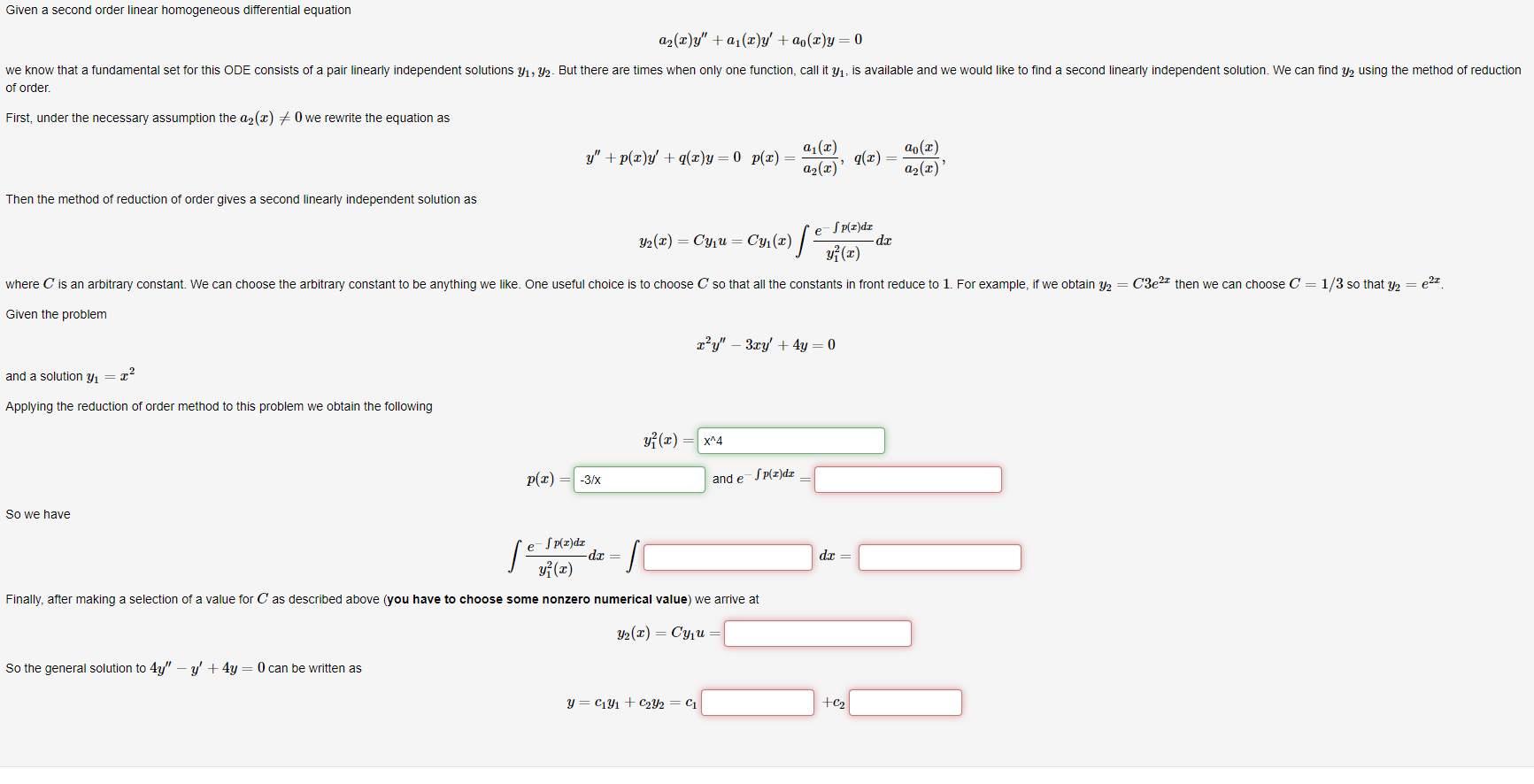
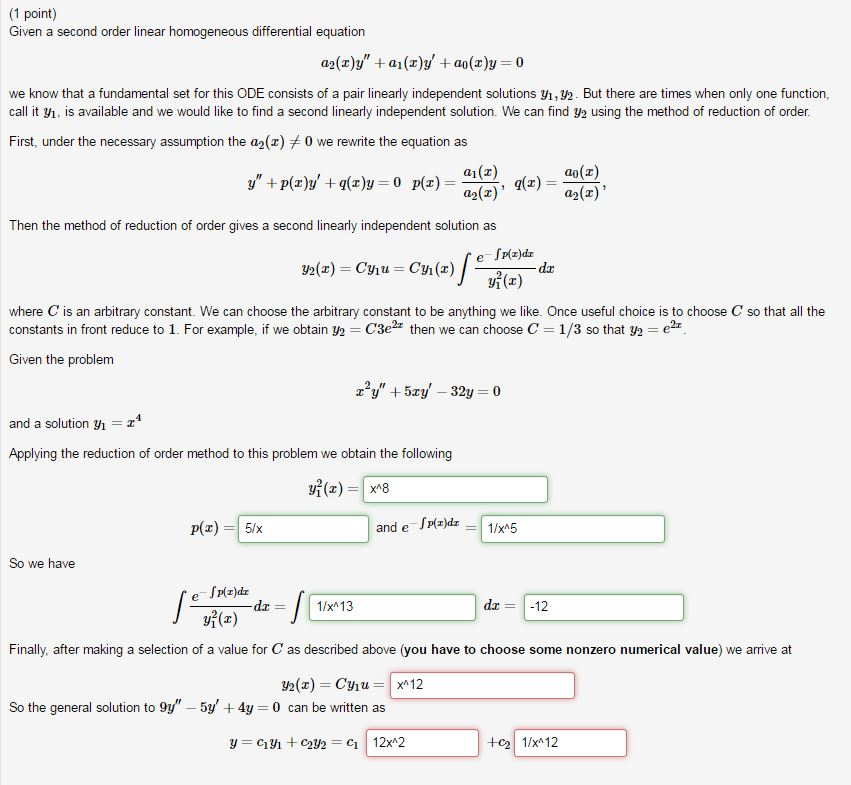
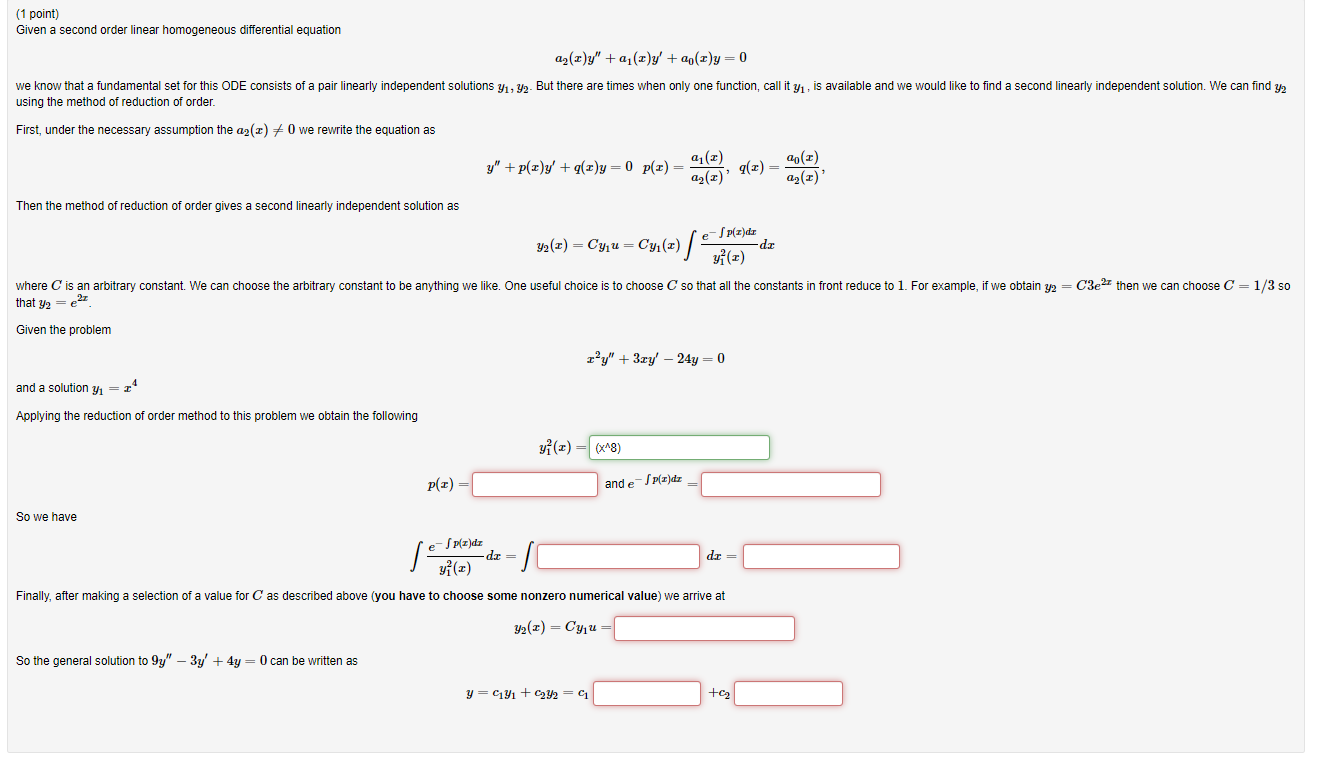
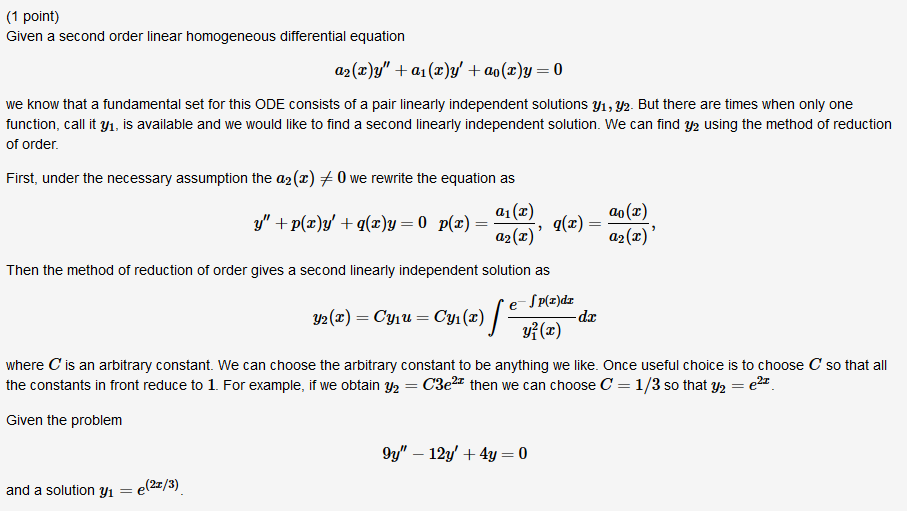
Second Order Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation - Se equations is achieved in stages. Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). There are two types of second order linear differential equations: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: The first stage is to find what is cal. We call the function \(f\).
Se equations is achieved in stages. A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We call the function \(f\). The first stage is to find what is cal. Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. There are two types of second order linear differential equations:
Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. The first stage is to find what is cal. A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Se equations is achieved in stages. We call the function \(f\). There are two types of second order linear differential equations:
Solved Given a second order linear homogeneous differential
Se equations is achieved in stages. A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the.
Solved Given a second order linear homogeneous differential
Se equations is achieved in stages. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We call the function \(f\). Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. There are two types of second order linear differential equations:
Solved Other questions 1. Given a homogeneous linear second
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). The first stage is to find what is cal. There are two types of second order linear differential equations: Se equations is achieved in stages.
Solved Second order homogeneous linear differential equation
There are two types of second order linear differential equations: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Se equations is achieved in stages. A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y.
Solved Given a second order linear homogeneous differential
We call the function \(f\). A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Se equations is achieved in stages. The first stage is to find what is cal. Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y.
Solved Given a second order linear homogeneous differential
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Se equations is achieved in stages. The first stage is to find what is cal. We call the function \(f\). A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x).
Solved Consider the homogeneous secondorder linear
A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). Se equations is achieved in stages. We call the function \(f\). Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. The first stage is to find what is cal.
Solved 1 point) Given a second order linear homogeneous
Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. The first stage is to find what is cal. There are two types of second order linear differential equations: We call the function \(f\). A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the.
SOLUTION Second order homogeneous linear differential equation Studypool
There are two types of second order linear differential equations: We call the function \(f\). The first stage is to find what is cal. A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). Se equations is achieved in stages.
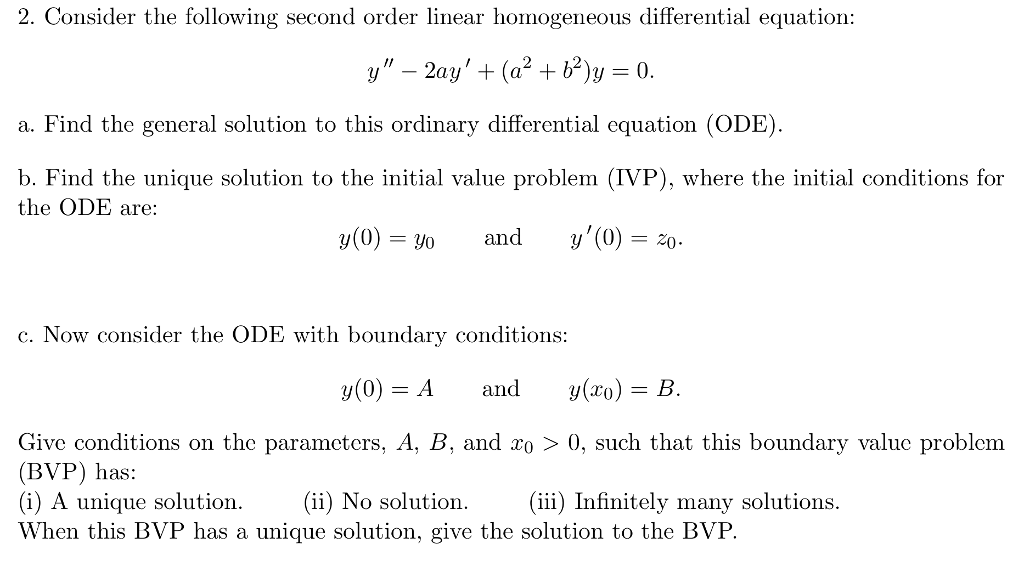
Solved 2. Consider the following second order linear
A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x). The first stage is to find what is cal. Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. There are two types of second order linear differential equations: A linear homogeneous.
A Linear Homogeneous Second Order Ode With Constant Coefficients Is An Ordinary Differential Equation In The Form:
Y'' + p(x)y' + q(x)y = f (x) y ′ ′ + p (x) y ′ + q (x) y. The first stage is to find what is cal. There are two types of second order linear differential equations: We call the function \(f\).
Se Equations Is Achieved In Stages.
A second order differential equation is said to be linear if it can be written as \[\label{eq:5.1.1} y''+p(x)y'+q(x)y=f(x).