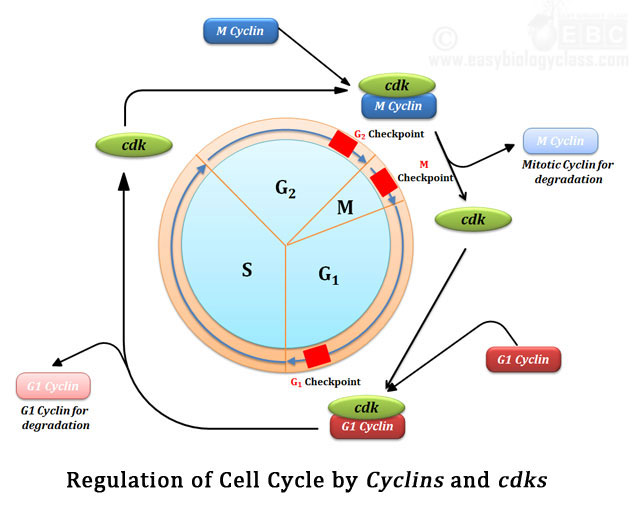
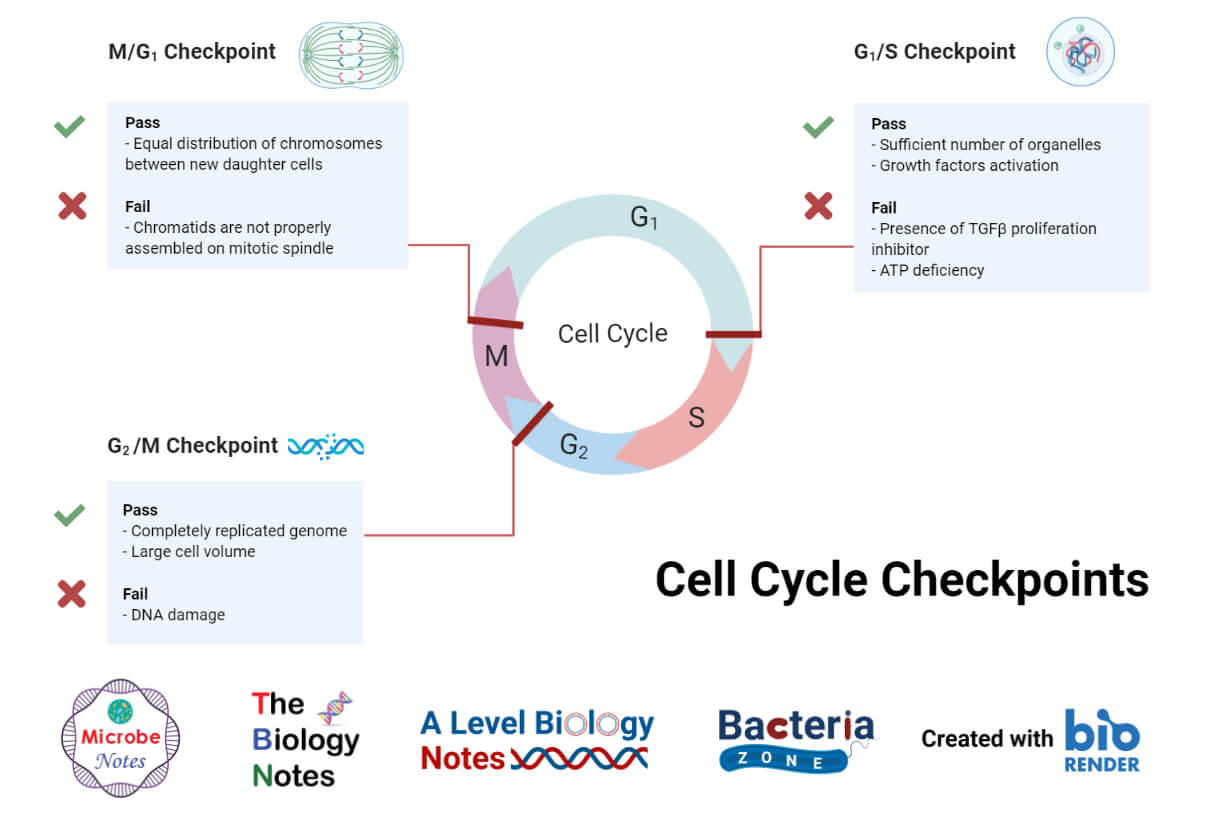
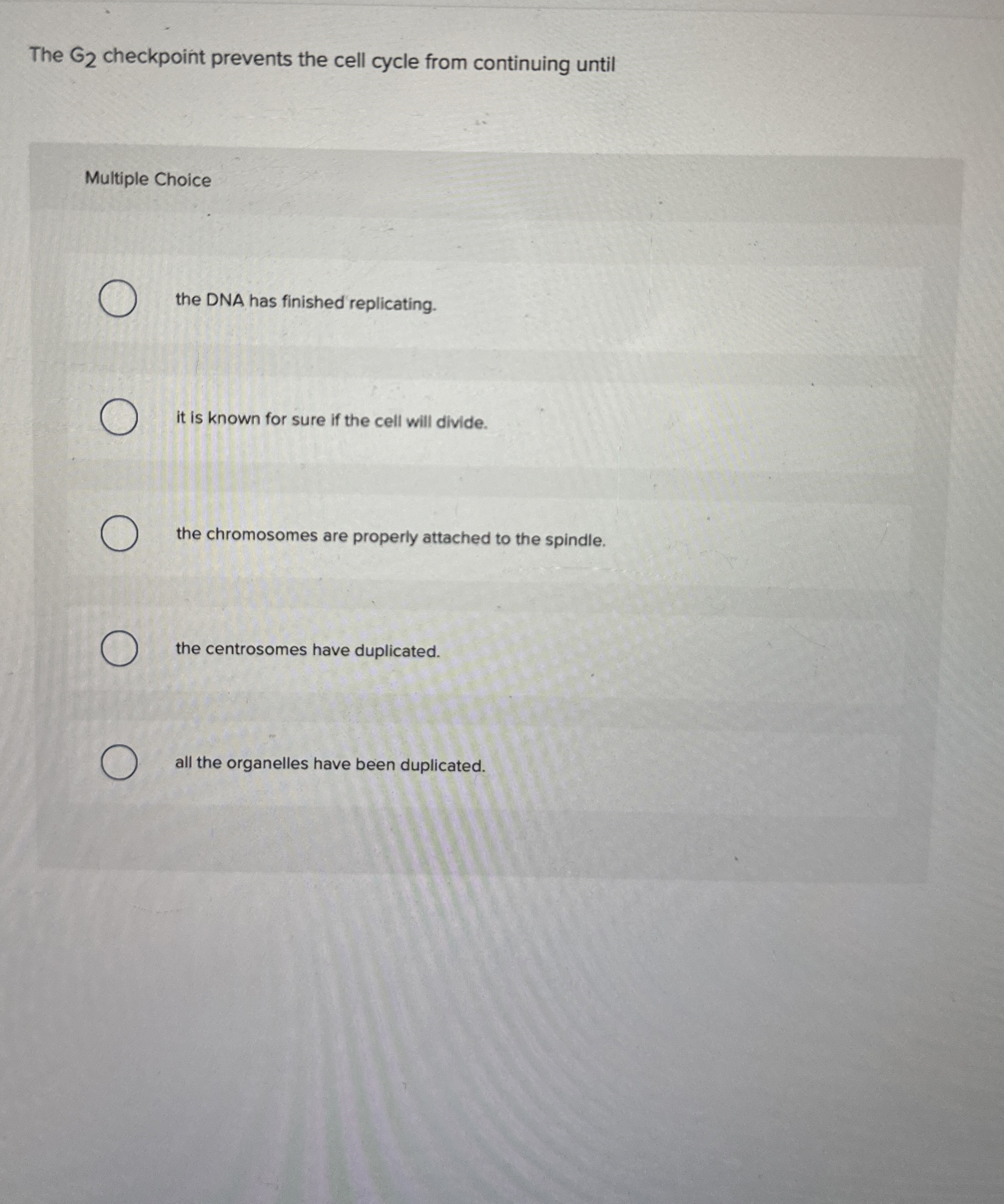
The G2 Checkpoint Prevents The Cell Cycle From Continuing Until - Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell.
The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle.
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,.
The G2 Checkpoint Prevents the Cell Cycle From Continuing Until
The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of.
(PDF) p53 prevents immature escaping from cell cycle G2 checkpoint
The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of.
Cell Cycle Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged.
SOLVED The G 2 checkpoint prevents the cell cycle from continuing
The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged.
G2/M cell cycle checkpoint activation in plants. The G2/M checkpoint is
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna.
The G2 checkpoint prevents the cell cycle from continuing un Quizlet
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged.
The Cell Cycle Checkpoint Response In response to DNA damage the cell
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna.
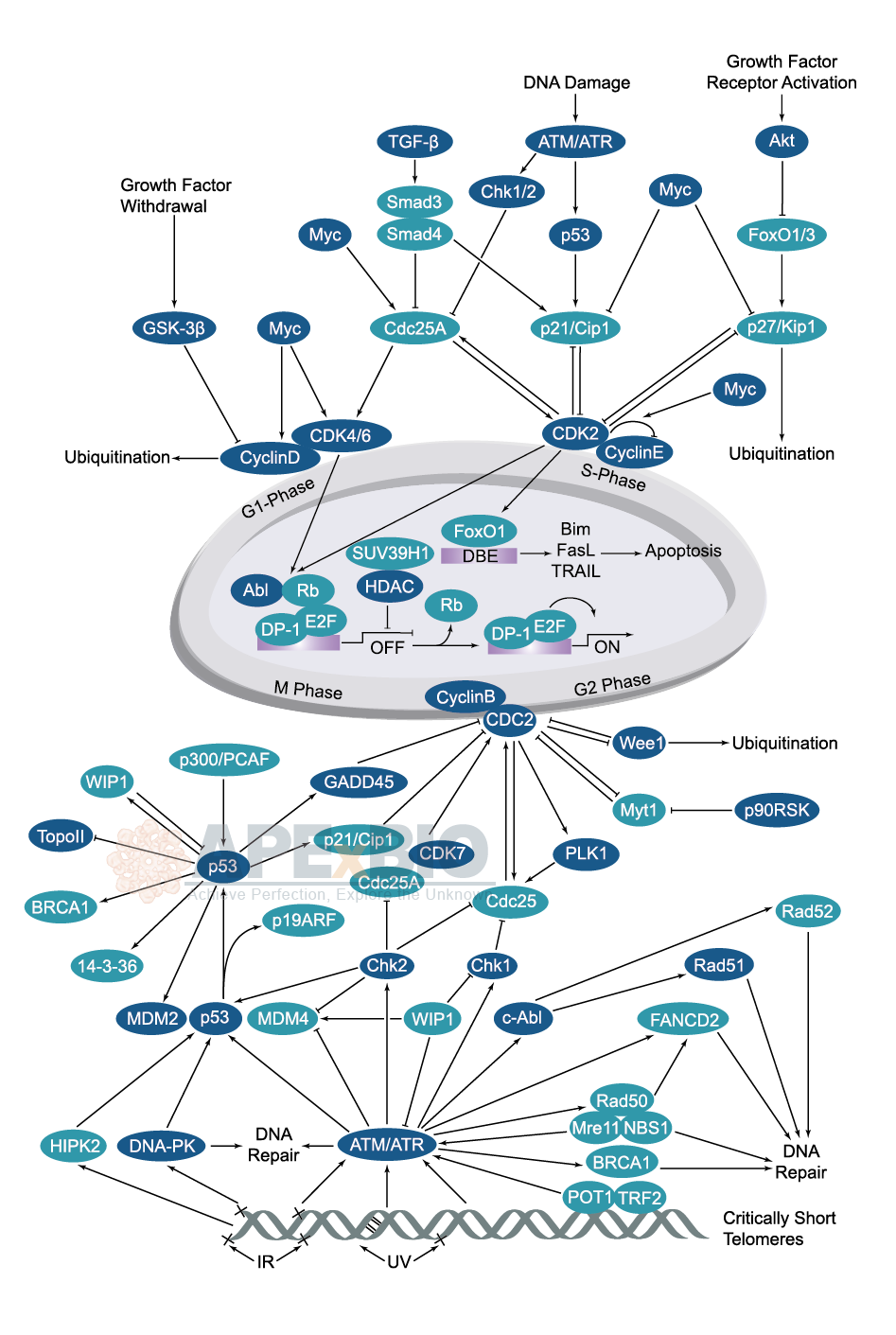
APExBIO Cell Cycle/Checkpoint Signaling Pathways
The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna.
Solved The G2 checkpoint prevents the cell cycle from
The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of.
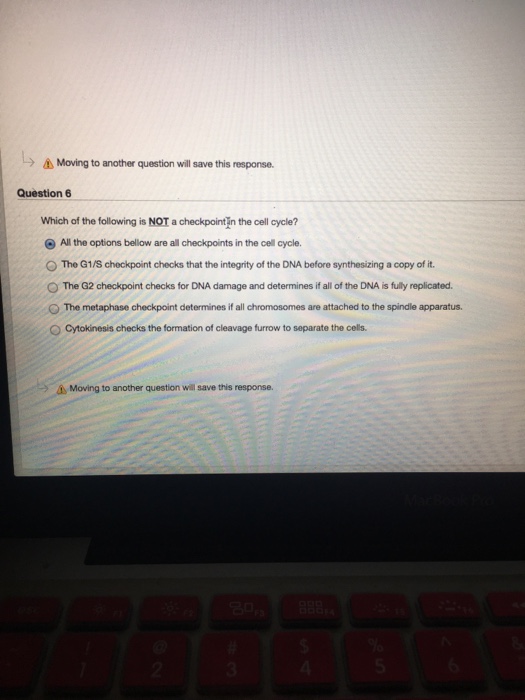
Solved Which of the following is NOT a checkpoint in the
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged.
The G2 Checkpoint Ensures All Of The Chromosomes Are Replicated And That The Replicated Dna Is Not Damaged Before The Cell.
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. The g2 checkpoint (also known as the g2/m checkpoint) prevents cells from initiating mitosis when they experience dna damage during g2,.