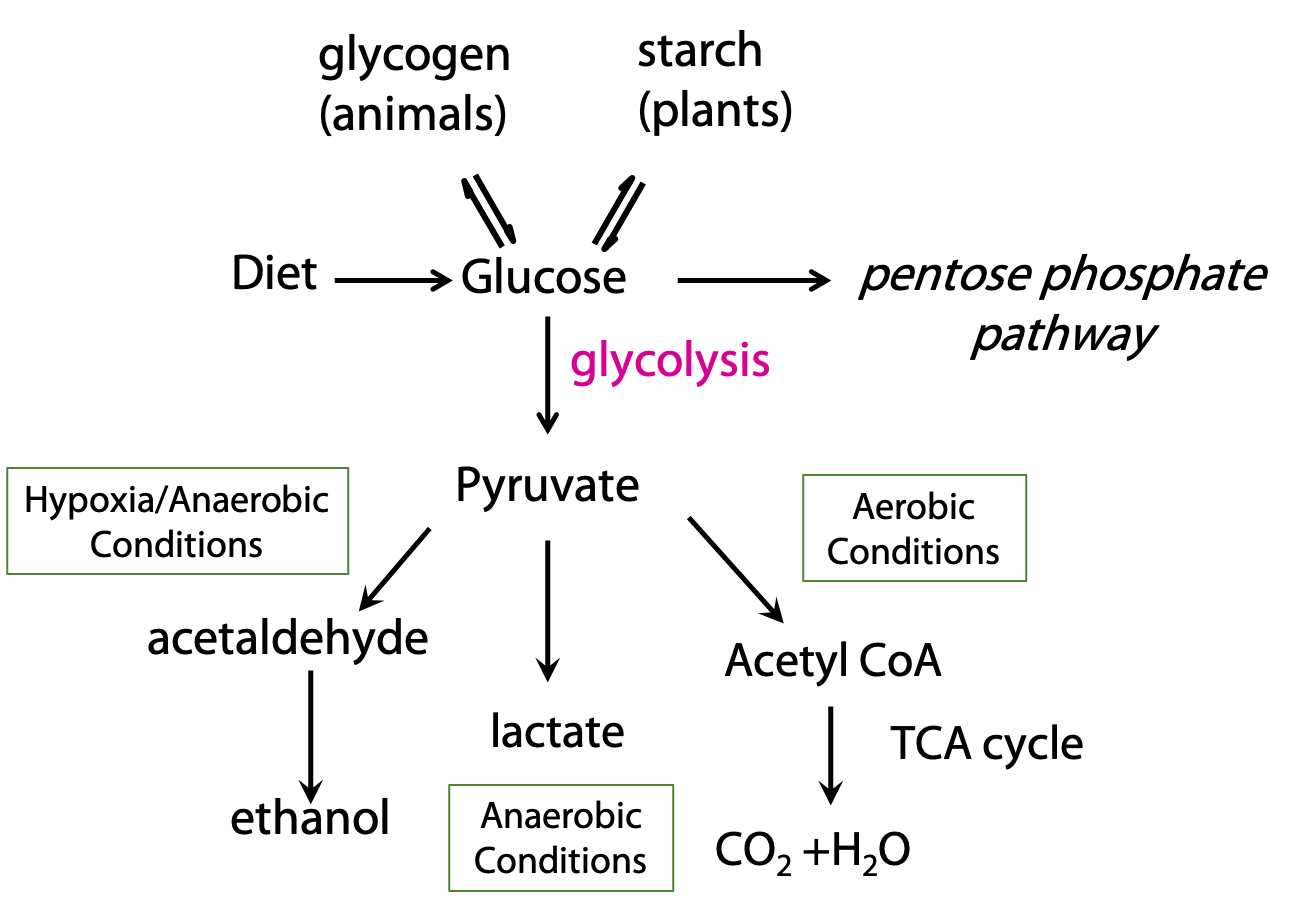
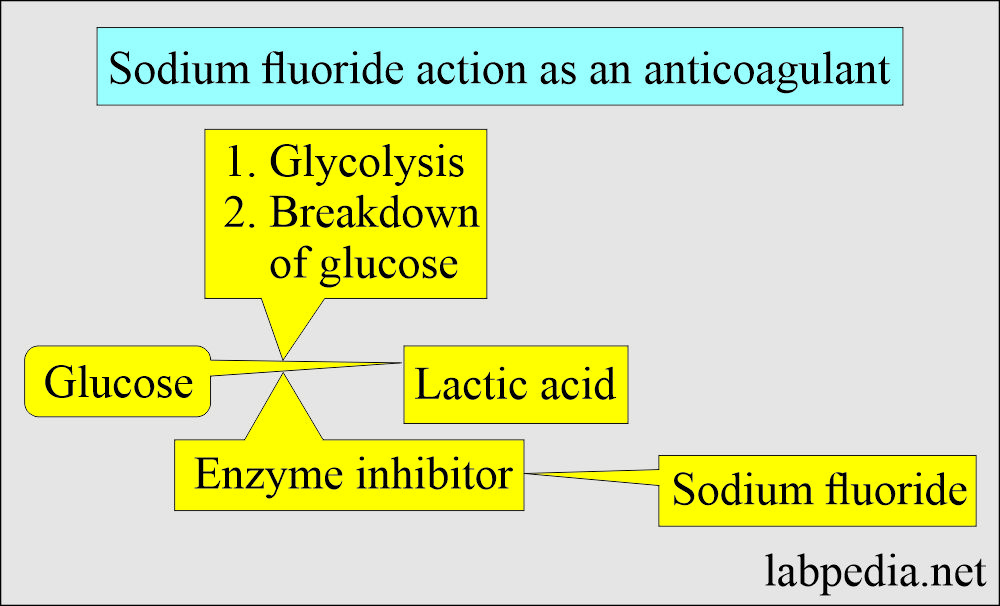
Which Additive Prevents Glycolysis - An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride.
An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis. Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in.
Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride.
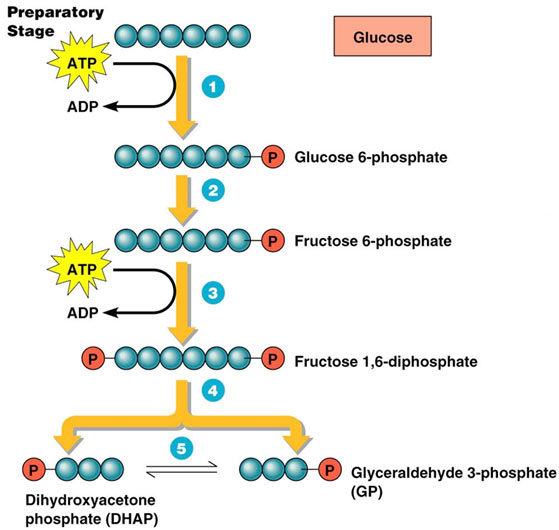
Glycolysis BIOC*2580 Introduction to Biochemistry
An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in.
Blood sample Types, Anticoagulants, Preservatives, Adverse effects of
Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of.
Easy Glycolysis Diagram
The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme.
9.3 Glycolysis Biology LibreTexts
Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis.
Unlocking the Power of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis.
Glycolysis, Pyruvic Oxidation, Krebs cycle, and Respiratory Chain
The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis.
GLYCOLYSIS
The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf).
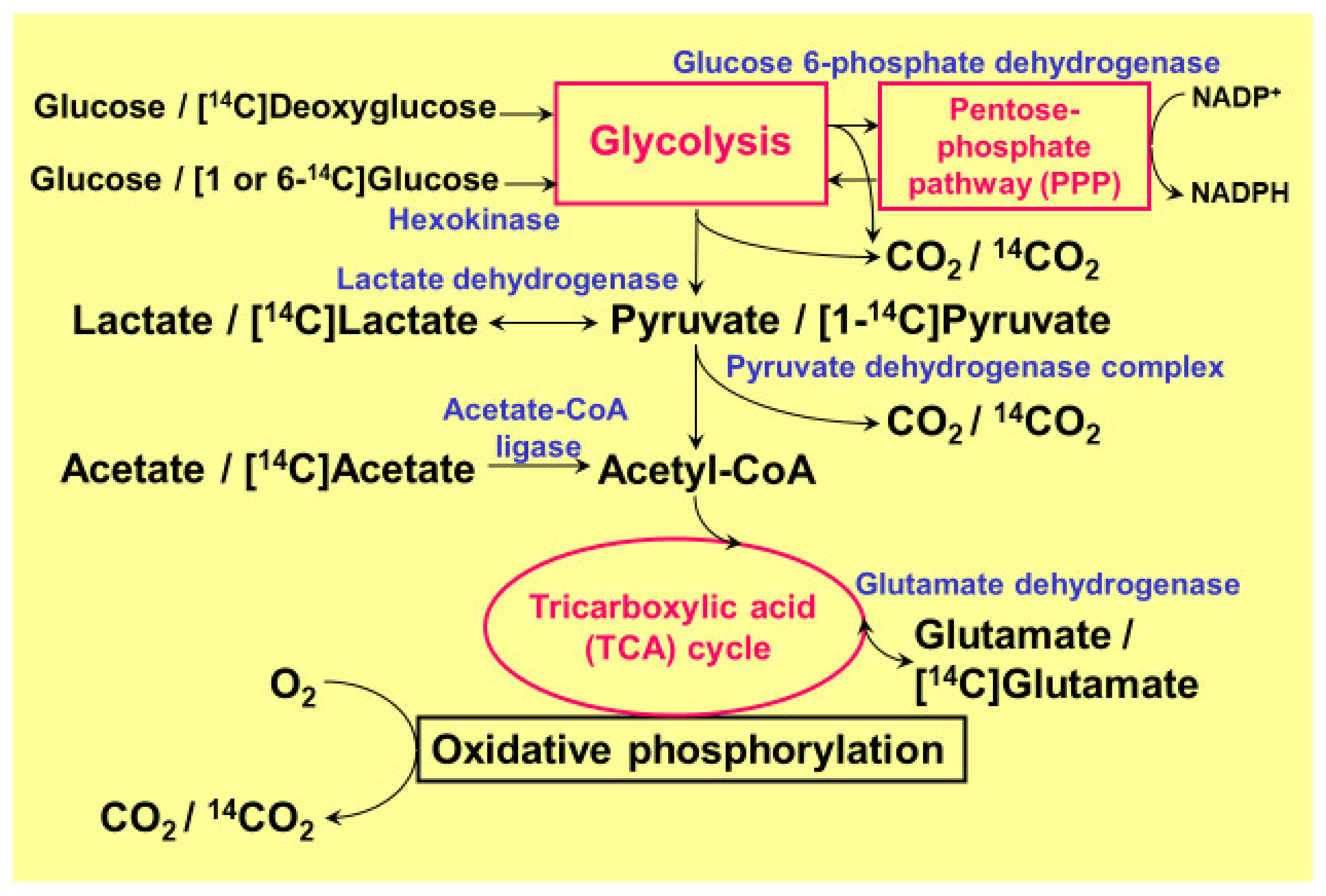
8 Inhibitors of Glycolysis Carbohydrates Metabolism8 Biochemistry
For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis. The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride.
Neuroprotective Function of High Glycolytic Activity in Astrocytes
The additive that prevents glycolysis is sodium fluoride. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in.
Is pyruvic acid the end product of glycolysis?
Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. Several substances can inhibit glycolysis. Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in. An antiglycolytic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents glycolysis (metabolism of.
The Additive That Prevents Glycolysis Is Sodium Fluoride.
Several substances can inhibit glycolysis. The additive that provides a physical barrier to prevent glycolysis is sodium fluoride. For instance, sodium fluoride (naf). Sodium fluoride is an additive that prevents glycolysis by inhibiting the enzyme.
An Antiglycolytic Agent Is A Substance That Inhibits Or Prevents Glycolysis (Metabolism Of.
Sodium fluoride (naf) inhibits the enzyme enolase, which is an essential step in.