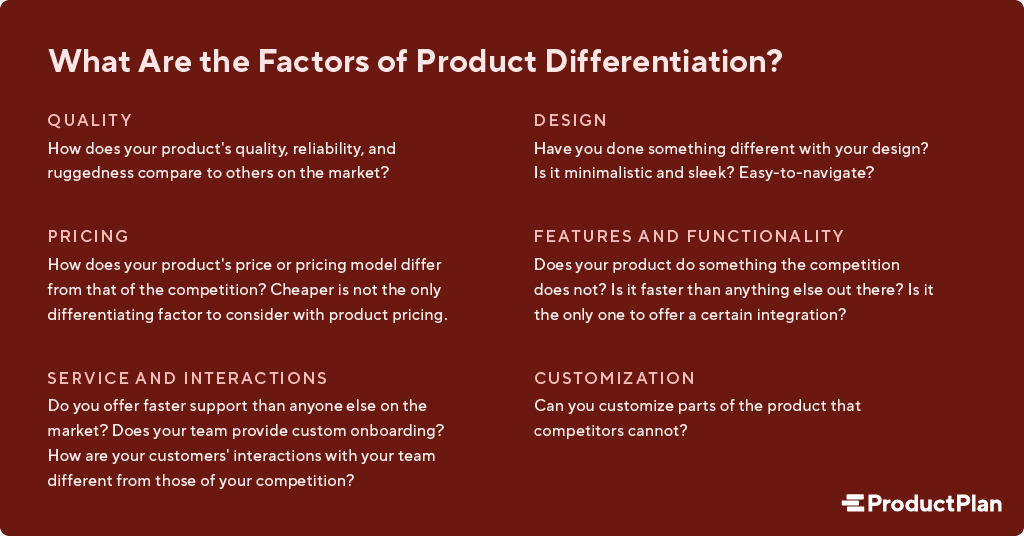
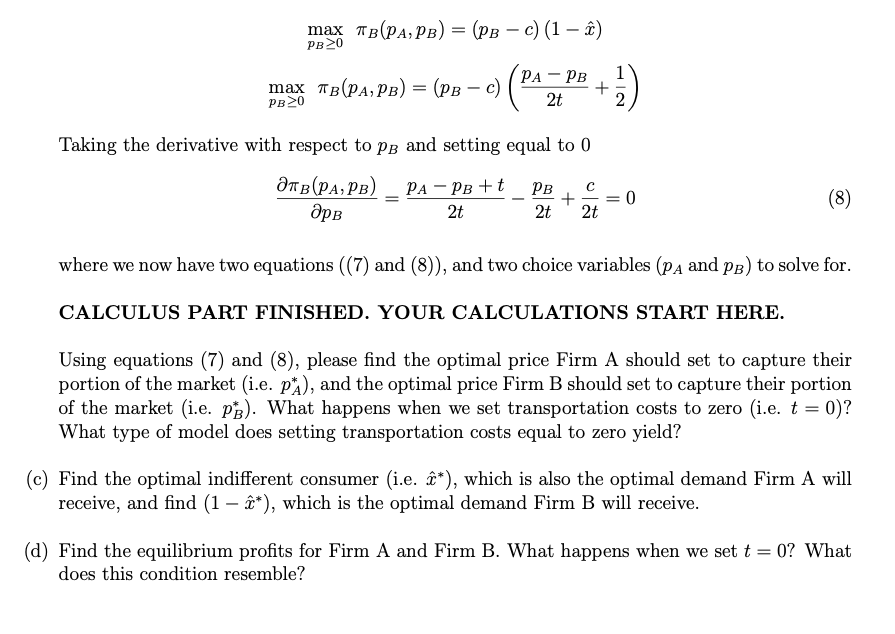
Product Differentiation Largely Quality Bertrand Model - The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation. Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate. Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. Different brands, different location) then a price reduction does not imply. If the products are not homogenous (e.g. Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios. Three critical assumptions were made: In this model, firms compete on. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. Recall that bertrand competition leads to intense price competition and prices get driven down to cost.
Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation. Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios. If the products are not homogenous (e.g. Different brands, different location) then a price reduction does not imply. Recall that bertrand competition leads to intense price competition and prices get driven down to cost. Three critical assumptions were made: Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate. In this model, firms compete on. It can manifest in relation with product quantity (cournot type), product price.
Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. Different brands, different location) then a price reduction does not imply. The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation. It can manifest in relation with product quantity (cournot type), product price. Three critical assumptions were made: If the products are not homogenous (e.g. In this model, firms compete on. Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate.
(PDF) Equilibrium payoffs in a BertrandEdgeworth model with product
Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. Recall that bertrand competition leads to intense price competition and prices get driven down to cost. Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate. If.
Product Differentiation in Marketing Definition, Real Examples
Different brands, different location) then a price reduction does not imply. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. If the products are not.
What is Product Differentiation? Definition and Examples
Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation. If the products are not homogenous (e.g. Three critical assumptions were made: Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios.
Product Differentiation And Why It Matters For Your Business LongTerm
Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate. Three critical assumptions were made: If the products are not homogenous (e.g. Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios.
What Is Product Differentiation? Ultimate Marketing Dictionary
The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation. Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. In this model, firms.
2. A Bertrand Model with Product Differentiation
Different brands, different location) then a price reduction does not imply. Recall that bertrand competition leads to intense price competition and prices get driven down to cost. Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range.
(PDF) The Bertrand Model and the Degree of Product Differentiation
In this model, firms compete on. Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios. Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate. Different brands, different location) then a price reduction does not imply. The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation.
Solved 4. A Bertrand Model with Product Differentiation by
Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate. Different brands, different location) then a price reduction does not imply. Recall that bertrand competition leads to intense price competition and prices get driven down to cost. Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios. Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type.
Solved 4. A Bertrand Model with Product Differentiation by
Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios. In this model, firms compete on. If the products are not homogenous (e.g. It can manifest in relation with product quantity (cournot type), product price. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under.
Solved 4. A Bertrand Model with Product Differentiation by
If the products are not homogenous (e.g. The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation. Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. It can manifest in relation with product quantity (cournot type), product price. Recall that bertrand competition leads to intense.
If The Products Are Not Homogenous (E.g.
Rms choose how to di erentiate from rivals, this impacts the type of products that they choose to o er and the. It can manifest in relation with product quantity (cournot type), product price. Three critical assumptions were made: Bertrand's approach (1883) has become the most used model in price competition scenarios.
In This Model, Firms Compete On.
The bertrand model extends the competitive duopoly model by introducing quality differentiation. Imperfect competition exists in the current economic climate. Investment in product differentiation takes place in a much wider range of cases and results in a greater difference between products under. Recall that bertrand competition leads to intense price competition and prices get driven down to cost.