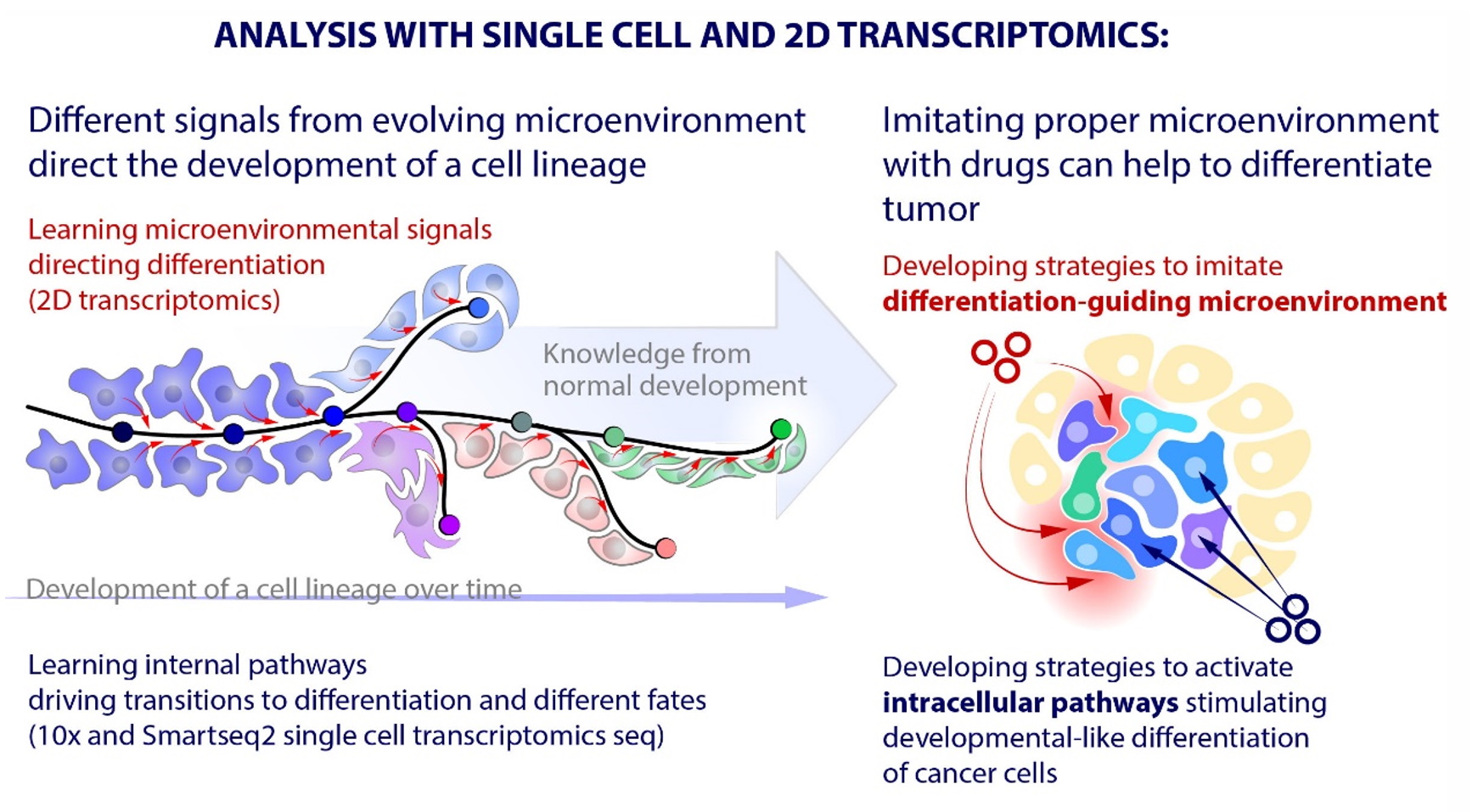
Tumor Differentiation - Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. For example, differentiation therapy has.
Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. For example, differentiation therapy has. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by.
Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. For example, differentiation therapy has. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies.
Returning neural crestderived tumors back onto developmental path
Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. For.
Notch and myeloid cells differentiation within tumor... Download
Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. For.
Tumor differentiation. Download Scientific Diagram
For example, differentiation therapy has. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention.
Tumor distribution by tumor differentiation. Tumor maps are merged
The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. For.
Additional assurance with the Tumor differentiation
The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. Tumor differentiation refers to.
Interpretable Tumor Differentiation Grade And, 52 OFF
The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. For example, differentiation therapy has. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention.
Additional assurance with the Tumor differentiation
Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. Tumor.
Comparison between tumor differentiation and some clinicopathological
Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. For.
Tumor differentiation and lymphocyte infiltration. Well, moderate, and
Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The.
Site wise tumor differentiation Download Scientific Diagram
Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. For example, differentiation therapy has. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal.
For Example, Differentiation Therapy Has.
The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The anaplasia of tumors can provide insights into their etiology, degree of malignancy, prognosis, and sensitivity to therapeutic intervention by. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3.