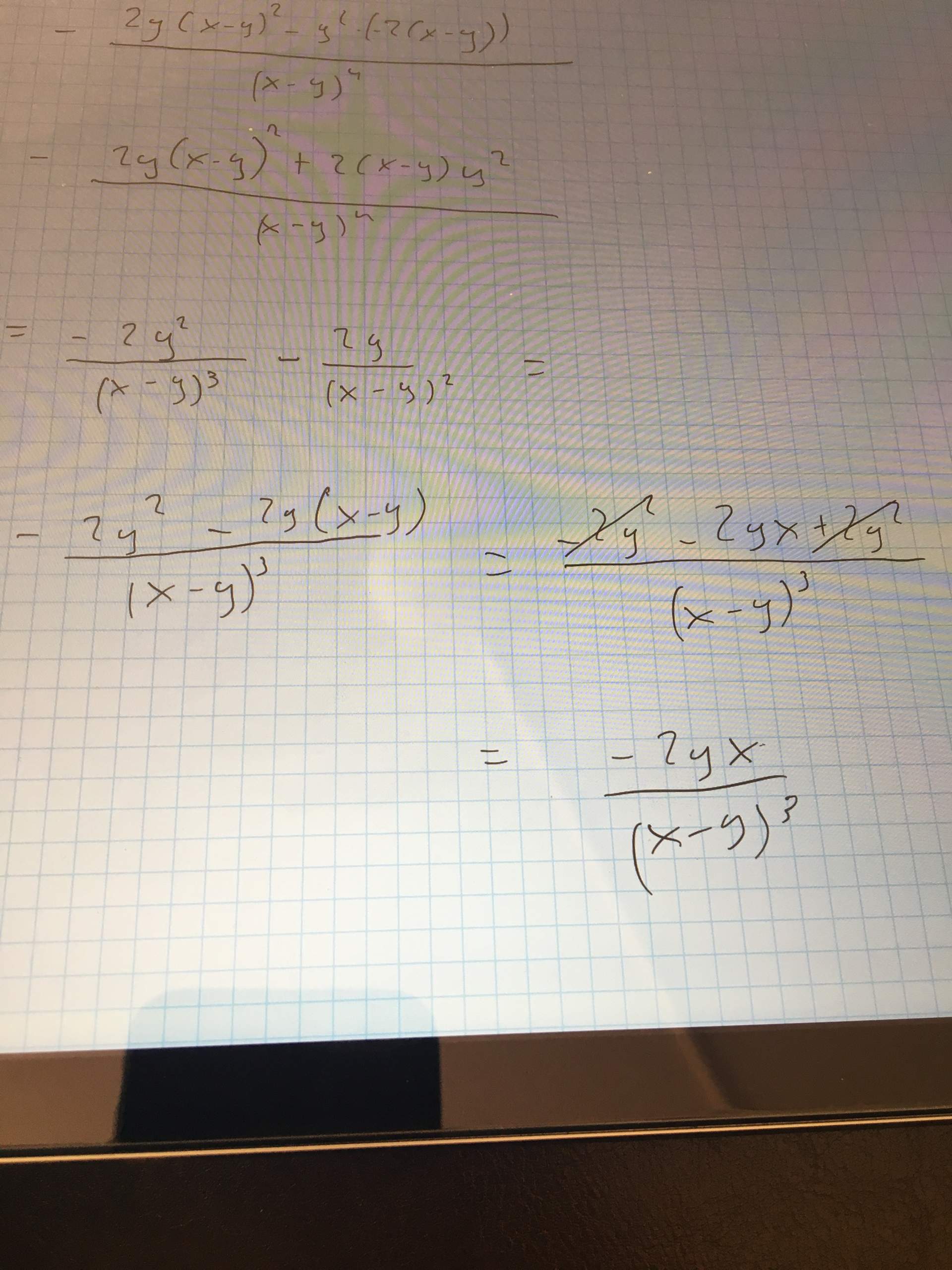Totales Differential - Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. Total differentials can be generalized. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\).
F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). Total differentials can be generalized. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted.
Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). Total differentials can be generalized. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z.
Totales Differential Mathelounge
F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z).
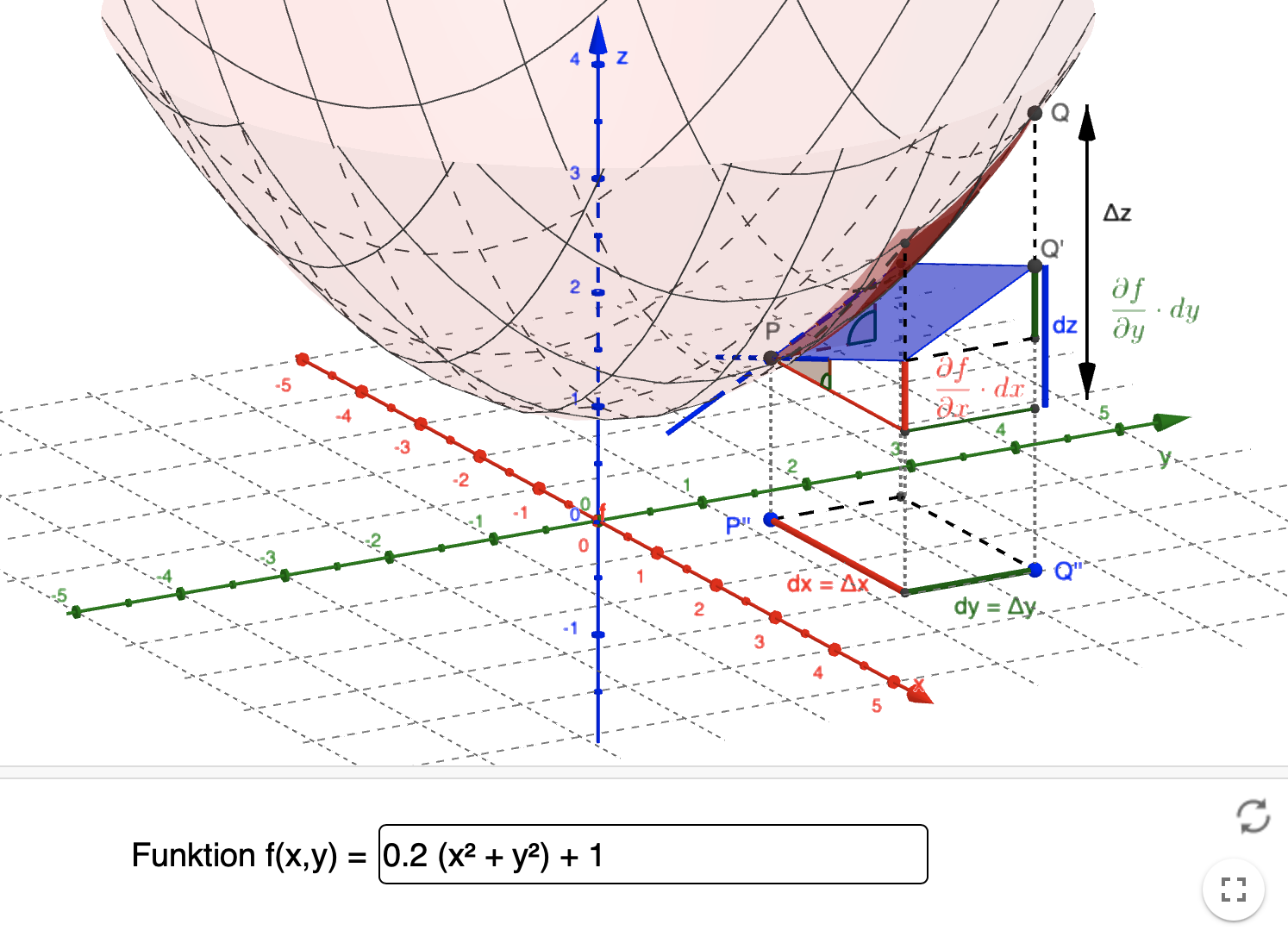
Total differential as estimation error, partial differentials as
Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. Total differentials can be generalized. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. For a function f =.
Totales Differential Aufgaben
Total differentials can be generalized. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. Let \(z=f(x,y)\).
Totales Differential berechnen und prüfen? (Schule, Mathe, Mathematik)
Total differentials can be generalized. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. F(x +.
Lösungen von Totalen Differential Aufgaben Tipps & Tricks zur
Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. Total differentials can be generalized. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z).
Totales Differential Mathelounge
Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists,.
partial derivative Total differential definition help Mathematics
F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. Total differentials can be generalized. Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on.
Totales Differential MathFlix
For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\). F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. Total differentials can be generalized. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in.
calculus Visualizing the total differential Mathematics Stack Exchange
For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. Total differentials can be generalized. F(x +.
Totales Differential
The former part of δ x is called the (total) differential or the exact differential of the function f in the point (x, y, z) and it is denoted. F(x + ∆x, y + ∆y) = f(x, y) + ∆z. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on.
The Former Part Of Δ X Is Called The (Total) Differential Or The Exact Differential Of The Function F In The Point (X, Y, Z) And It Is Denoted.
Let \(dx\) and \(dy\) represent changes in \(x\) and. Total differentials can be generalized. For a function f = f(x, y, z) whose partial derivatives exists, the total. Let \(z=f(x,y)\) be continuous on an open set \(s\).