Techniques For Solving Differential Equations - When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy.
First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation.
First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy.
Solving Differential Equations
In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 0 the equation can.
"Analytical techniques for solving partial differential
First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n = 0 the equation can.
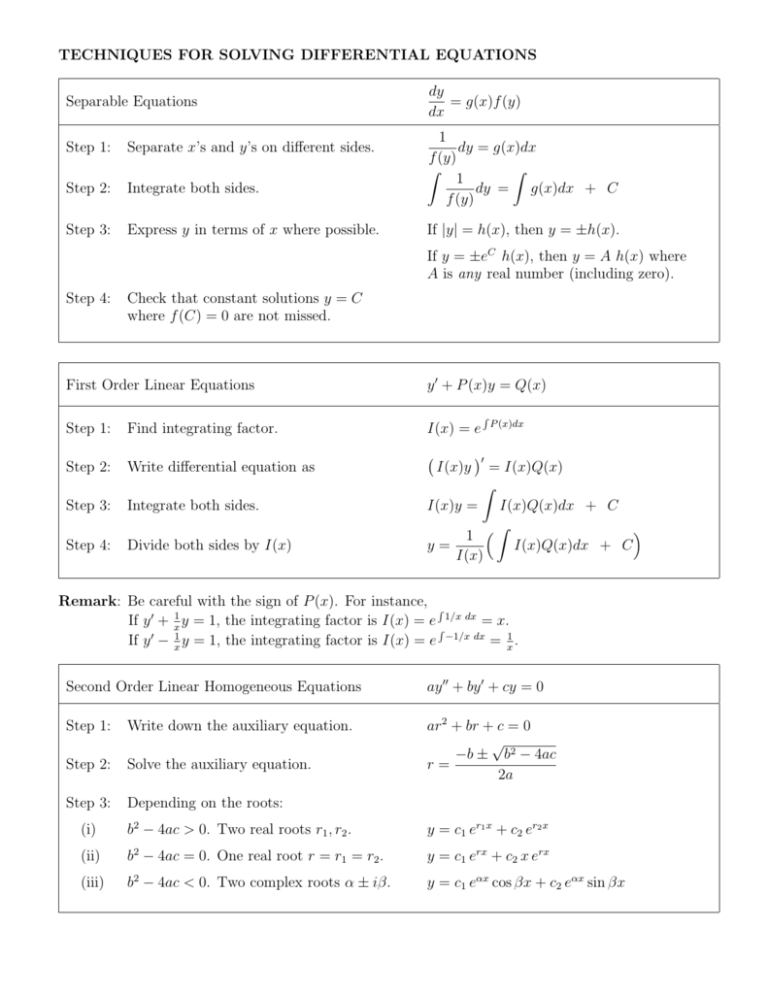
TECHNIQUES FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. When n = 0 the equation can.
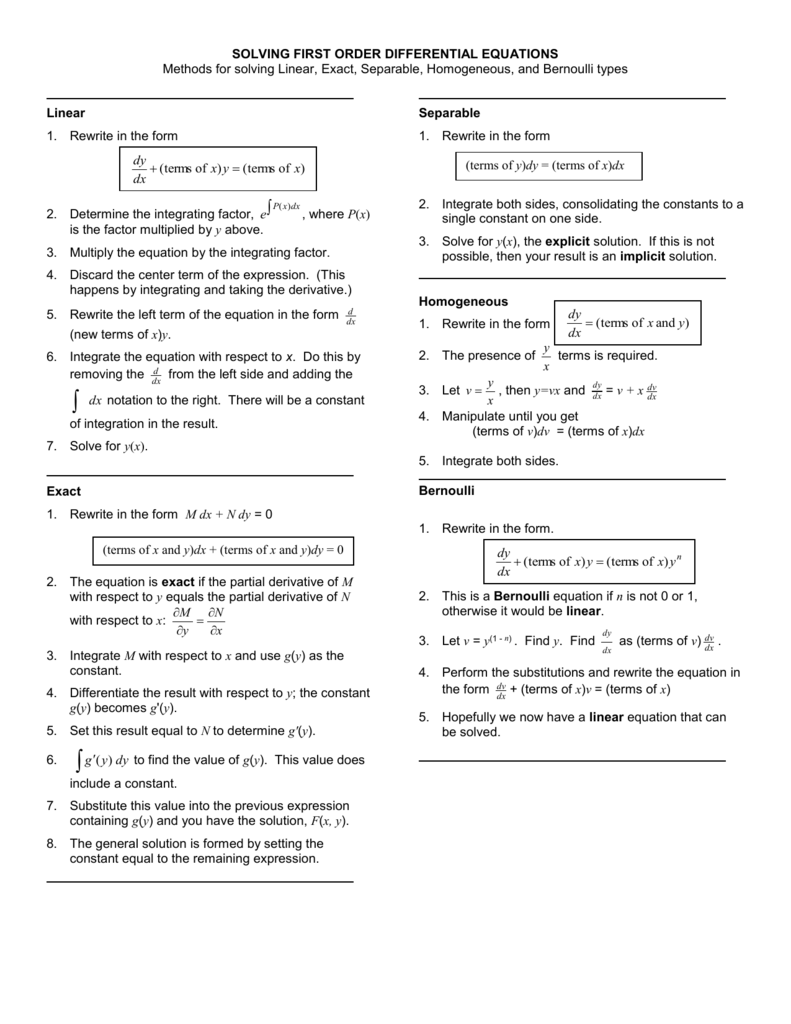
SOLVING FIRST ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first.
Solving Complexity Advanced Techniques in Differential Equations
First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. When n = 0 the equation can.
Differential Equations Solving Techniques and Applications
In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. When n =.
Solving differential equations is not like solving
When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n =.
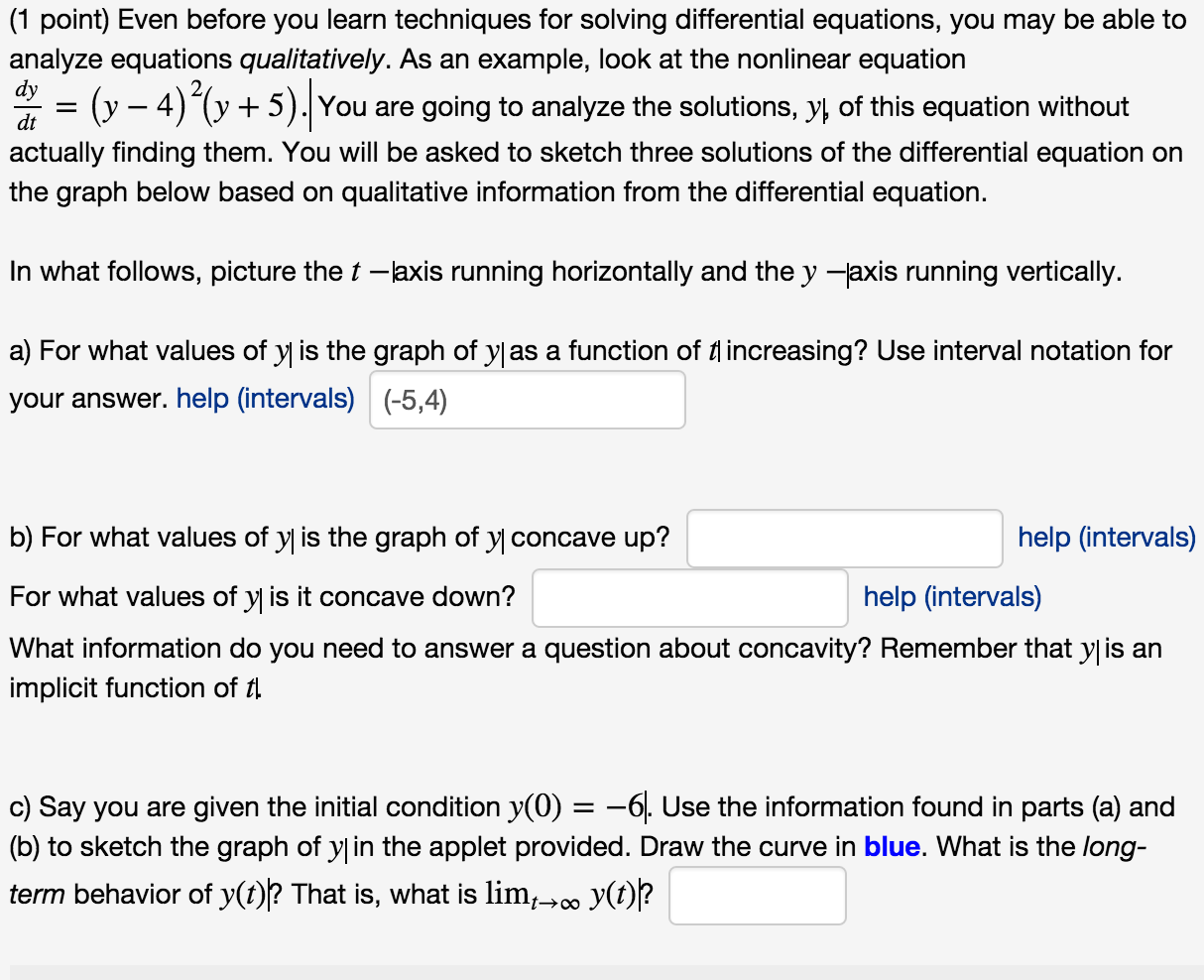
Solved Even before you learn techniques for solving
When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n = 0 the equation can.
Textbooks Differential Equations Freeup
First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n =.
EXP1 Solving Differential Equations Download Free PDF Electrical
When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical.
When N = 0 The Equation Can Be Solved As A First Order Linear Differential Equation.
First, we will review some basic concepts of numerical approximations and then introduce euler’s method, the simplest method. In this lecture we will briefly review some of the techniques for solving first order ode and second order linear ode, including cauchy. When n = 1 the equation can be solved using separation of.





/aae14611c6e6e45b3bd99783f827f01c.jpg)
