What Is An Implicit Solution To A Differential Equation - $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Below we show how this method. In the integral equation you need the. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0.
$\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. In the integral equation you need the. The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Below we show how this method. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined.
In the integral equation you need the. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. Below we show how this method. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the.
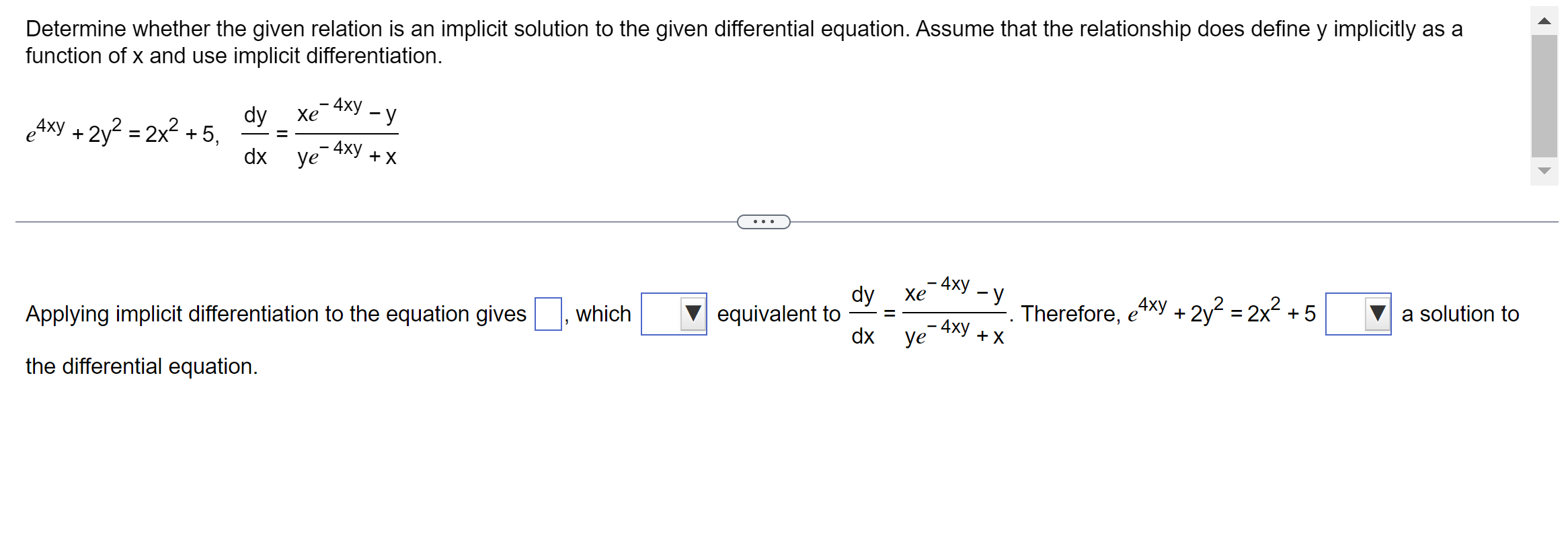
Solved Determine whether the given relation is an implicit
In the integral equation you need the. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. Below we show how this method. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t.
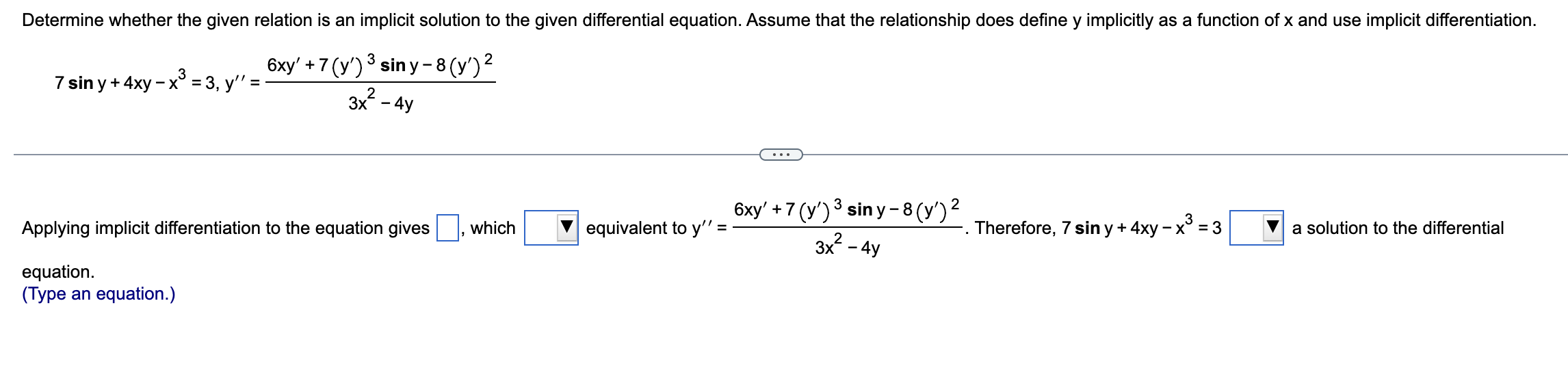
Solved Determine whether the given relation is an implicit
The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. In the integral equation you need the. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit.
Show that the given relation defines an implicit solution to Quizlet
Below we show how this method. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be.
How to solve implicit differential equation? Mathematics Stack Exchange
Below we show how this method. In the integral equation you need the. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution.
Solved Determine whether the given relation is an implicit
In the integral equation you need the. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit.
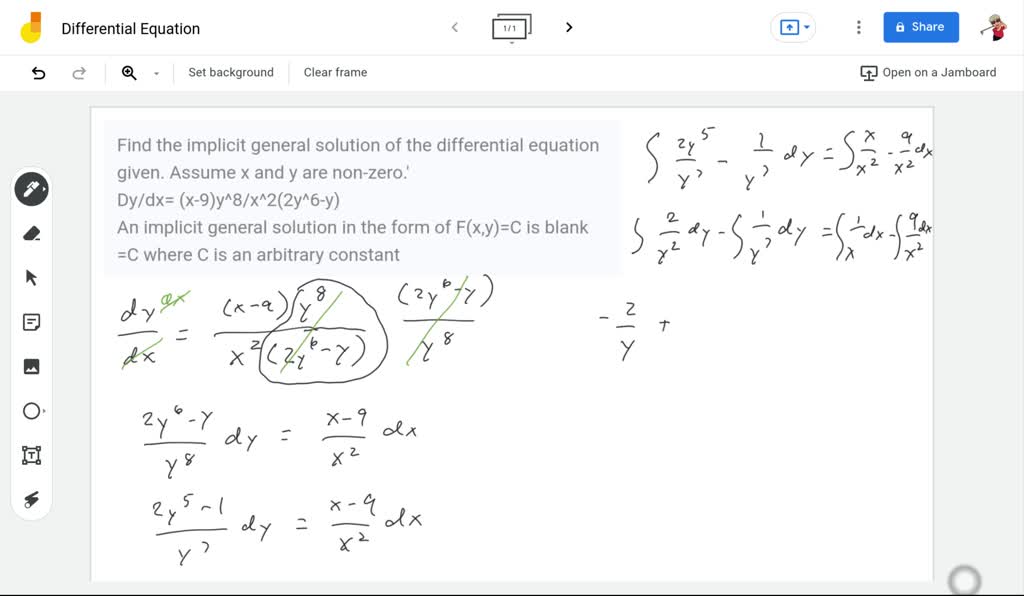
SOLVED Find the implicit general solution of the differential equation
Below we show how this method. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. The main techniques for.
SOLVED Solve for the implicit general solution for the below
Below we show how this method. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval.
calculus Verify that an implicit equation is the solution to the
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Below we show how this method.
Solved 6. Find the implicit solution to the differential
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. In the integral equation you need the. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly.
Solved Find the general solution for the differential
Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\).
In The Integral Equation You Need The.
Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter.
Here $Y(X)$ Is Implicitly Defined.
$\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. Below we show how this method. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0.