Tumour Differentiation - Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. For example, differentiation therapy has. In biology, describes the processes by which. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer.
Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: For example, differentiation therapy has. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. In biology, describes the processes by which. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3.
Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. In biology, describes the processes by which. For example, differentiation therapy has. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3.
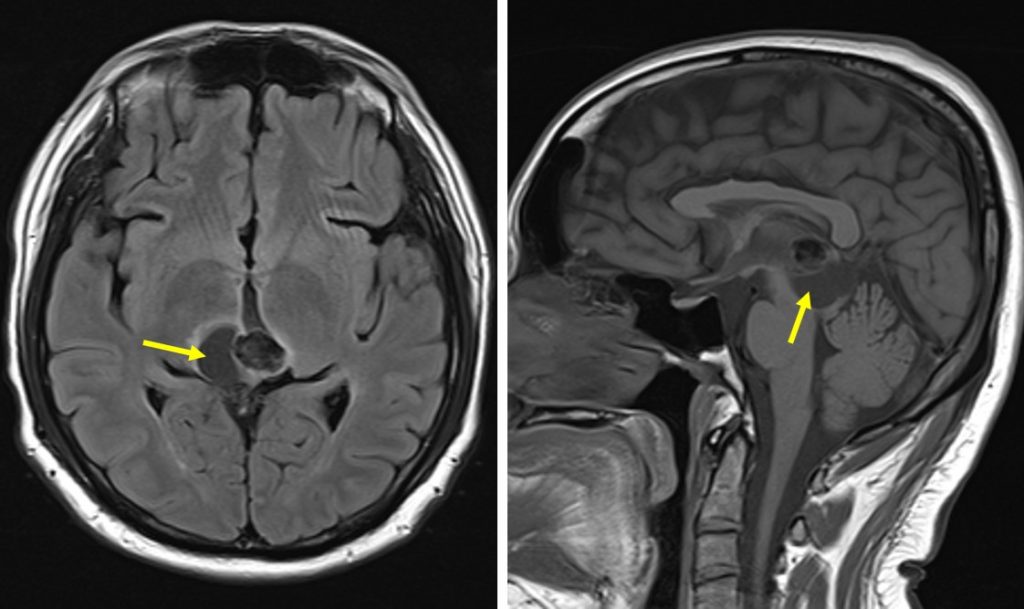
Pineal Parenchymal Tumour of Intermediate Differentiation Radiology Cases
Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: For example, differentiation therapy has. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation stage of tumors.
Mesothelioma tumour types, illustration Stock Photo Alamy
The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor.
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour Atlas of Pathology
For example, differentiation therapy has. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. The differentiation process differs.
How Can A Pathologist Differentiate Between a Benign Tumour and a
Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The.
Degree of tumour differentiation, tumour EpCAM and tumour cytokeratin
In biology, describes the processes by which. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. For example, differentiation.
Origin of tumour samples. The primary tumour samples were grade 4
The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. Differentiation is.
Mesothelioma tumour types, illustration Stock Photo Alamy
In biology, describes the processes by which. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. For example, differentiation therapy has. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification.
(PDF) Brain tumour differentiation rapid stratified serum diagnostics
Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. In.
(PDF) Tumour differentiation grade is associated with TNM staging and
For example, differentiation therapy has. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer. In biology, describes the processes by which. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal.
Well differentiated neuroendocrine tumour MyPathologyReport.ca
For example, differentiation therapy has. The differentiation process differs from one tumor to another, and it can be characterized by: Tumor differentiation refers to the scoring system used to assess how closely sarcomas resemble normal tissue, with scores ranging from 1 to 3. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal.
The Differentiation Process Differs From One Tumor To Another, And It Can Be Characterized By:
In biology, describes the processes by which. The differentiation stage of tumors is a central aspect in the histopathological classification of solid malignancies. Tumor differentiation is a combination of ‘true’ differentiation (i.e., the extent to which tumor cells resemble normal mesenchymal cells) and. Differentiation is used in tumor grading systems, which are different for each type of cancer.
Tumor Differentiation Refers To The Scoring System Used To Assess How Closely Sarcomas Resemble Normal Tissue, With Scores Ranging From 1 To 3.
For example, differentiation therapy has.