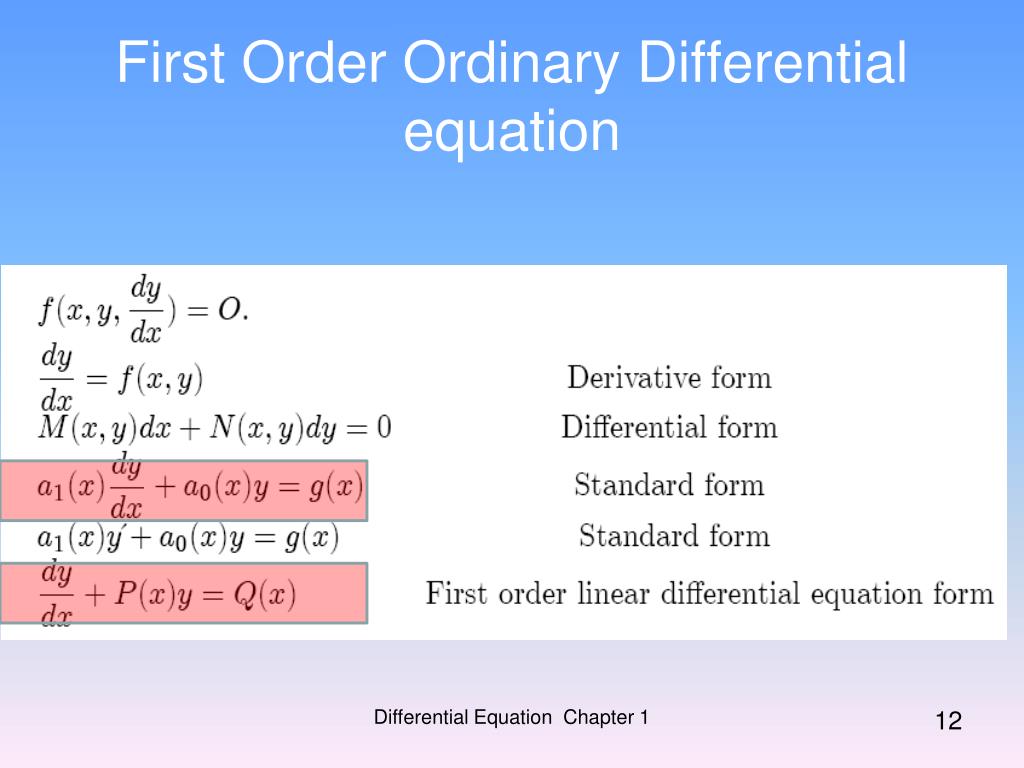
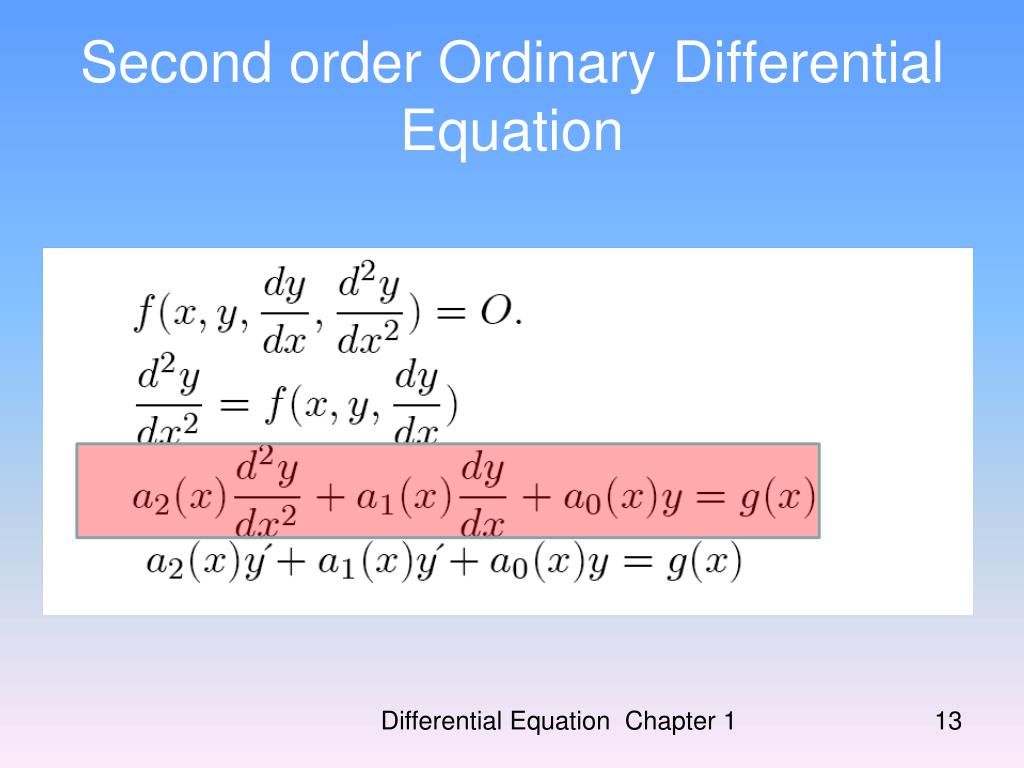
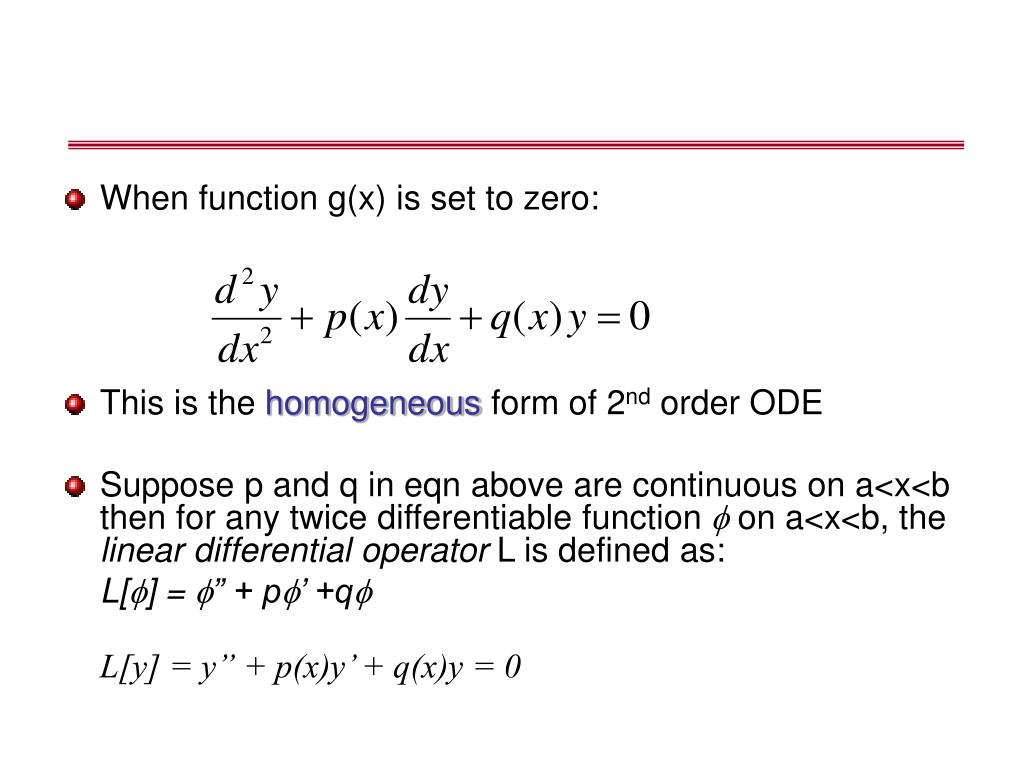
Second Order Ordinary Differential Equations - Those that are linear and have constant. Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type:
Those that are linear and have constant. Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type:
Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. Those that are linear and have constant.
PPT Ordinary Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free
In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x),.
(PDF) Second Order Differential Equations
Those that are linear and have constant. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p.
Second order Ordinary Differential Equations 1 Second Order Linear
Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x),.
PPT Ordinary Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free
Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear).
Solving secondorder differential equations. Mathematics Stack Exchange
Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Those that are linear and have constant. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p.
Secondorder ordinary differential equations Special functions, Sturm
Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. Those that are linear and have constant. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p.
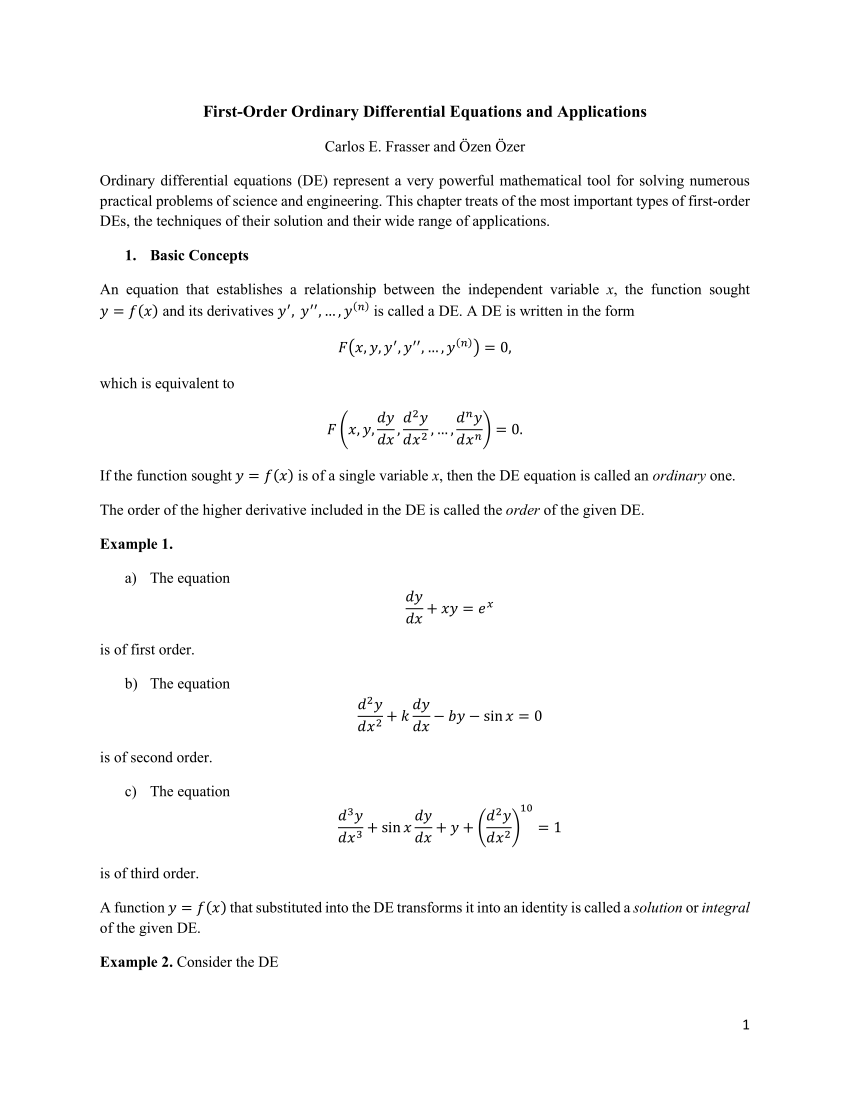
(PDF) Firstorder Ordinary Differential Equations and Applications
Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. Those that are linear and have constant. Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of.
Ordinary Differential Equations
Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear).
PPT LINEAR SECOND ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS PowerPoint
Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. Those that are linear and have constant. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16).
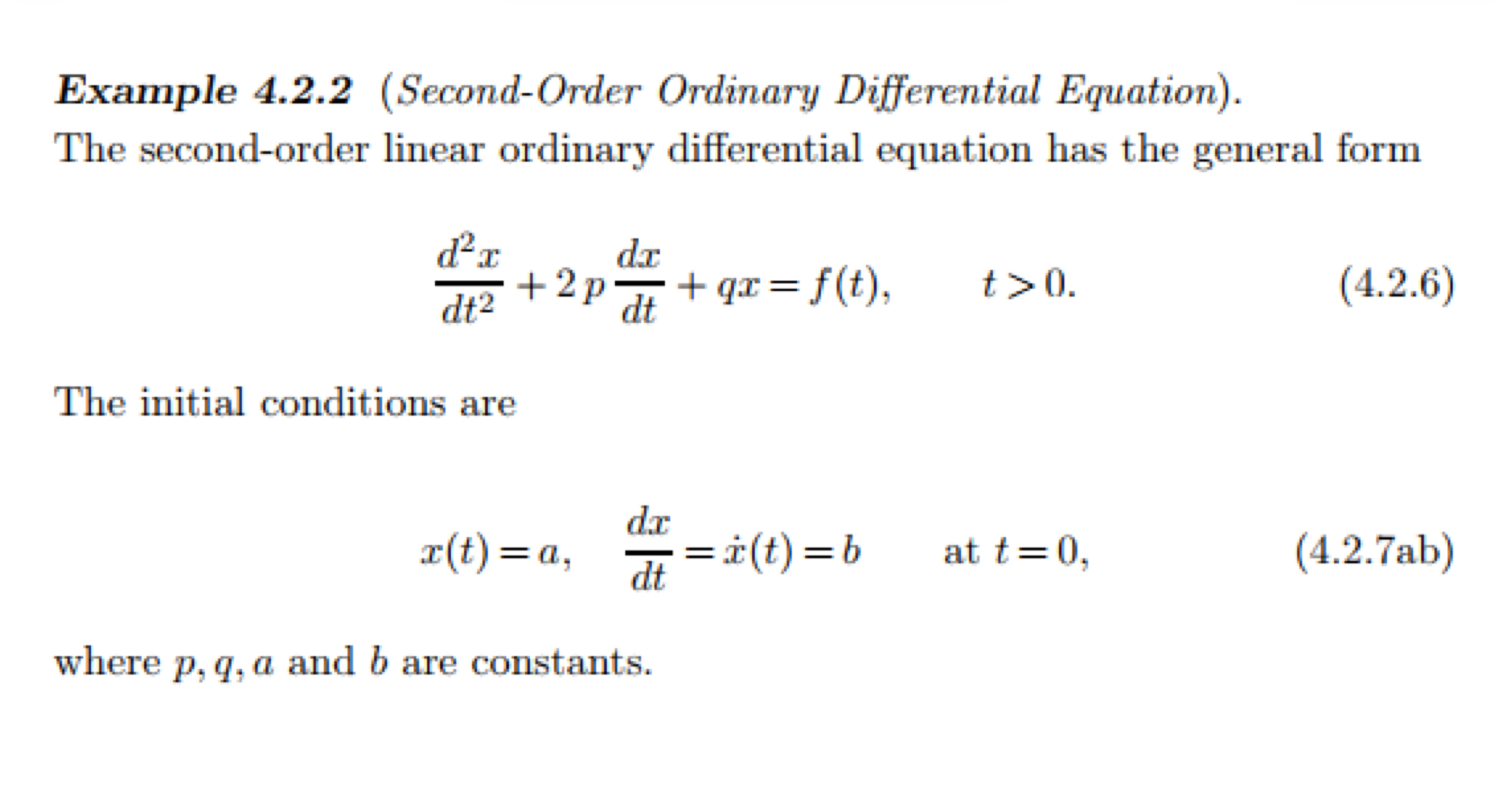
Example 4.2.2 (SecondOrder Ordinary Differential
Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. Those that are linear and have constant. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p.
Generally, We Write A Second Order Differential Equation As Y'' + P (X)Y' + Q (X)Y = F (X), Where P (X), Q (X), And F (X) Are Functions Of X.
Equations (1.3.15) and (1.3.16) are indicative of the type of (nonlinear) first order ode whose solution can be expressed in terms of tangent. In this section we start to learn how to solve second order differential equations of a particular type: Those that are linear and have constant.