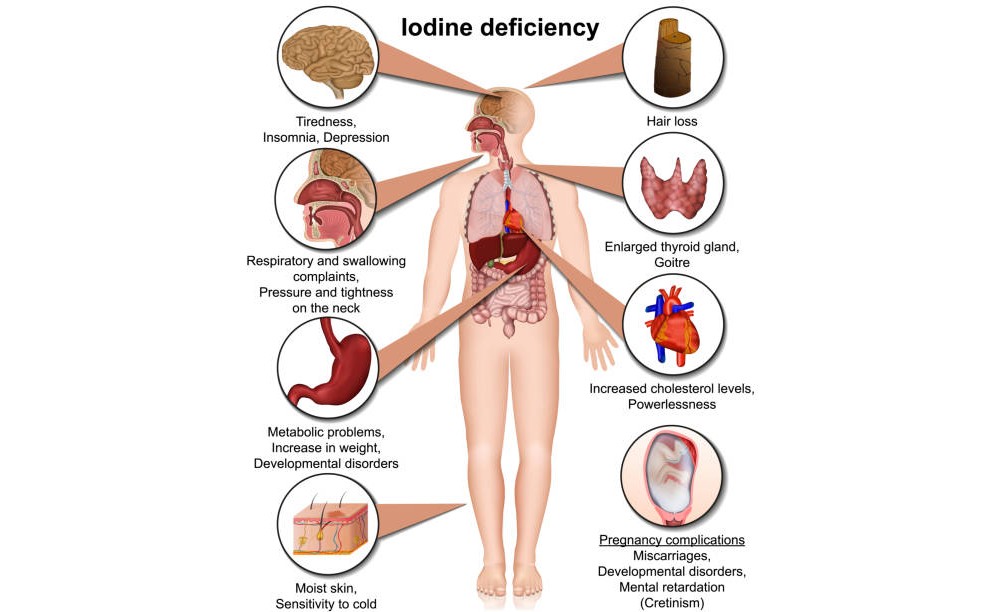
What Does Iodine Deficiency During Pregnancy Cause - Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and impair neurological development of the fetus. Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as perinatal and. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. As adequate thyroid hormone is required for normal fetal development, iodine deficiency in pregnancy is associated with congenital. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant.
As adequate thyroid hormone is required for normal fetal development, iodine deficiency in pregnancy is associated with congenital. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and impair neurological development of the fetus. Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as perinatal and.
Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as perinatal and. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. As adequate thyroid hormone is required for normal fetal development, iodine deficiency in pregnancy is associated with congenital. Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and impair neurological development of the fetus.
What Are the deficiency of iodine causes? My Medi Times
In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. Depending.
SciELO Brasil Implications of iodine deficiency by gestational
In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. As adequate thyroid hormone is required for normal fetal development, iodine deficiency in pregnancy is associated with congenital..
What condition is caused by iodine deficiency during pregnancy and is
In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as.
title Artemis Salt
As adequate thyroid hormone is required for normal fetal development, iodine deficiency in pregnancy is associated with congenital. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Iodine deficiency during pregnancy.
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause miscarriage GoMedii
In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as perinatal and. As adequate thyroid hormone is required for normal fetal development, iodine deficiency in pregnancy is associated with congenital. Iodine.
Iodine Deficiency During Pregnancy Being The Parent
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and impair neurological development of the fetus. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. Depending on the timing and.
(PDF) Iodine deficiency in pregnancy
Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as perinatal and. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further.
Importance of Iodine during pregnancy and lactation
Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as perinatal and. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further.
What is iodine deficiency? Causes, Symptoms & Cure Birla Hospital
As adequate thyroid hormone is required for normal fetal development, iodine deficiency in pregnancy is associated with congenital. Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and impair neurological development of the fetus. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. Depending on the timing.
Iodine Deficiency In Pregnancy
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and impair neurological development of the fetus. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. Some studies suggest that severe iodine deficiency (very low levels of iodine) could increase the chance of stillbirth or of infant. Depending on the timing and.
As Adequate Thyroid Hormone Is Required For Normal Fetal Development, Iodine Deficiency In Pregnancy Is Associated With Congenital.
Depending on the timing and severity, insufficient iodine intake increases the risk of negative reproductive outcomes, such as perinatal and. Severe iodine deficiency during development results in maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and associated serious adverse health effects,. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e., low maternal ft 4) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by. Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause maternal and fetal hypothyroidism and impair neurological development of the fetus.