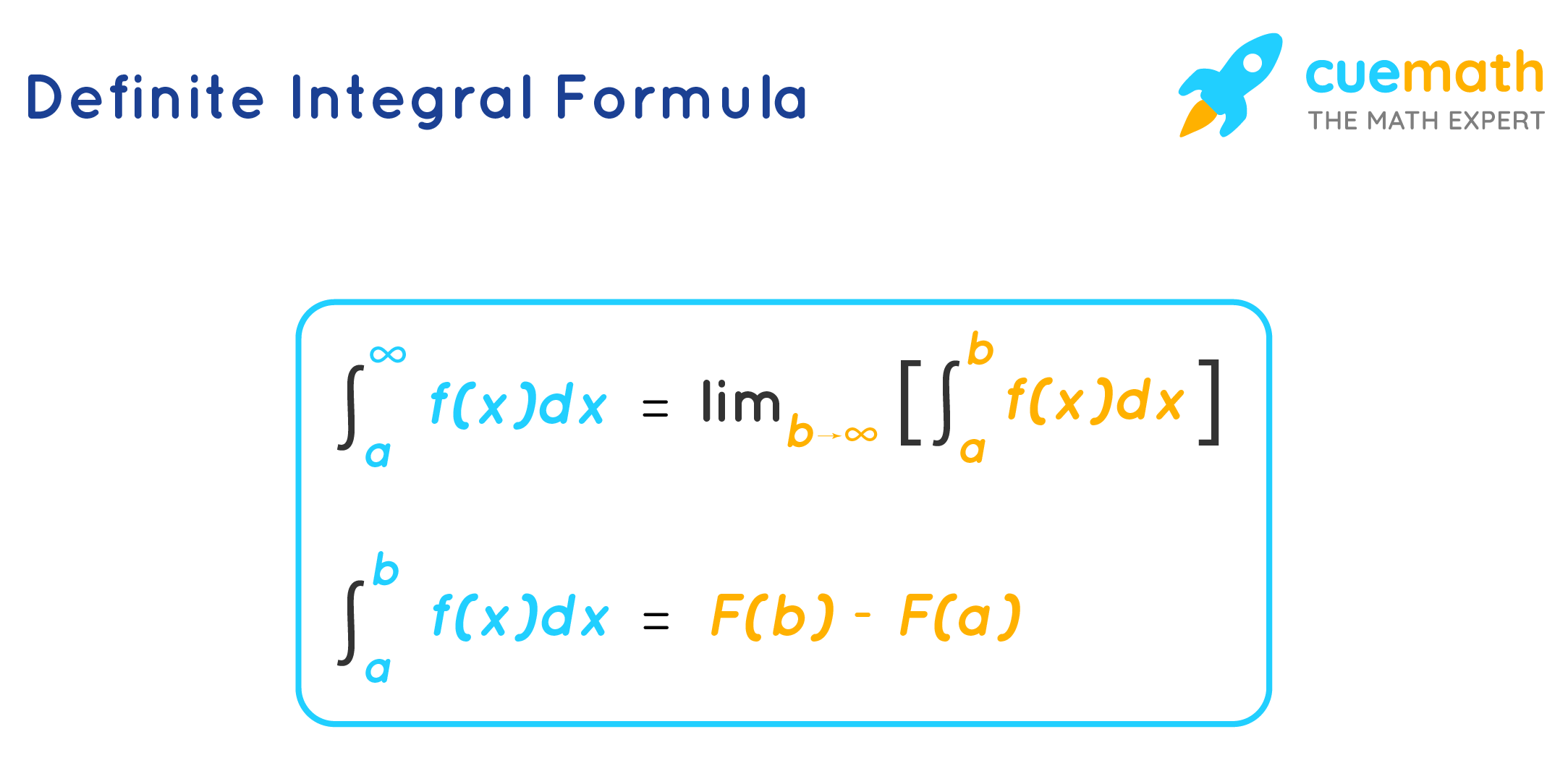
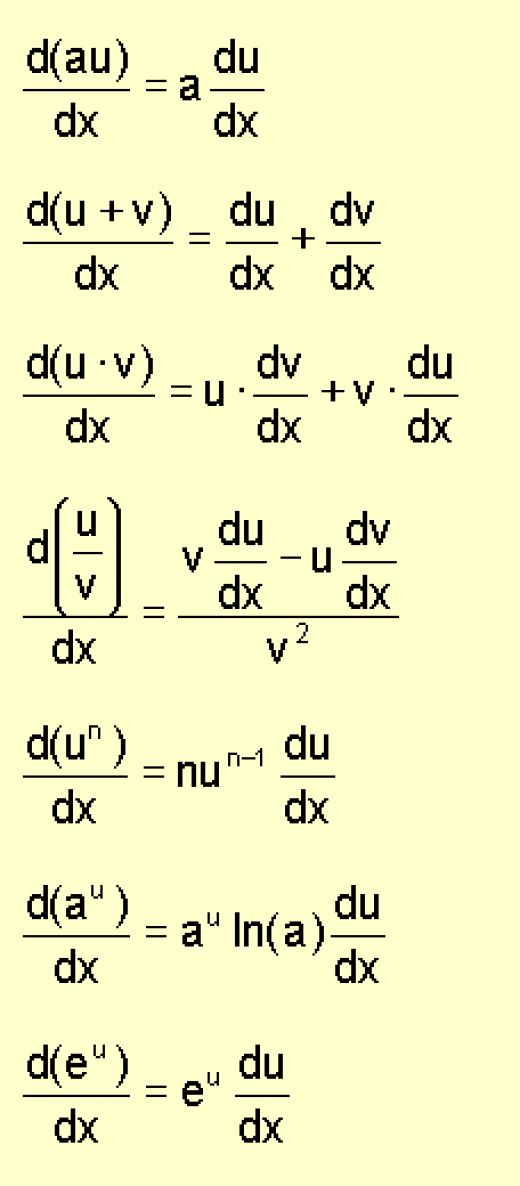Differentiation Of Definite Integral - For a definite integral with a variable upper limit of integration $\int_a^xf(t)\,dt$, you have ${d\over dx} \int_a^xf(t)\,dt=f(x)$. How to differentiate a definite integral? Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. When dealing with a definite integral where both limits of integration involve variables, finding the derivative can be a bit trickier. If you were to differentiate an integral. T) is a function of two variables like f(x; In general, we might write such an integral as. For an integral of the. T) = (2x + t3)2. Under fairly loose conditions on the.
For a definite integral with a variable upper limit of integration $\int_a^xf(t)\,dt$, you have ${d\over dx} \int_a^xf(t)\,dt=f(x)$. If you were to differentiate an integral. T) = (2x + t3)2. It depends upon the definite integral in question. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. T) is a function of two variables like f(x; Under fairly loose conditions on the. For an integral of the. When dealing with a definite integral where both limits of integration involve variables, finding the derivative can be a bit trickier. In general, we might write such an integral as.
If you were to differentiate an integral. T) = (2x + t3)2. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. How to differentiate a definite integral? Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. In general, we might write such an integral as. It depends upon the definite integral in question. T) is a function of two variables like f(x; Under fairly loose conditions on the. When dealing with a definite integral where both limits of integration involve variables, finding the derivative can be a bit trickier.
Maths Tips and Tricks INDEFINITE INTEGRAL , DIFFERENTIATION , DEFINITE
Under fairly loose conditions on the. If you were to differentiate an integral. For an integral of the. T) = (2x + t3)2. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative.
Maths Tips and Tricks INDEFINITE INTEGRAL , DIFFERENTIATION , DEFINITE
How to differentiate a definite integral? T) = (2x + t3)2. For an integral of the. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. When dealing with a definite integral where both limits of integration involve variables, finding the derivative.
Maths Tips and Tricks INDEFINITE INTEGRAL , DIFFERENTIATION , DEFINITE
How to differentiate a definite integral? Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. For an integral of the. When dealing with a definite integral where both limits of integration involve variables, finding the derivative can be a bit trickier..
Maths Tips and Tricks INDEFINITE INTEGRAL , DIFFERENTIATION , DEFINITE
If you were to differentiate an integral. In general, we might write such an integral as. For a definite integral with a variable upper limit of integration $\int_a^xf(t)\,dt$, you have ${d\over dx} \int_a^xf(t)\,dt=f(x)$. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits.
Definite Integral Formula Learn Formula to Calculate Definite Integral
Under fairly loose conditions on the. It depends upon the definite integral in question. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. When dealing with a definite integral where both limits of integration involve variables, finding the derivative can be.
Integral Wikipedia
How to differentiate a definite integral? If you were to differentiate an integral. In general, we might write such an integral as. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. It depends upon the definite integral in question.
The Definite Integral The Definite Integral What is the Definite
In general, we might write such an integral as. For a definite integral with a variable upper limit of integration $\int_a^xf(t)\,dt$, you have ${d\over dx} \int_a^xf(t)\,dt=f(x)$. T) = (2x + t3)2. Under fairly loose conditions on the. T) is a function of two variables like f(x;
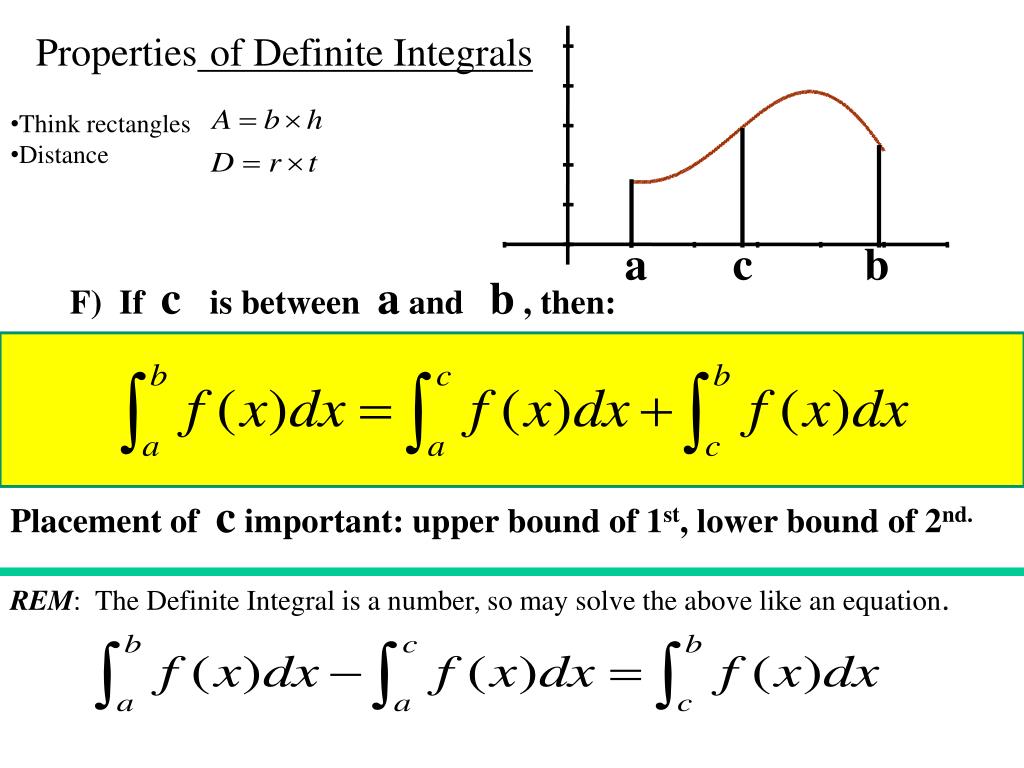
PPT 4010Properties of the Definite Integral (5.3) PowerPoint
In general, we might write such an integral as. T) = (2x + t3)2. It depends upon the definite integral in question. For an integral of the. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals.
SOLUTION Differentiation under integral sign Studypool
For an integral of the. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. If you were to differentiate an integral. When dealing with a definite.
Maths Tips and Tricks INDEFINITE INTEGRAL , DIFFERENTIATION , DEFINITE
Under fairly loose conditions on the. T) is a function of two variables like f(x; For a definite integral with a variable upper limit of integration $\int_a^xf(t)\,dt$, you have ${d\over dx} \int_a^xf(t)\,dt=f(x)$. It depends upon the definite integral in question. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals.
Unless The Variable X Appears In Either (Or Both) Of The Limits Of Integration, The Result Of The Definite Integral Will Not Involve X, And So The Derivative.
It depends upon the definite integral in question. When dealing with a definite integral where both limits of integration involve variables, finding the derivative can be a bit trickier. In general, we might write such an integral as. If you were to differentiate an integral.
T) Is A Function Of Two Variables Like F(X;
How to differentiate a definite integral? For a definite integral with a variable upper limit of integration $\int_a^xf(t)\,dt$, you have ${d\over dx} \int_a^xf(t)\,dt=f(x)$. For an integral of the. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals.
Under Fairly Loose Conditions On The.
T) = (2x + t3)2.